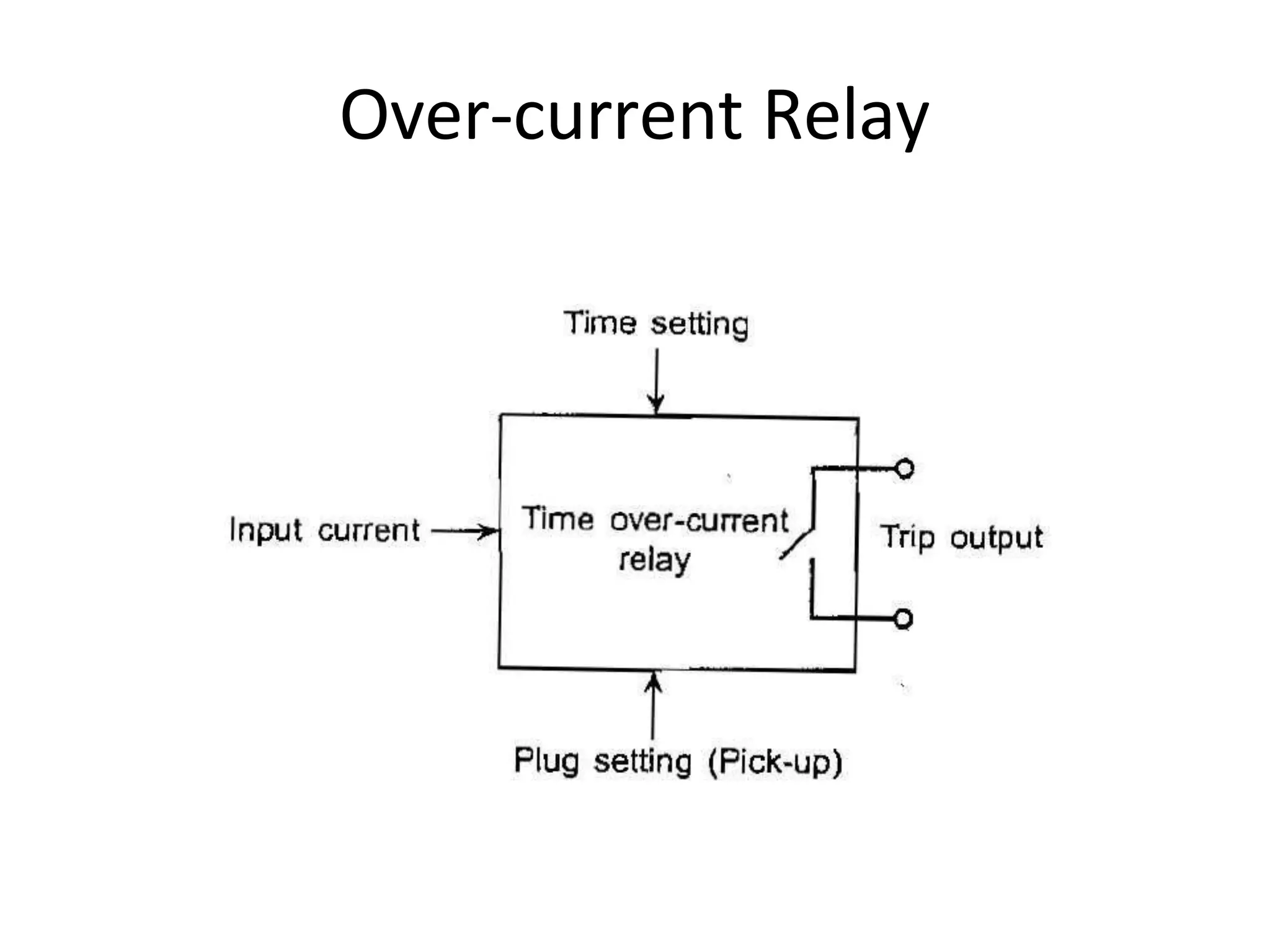
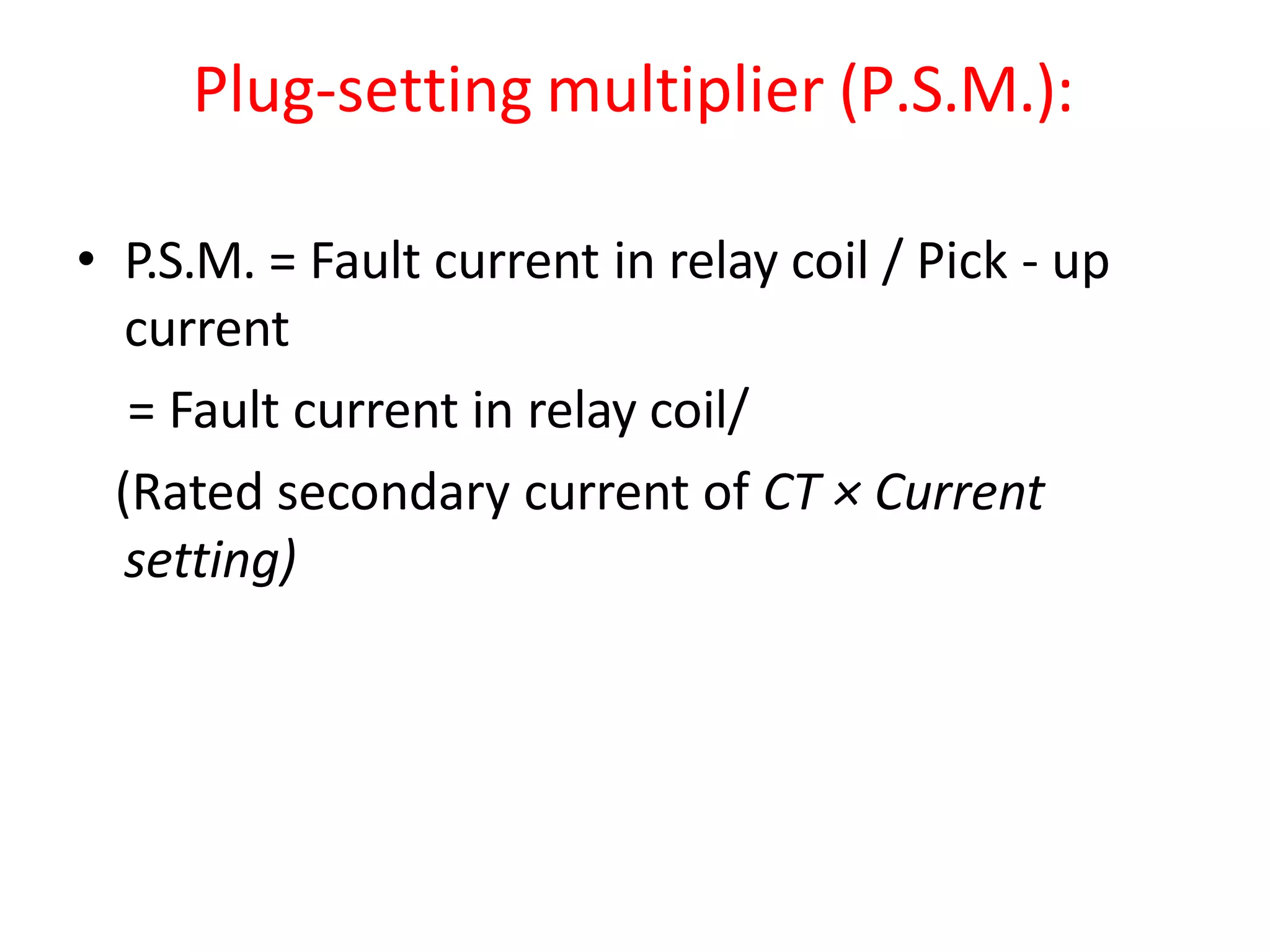
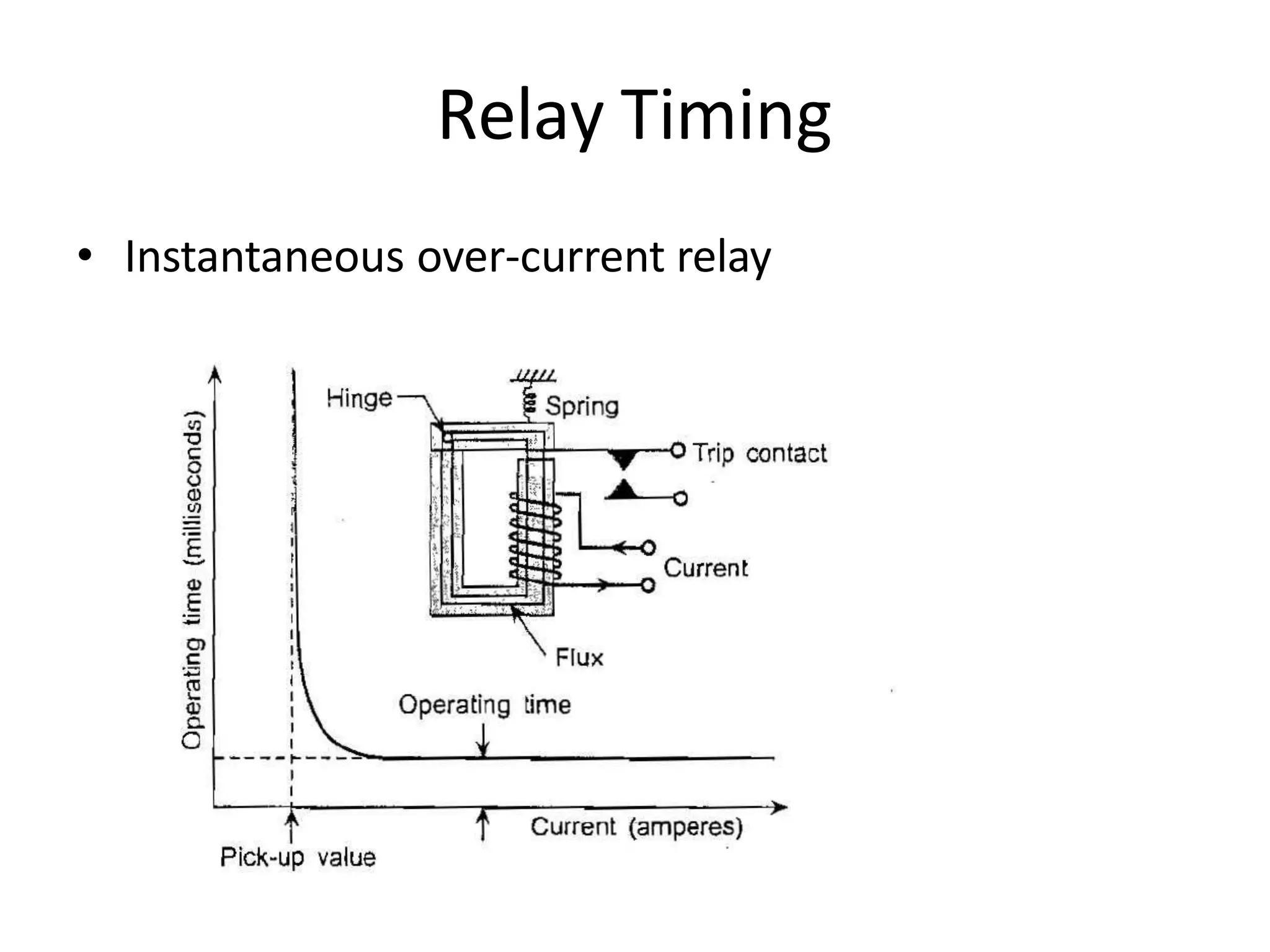
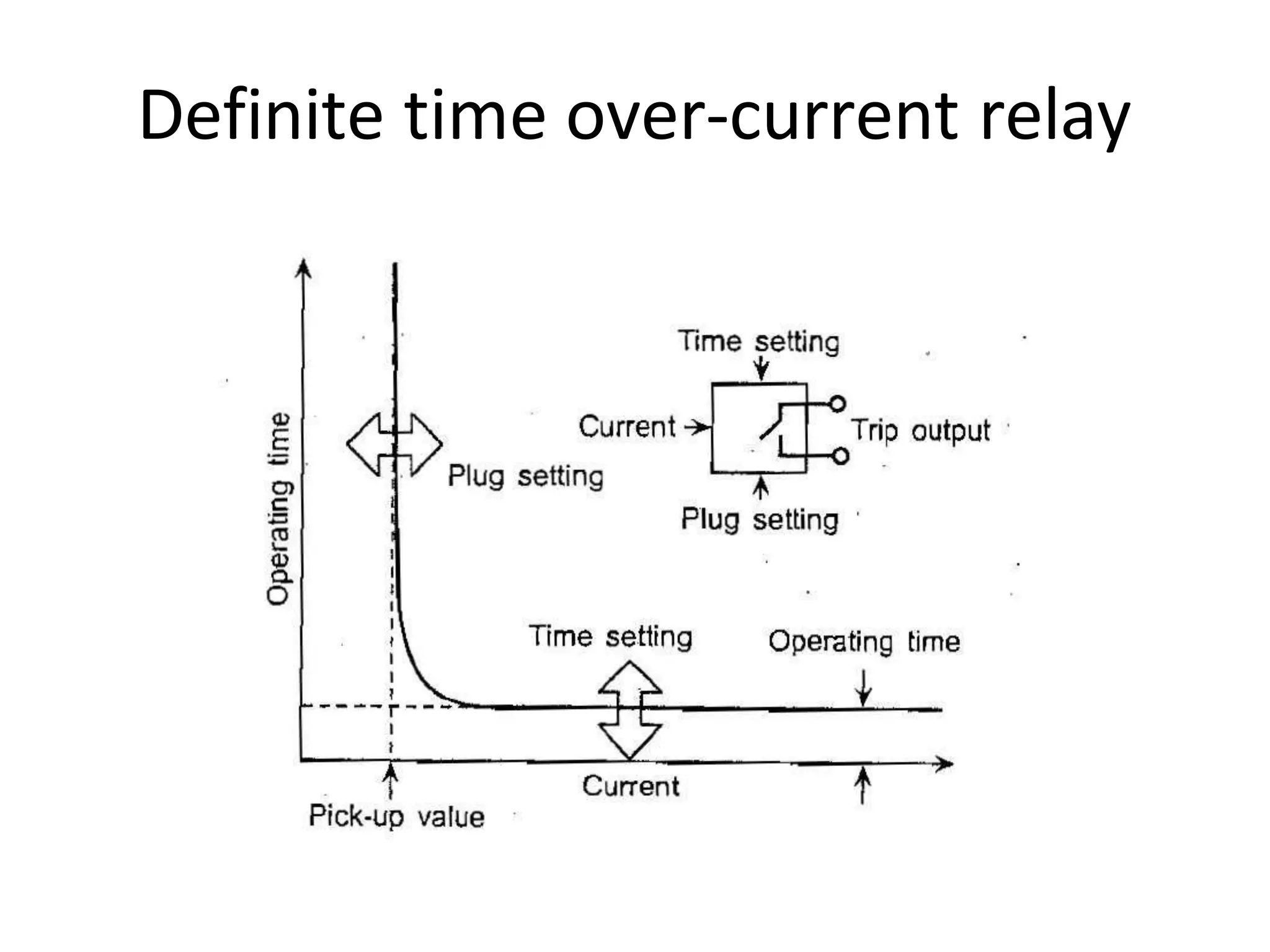
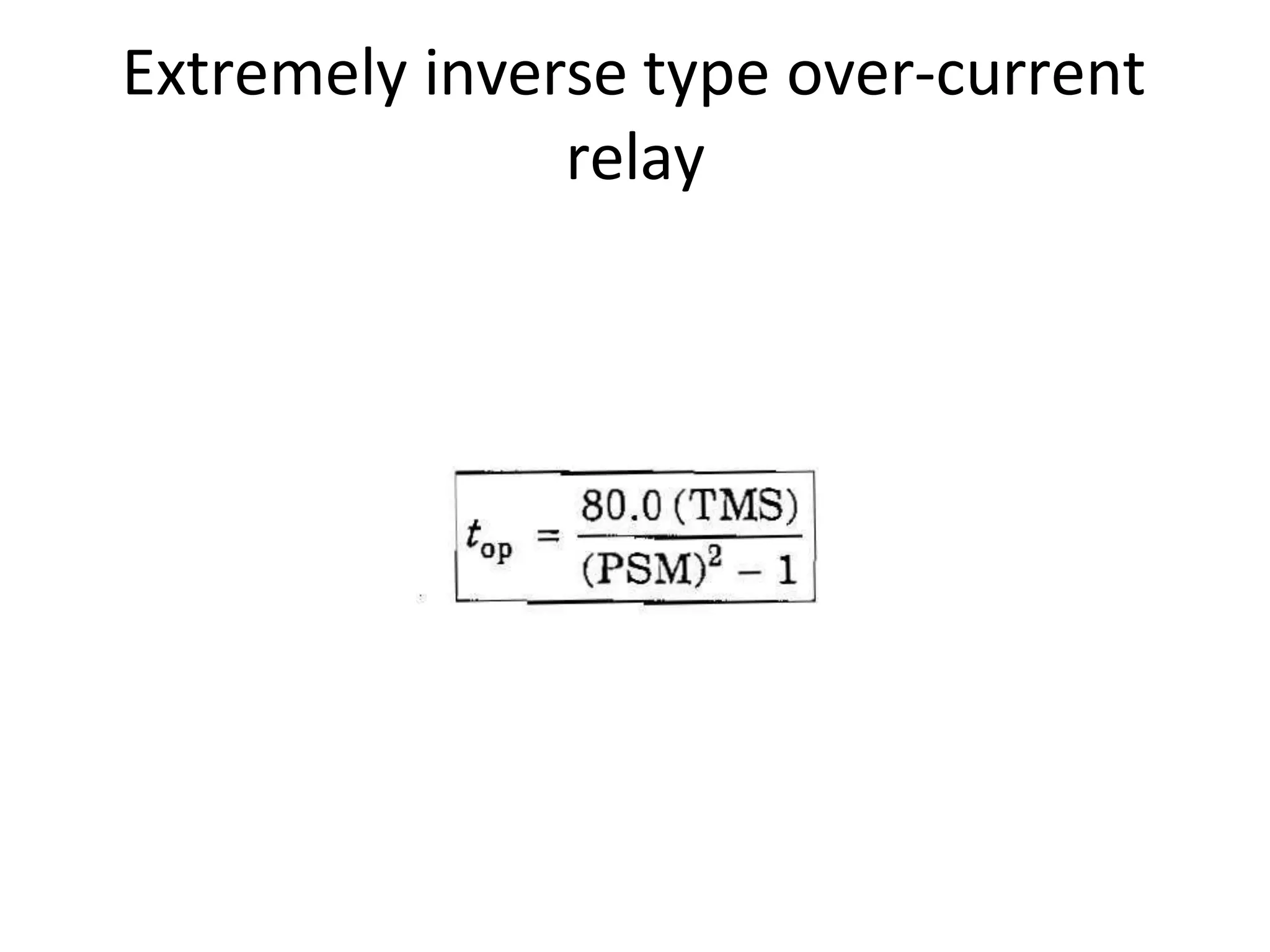
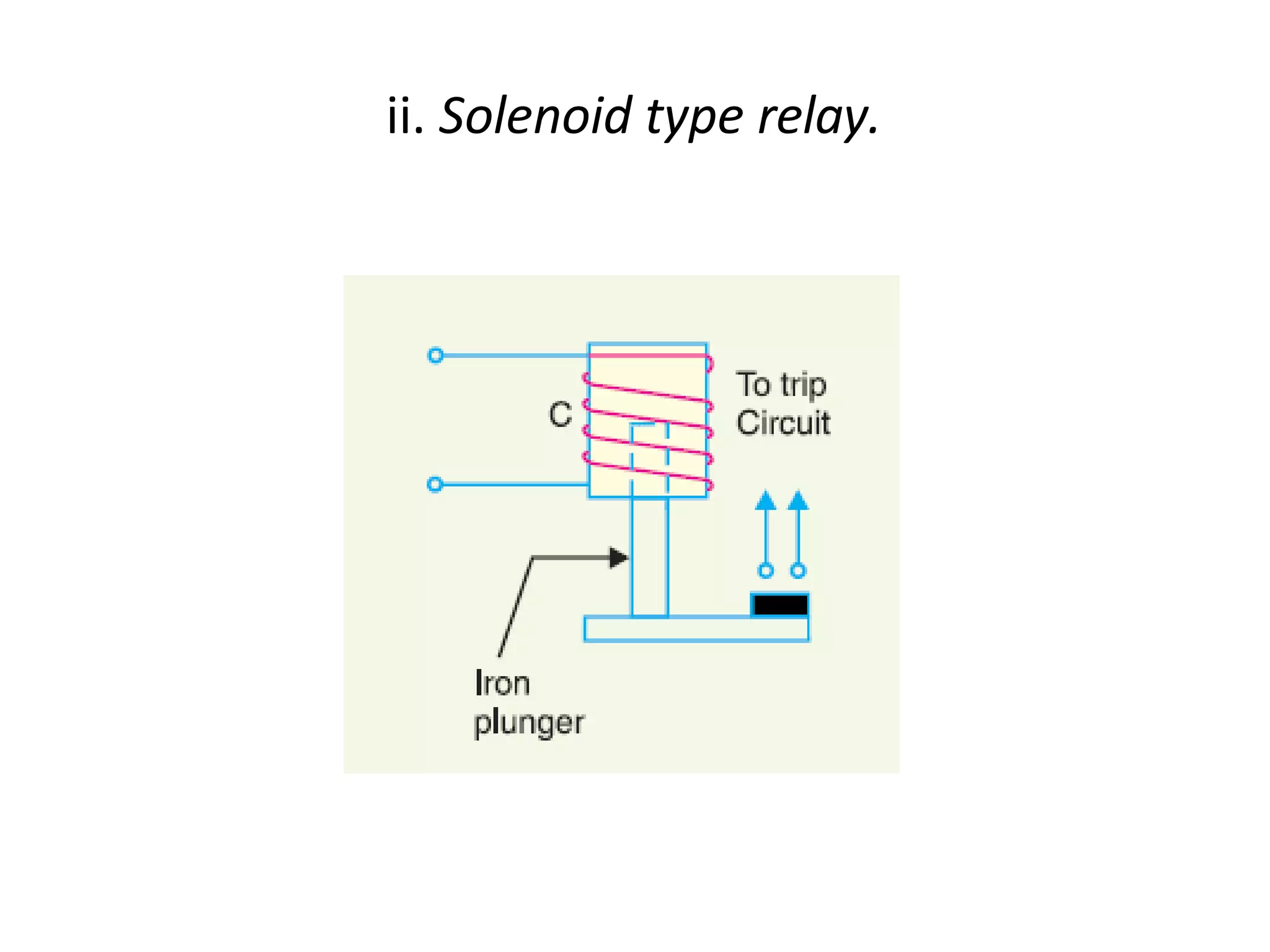
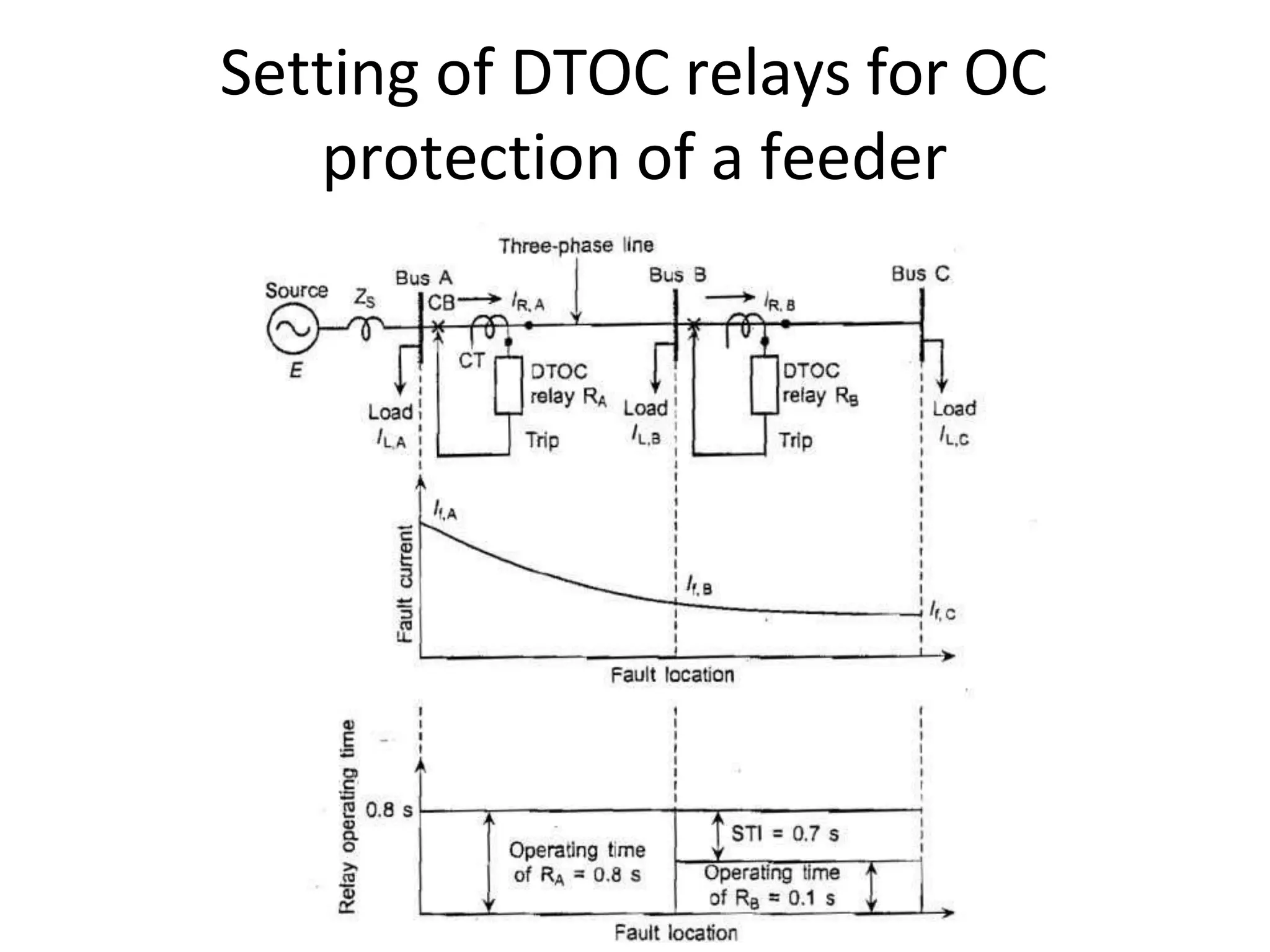
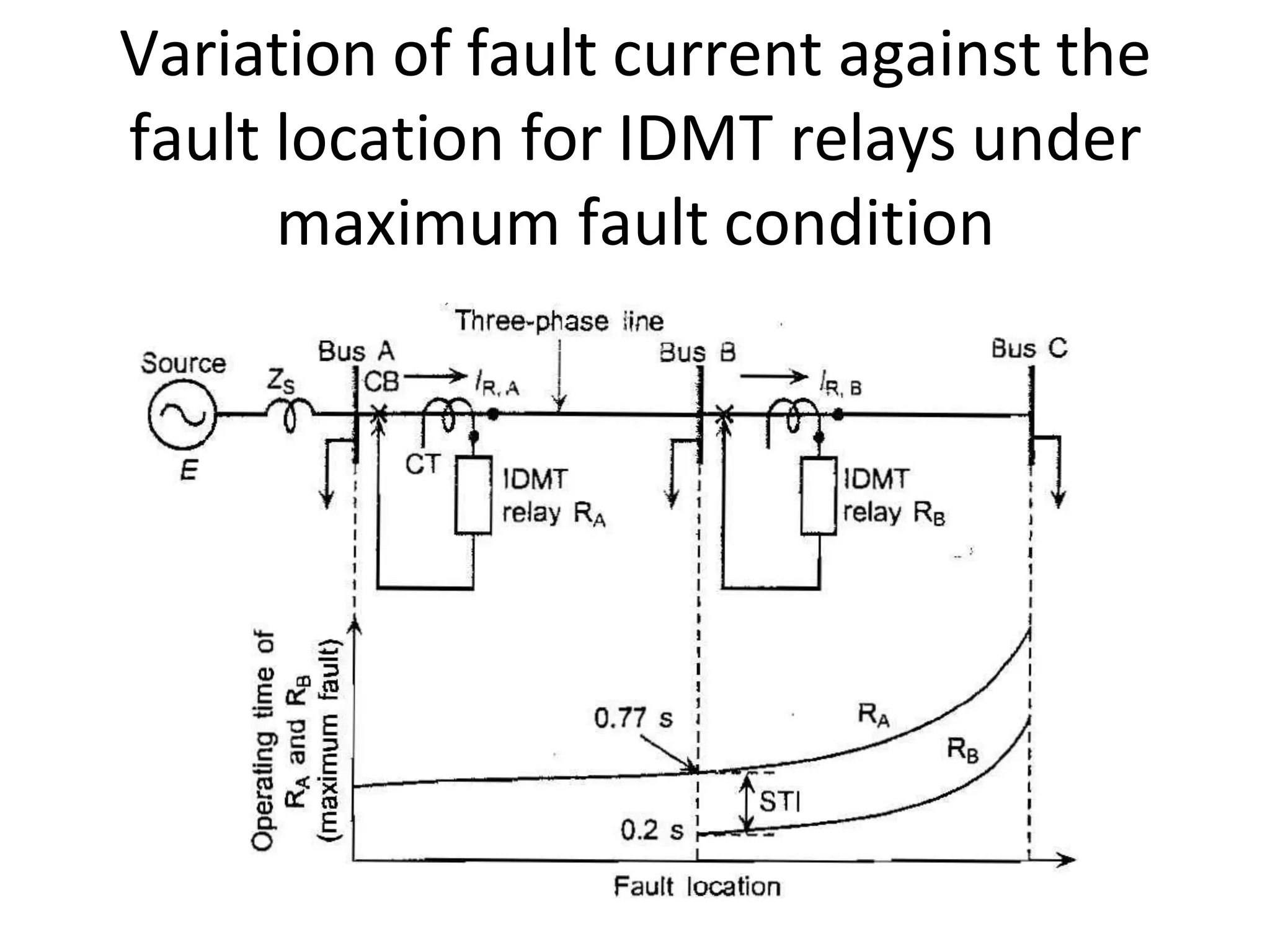
This document discusses over-current protection of transmission lines and describes various types of relays used for over-current protection including fuse, thermal relays, bimetallic relay, over-current relay. It defines important terms related to over-current relay operation such as pick up current, current setting, plug setting multiplier, and time setting multiplier. The document also discusses different types of over-current relays based on operation including instantaneous, definite time, inverse time, and various inverse relays. It describes electromagnetic attraction relays and induction type relays. Finally, it covers applications of definite time and inverse definite minimum time relays for distribution feeder protection and over-current protection of a three phase feeder.