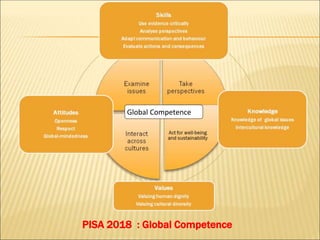
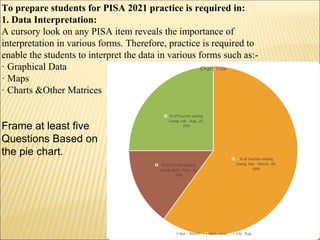
PISA is a global assessment that measures 15-year-old students' ability to apply their reading, mathematical, and scientific knowledge to real-life problems and situations. It is administered by the OECD every three years. India will participate for the second time in 2021 after its initial participation in 2009. PISA assesses students' capacity to comprehend complex texts, interpret data, and solve problems. It emphasizes skills like critical thinking instead of just testing content knowledge. Preparing Indian students for PISA involves practicing skills like data interpretation, reading comprehension, note-making, and developing open-minded and collaborative problem-solving abilities.