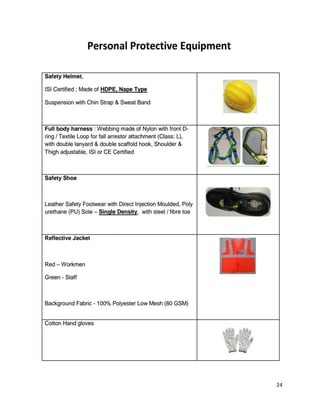
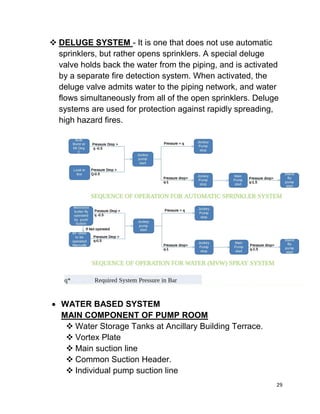
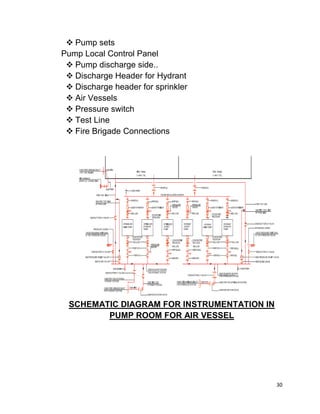
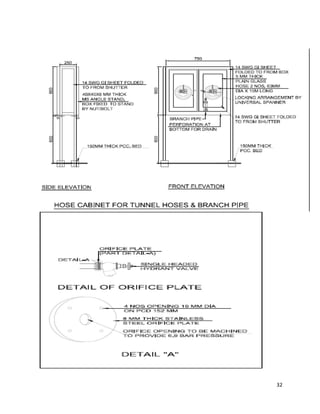
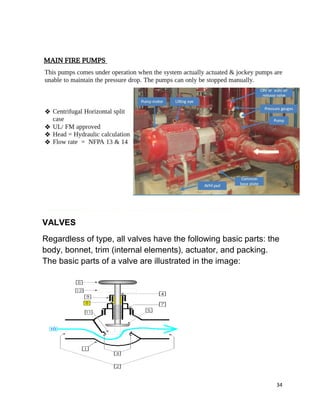
This document contains a certificate from Altaf Nazeer certifying that the attached project report on E&M works for 10 underground metro stations was completed under the guidance of Mr. Aniruddha Kayet at Larsen & Toubro Construction Limited from January 20th to February 20th, 2016. It also contains an acknowledgement thanking Larsen & Toubro for the internship opportunity. The majority of the document then outlines Larsen & Toubro's quality management system which is in line with ISO 9001, including discussions of ISO standards, the eight clauses of the quality management system, management responsibility, resource management, and product realization.