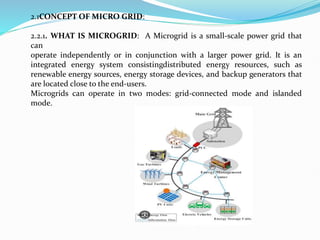
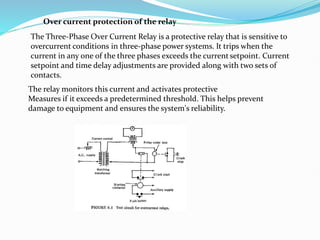
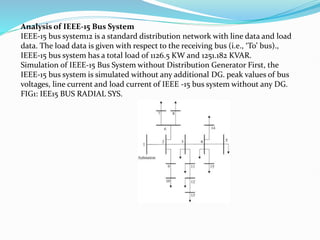
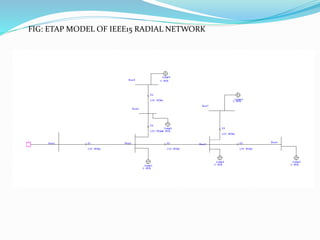
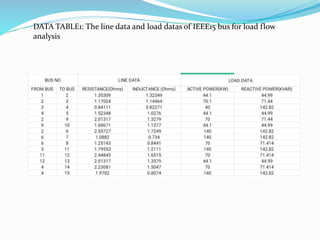
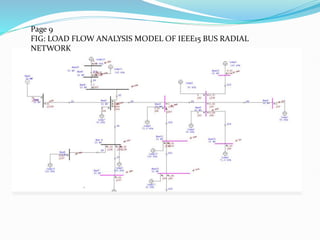
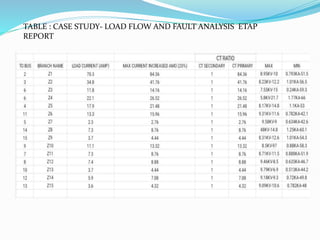
This document discusses optimal coordination of overcurrent relays in microgrids. It begins with an introduction to microgrids and distribution systems. It then discusses the IEEE 15-bus system which will be used as a case study. Load flow and fault analysis will be performed on the IEEE 15-bus ETAP model. Algorithms are proposed to coordinate overcurrent relays by analyzing line and load data from the IEEE 15-bus standard model. Key parameters like maximum load current and fault locations will be identified.