The document discusses key aspects of project management and product development including:
1) It defines a project as a temporary endeavor undertaken to produce a unique product or service. Characteristics include having a definitive beginning and end and being a new, unique undertaking.
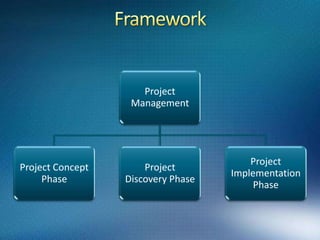
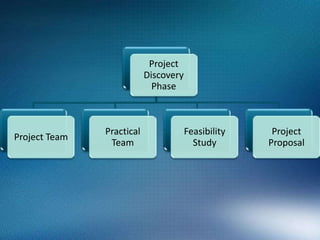
2) It outlines several phases of project management including concept, discovery, implementation, verification, and beta testing.
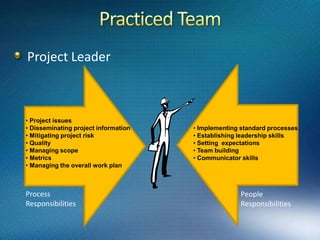
3) Within each phase it discusses important documents, processes, and considerations such as establishing feasibility, creating requirements documents, conducting feasibility studies, and developing test plans.