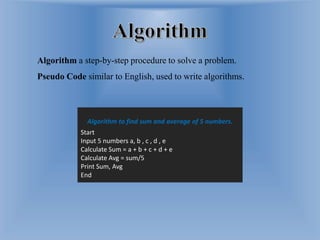
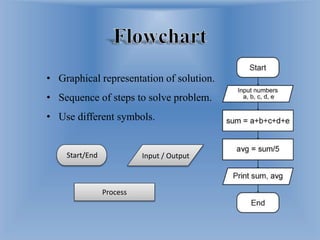
The document discusses computer programming languages and problem solving techniques. It describes different types of programming languages like low-level languages (machine and assembly), high-level languages (procedural, object-oriented, non-procedural), and how compilers and interpreters are used to translate between languages. It also provides an example algorithm to calculate the sum and average of 5 numbers and explains that algorithms and pseudocode can be used to represent problem solving steps.