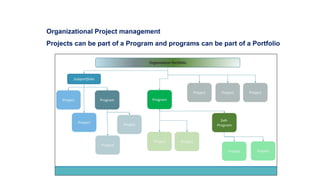
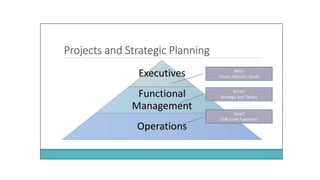
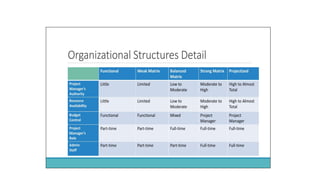
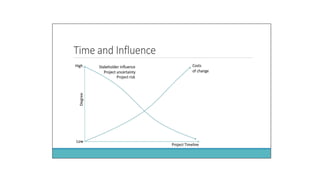
The document outlines project design and management, detailing the processes involved in effectively managing urban design projects. It covers the project lifecycle, organizational structures, and key project management areas such as scope, time, cost, quality, risk, and stakeholder management. It also emphasizes the roles and responsibilities of project managers, organizational influences, and the importance of aligning projects with business strategy and goals.