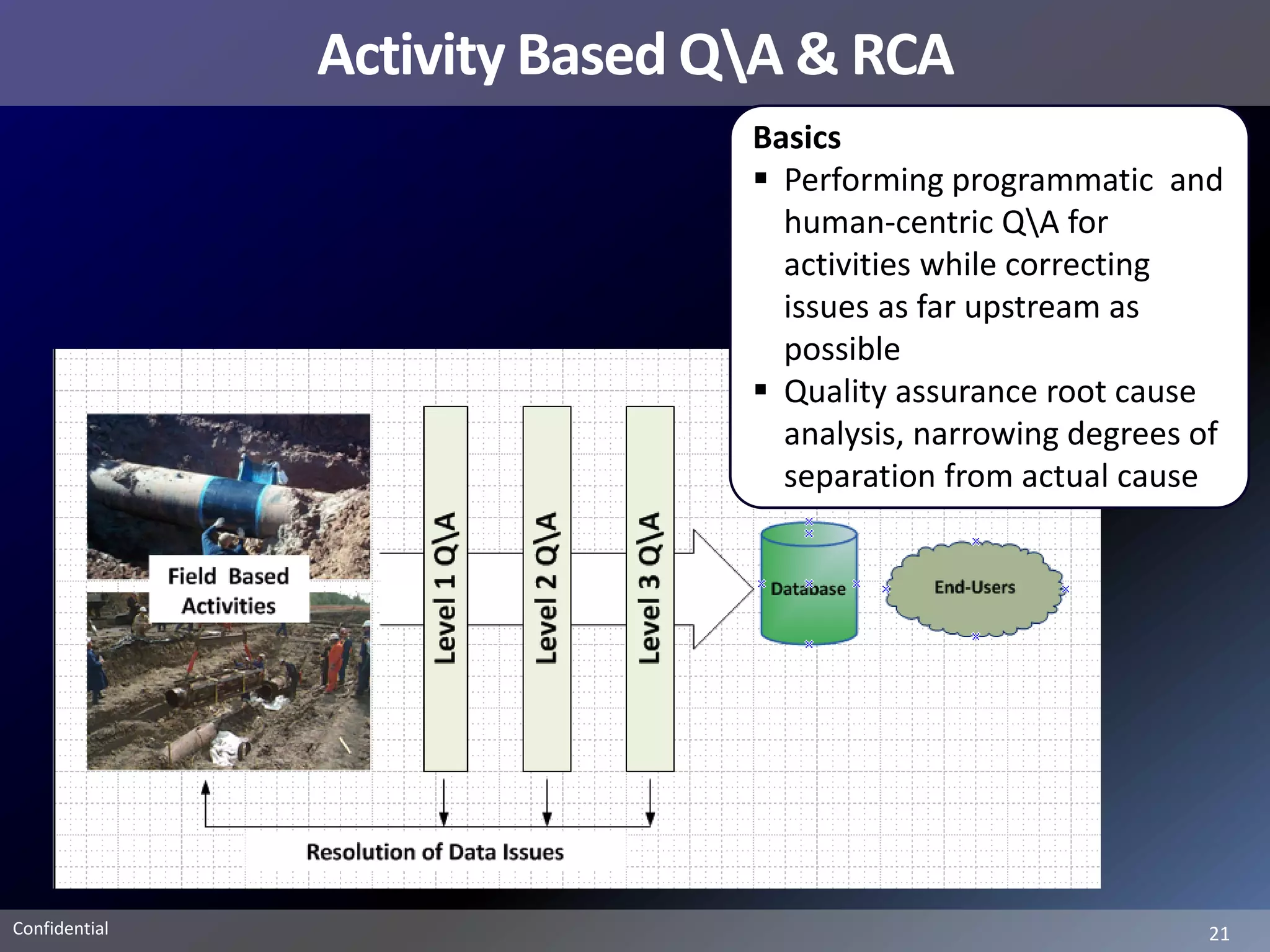
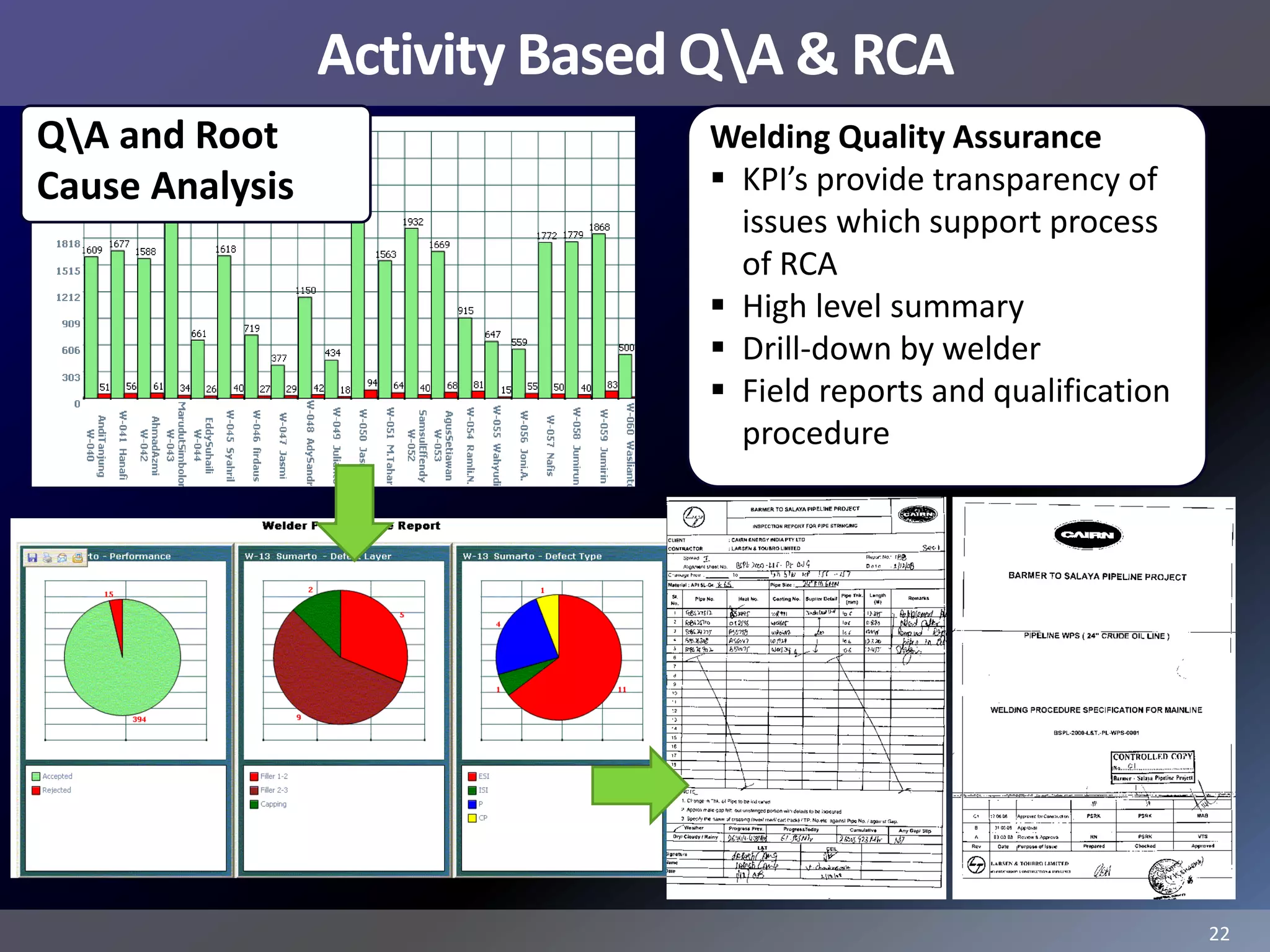
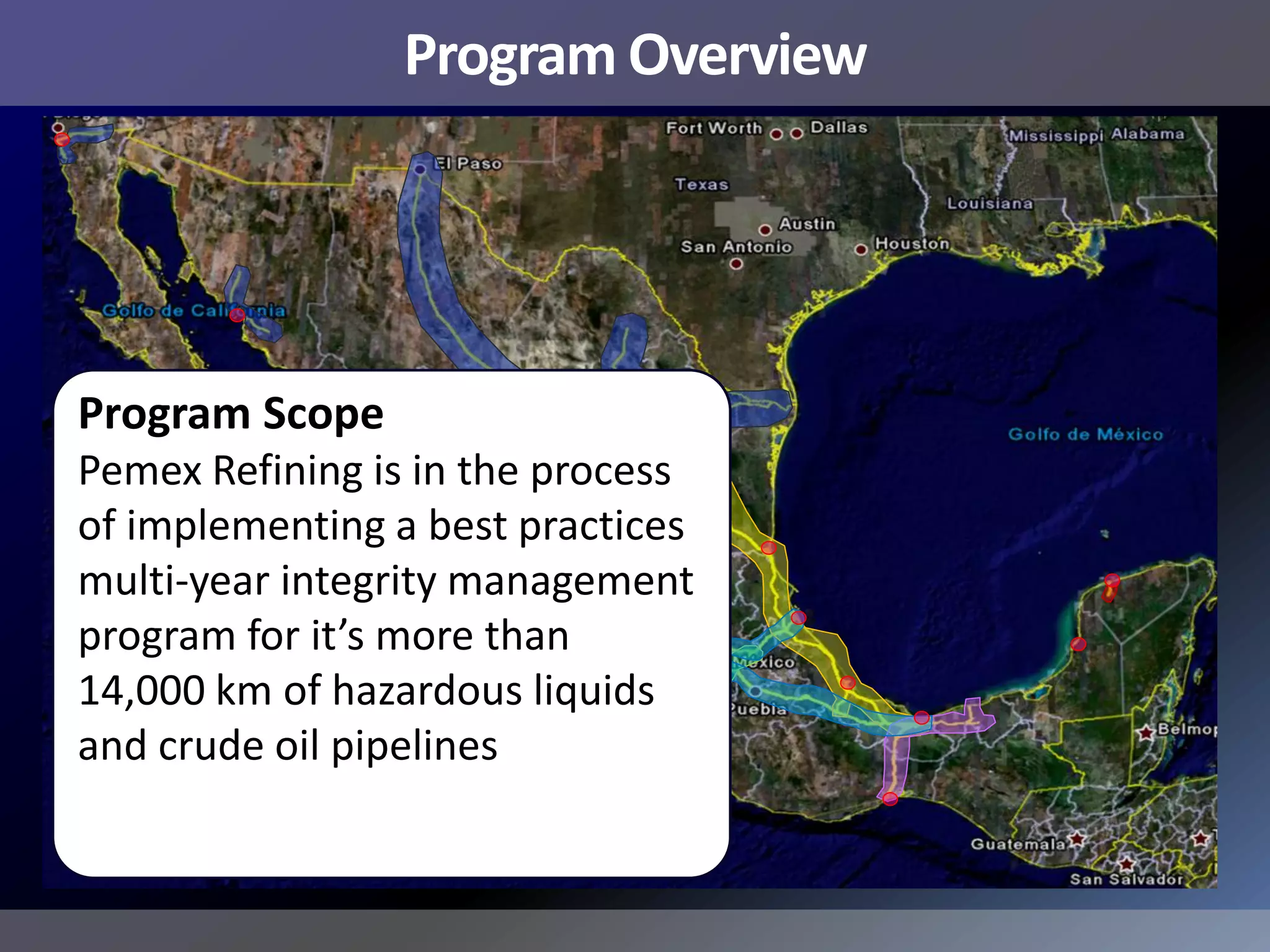
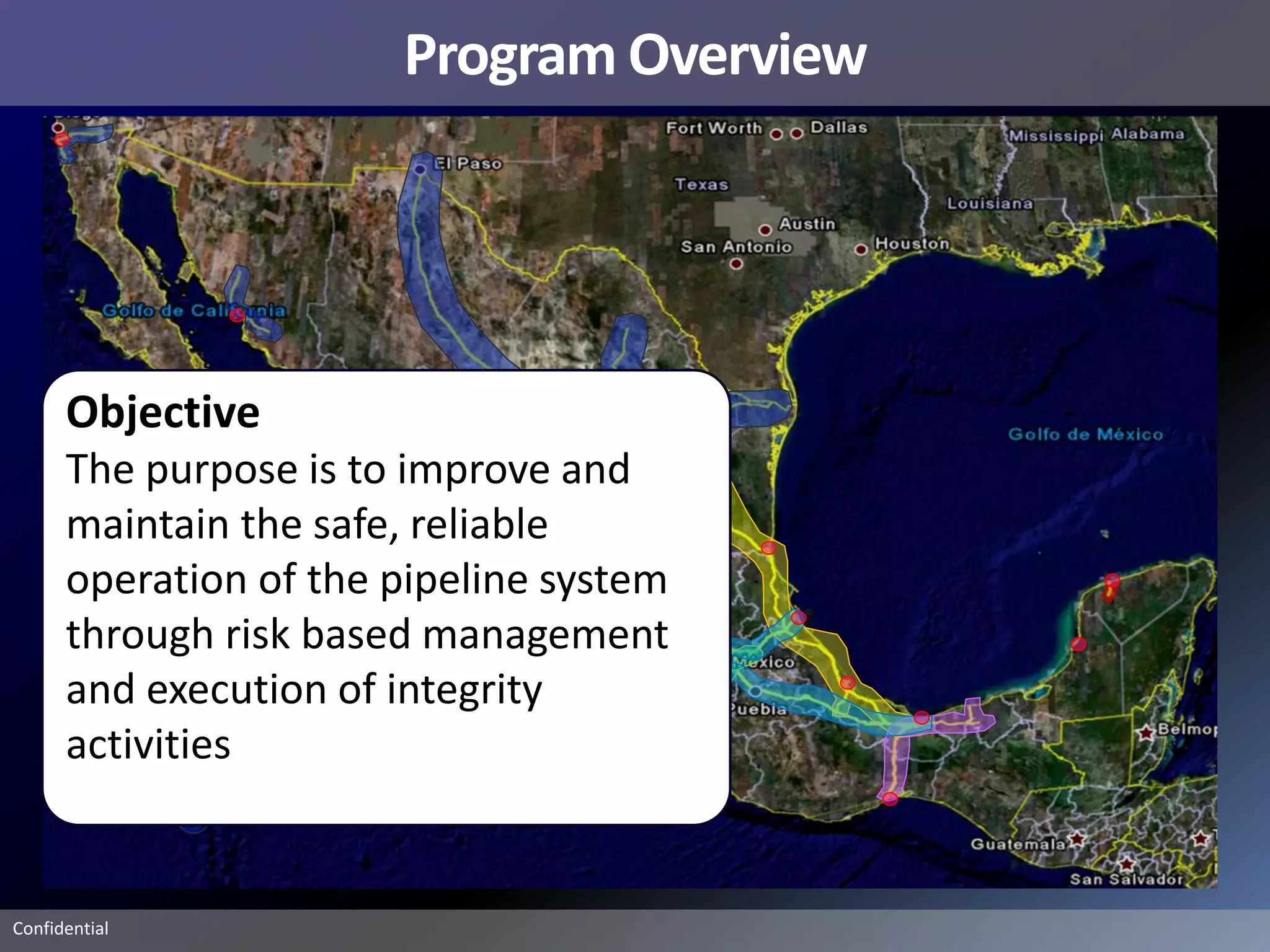
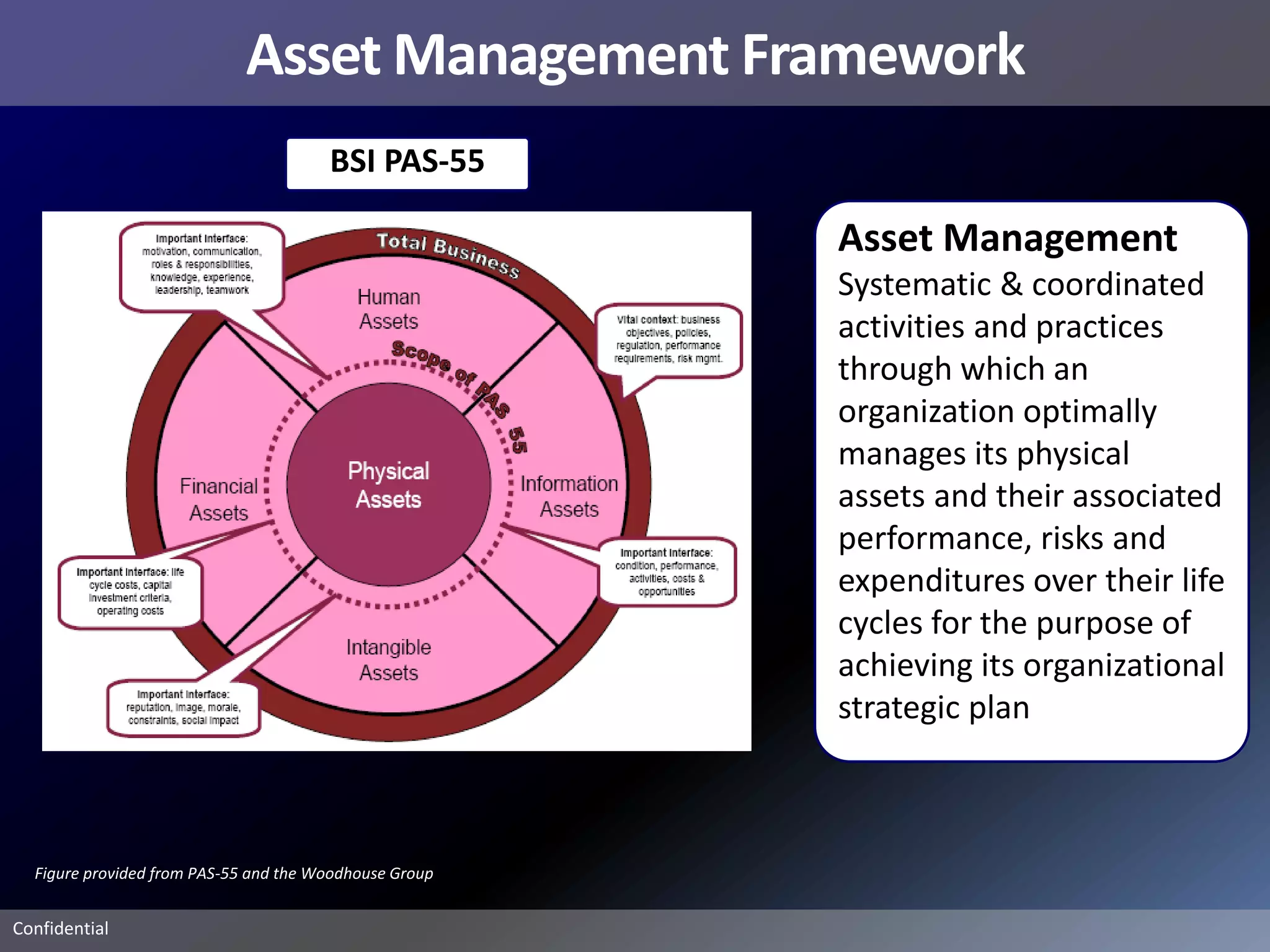
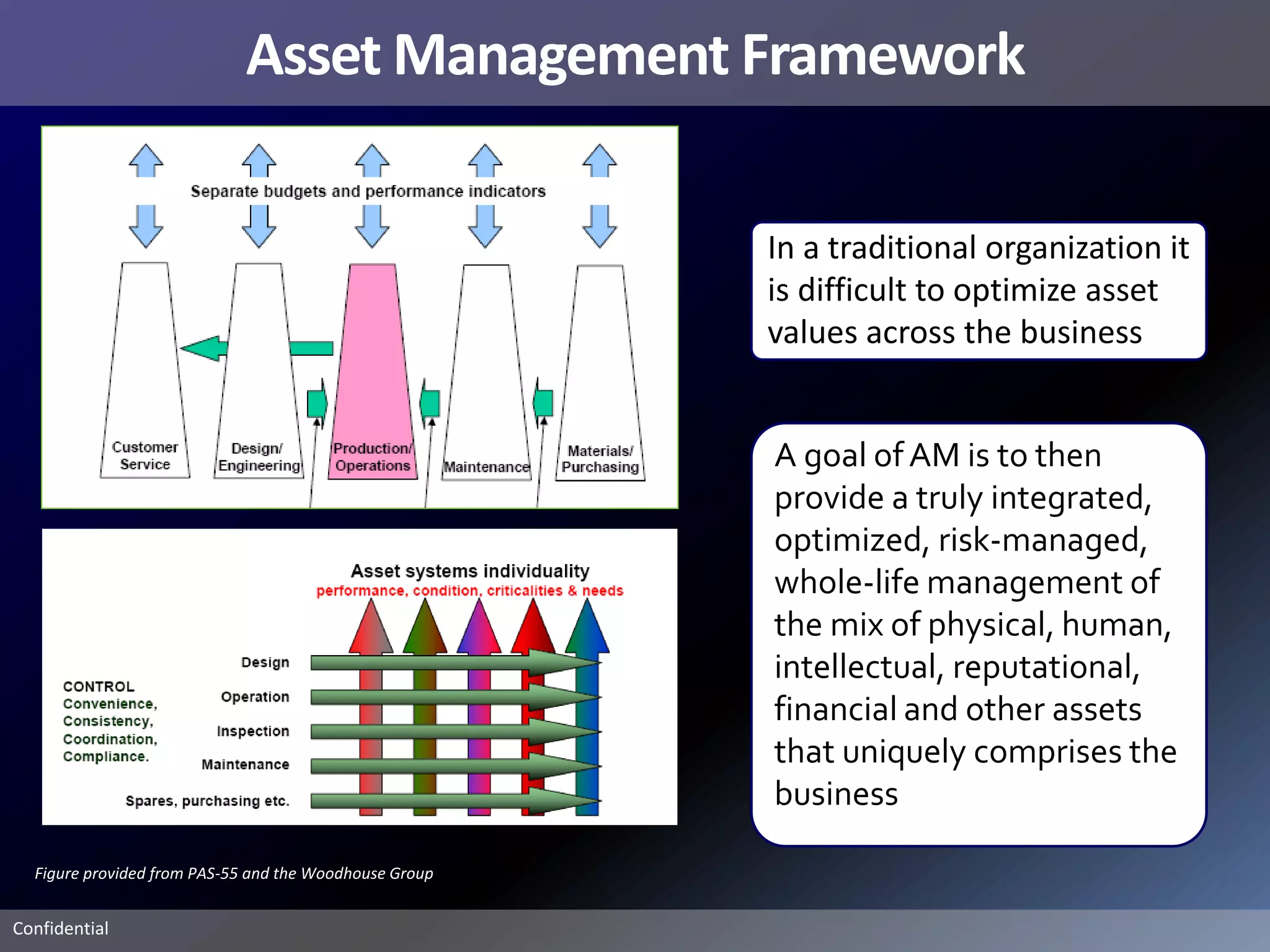
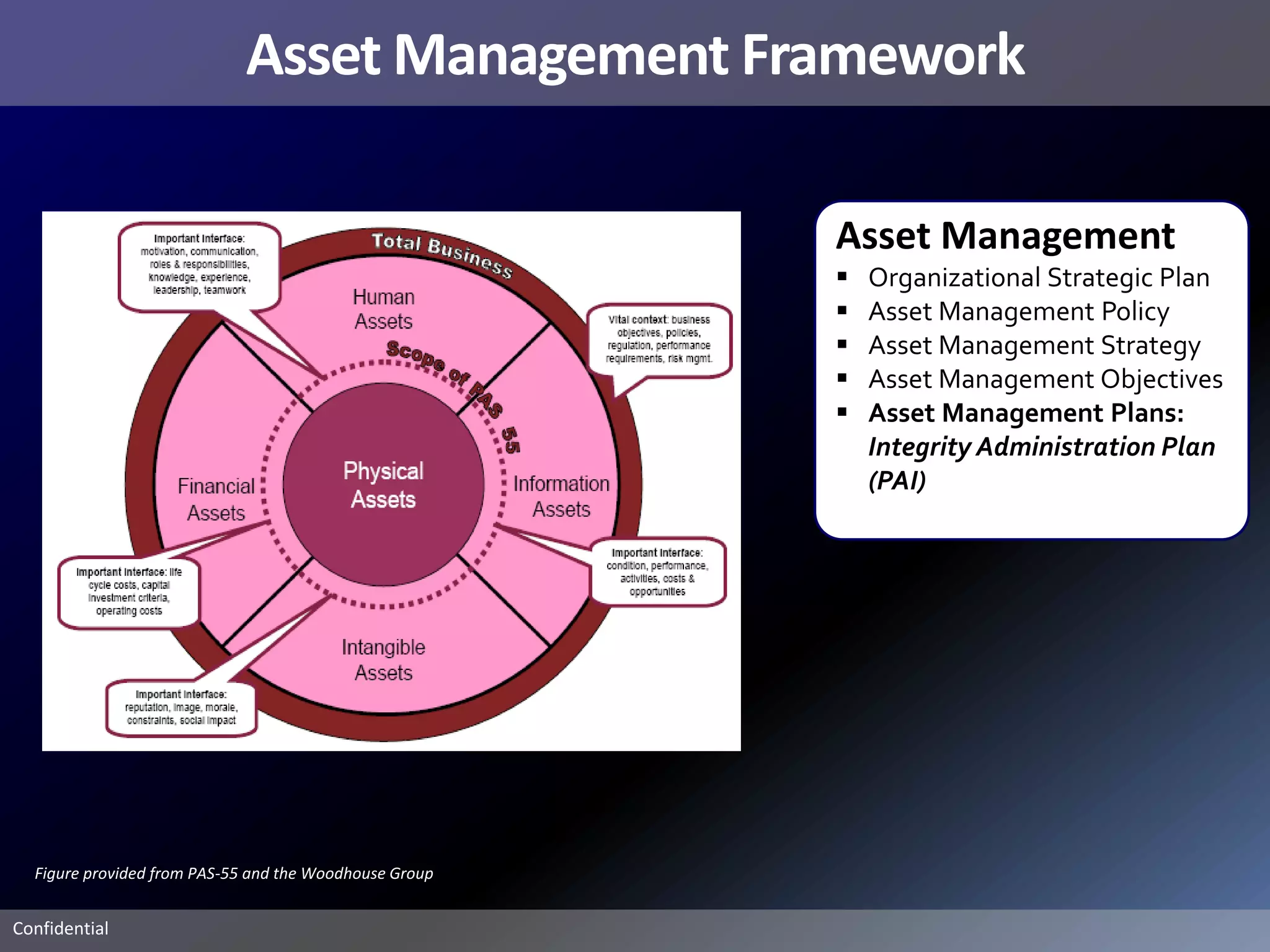
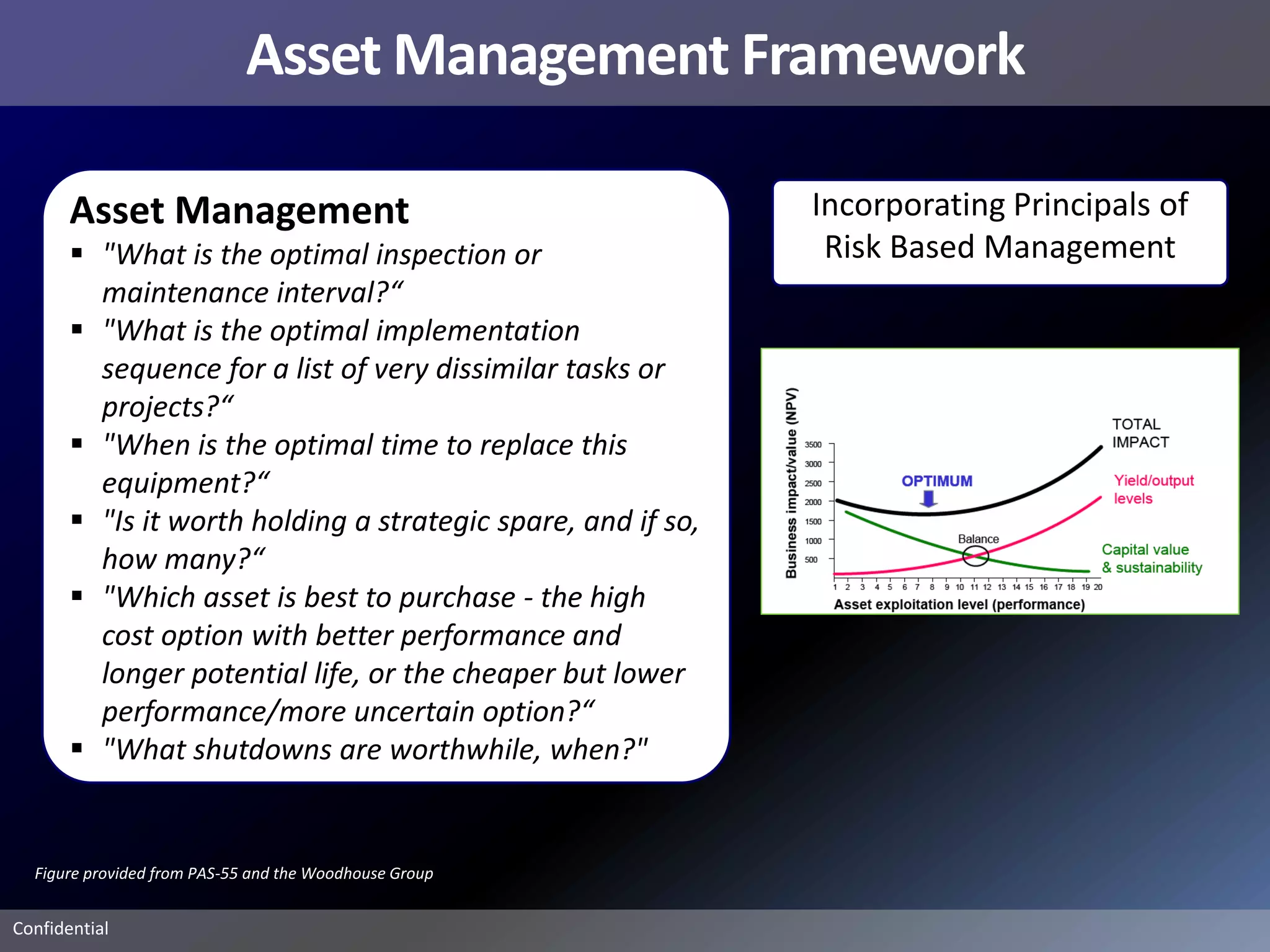
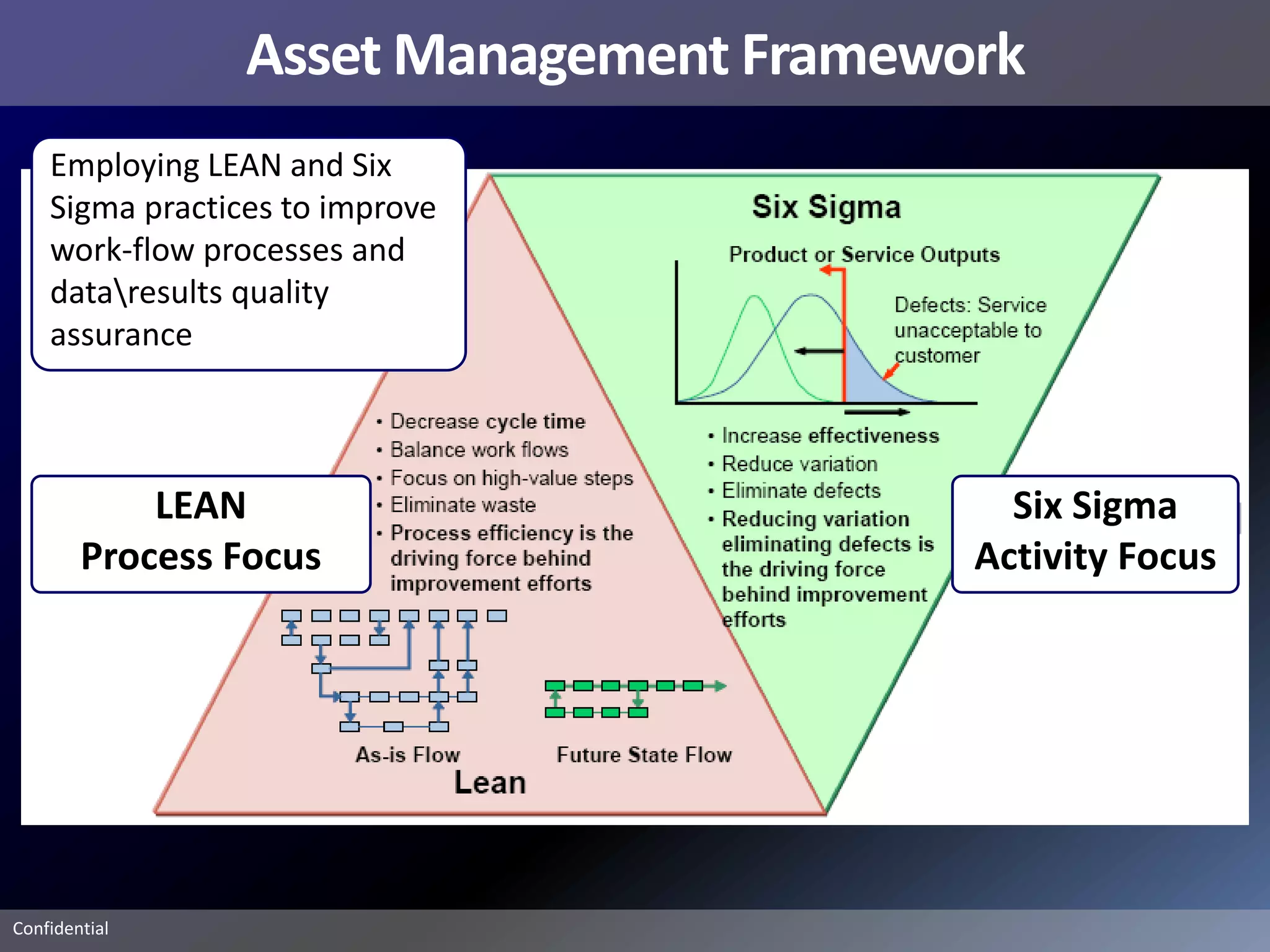
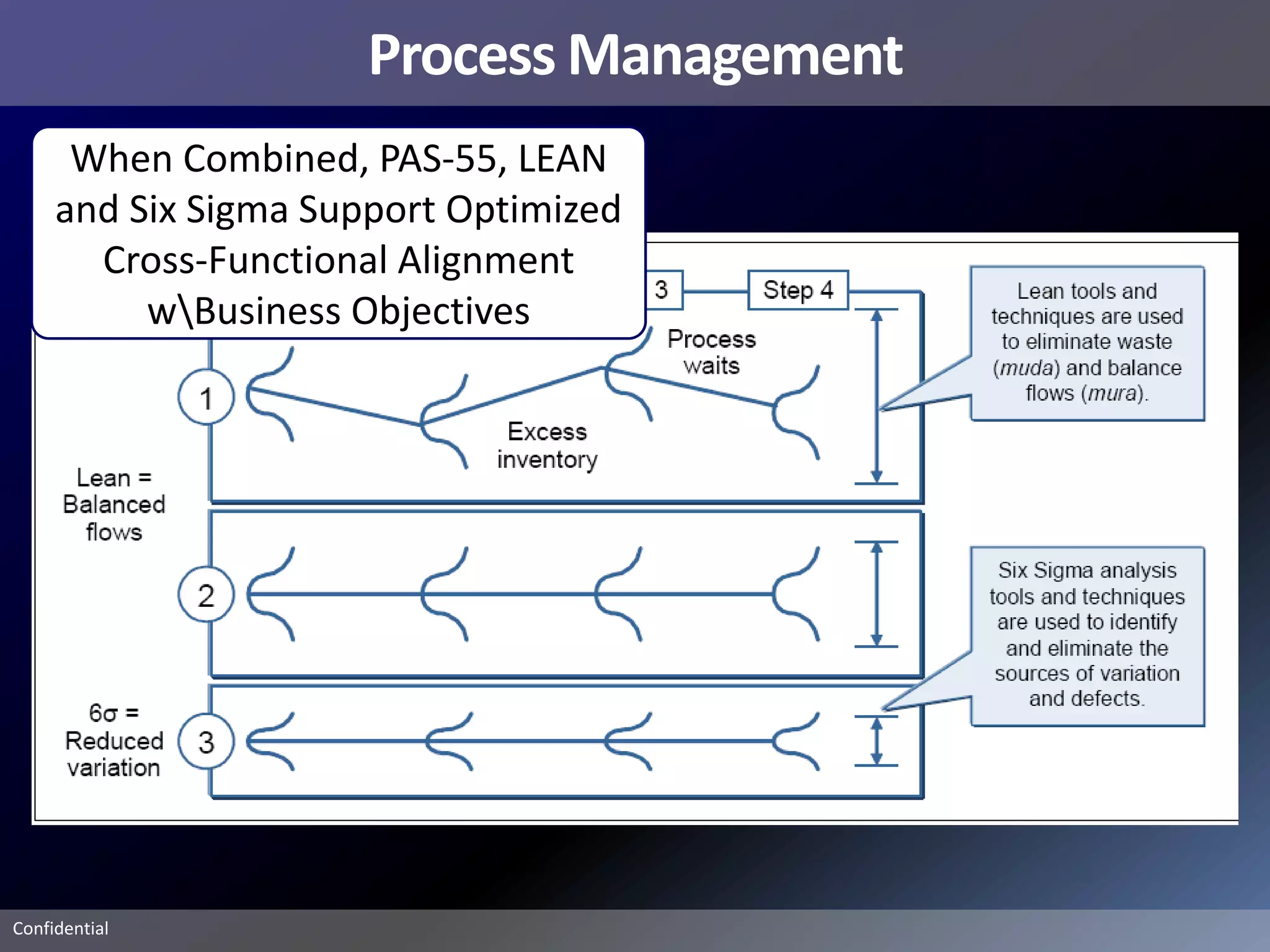
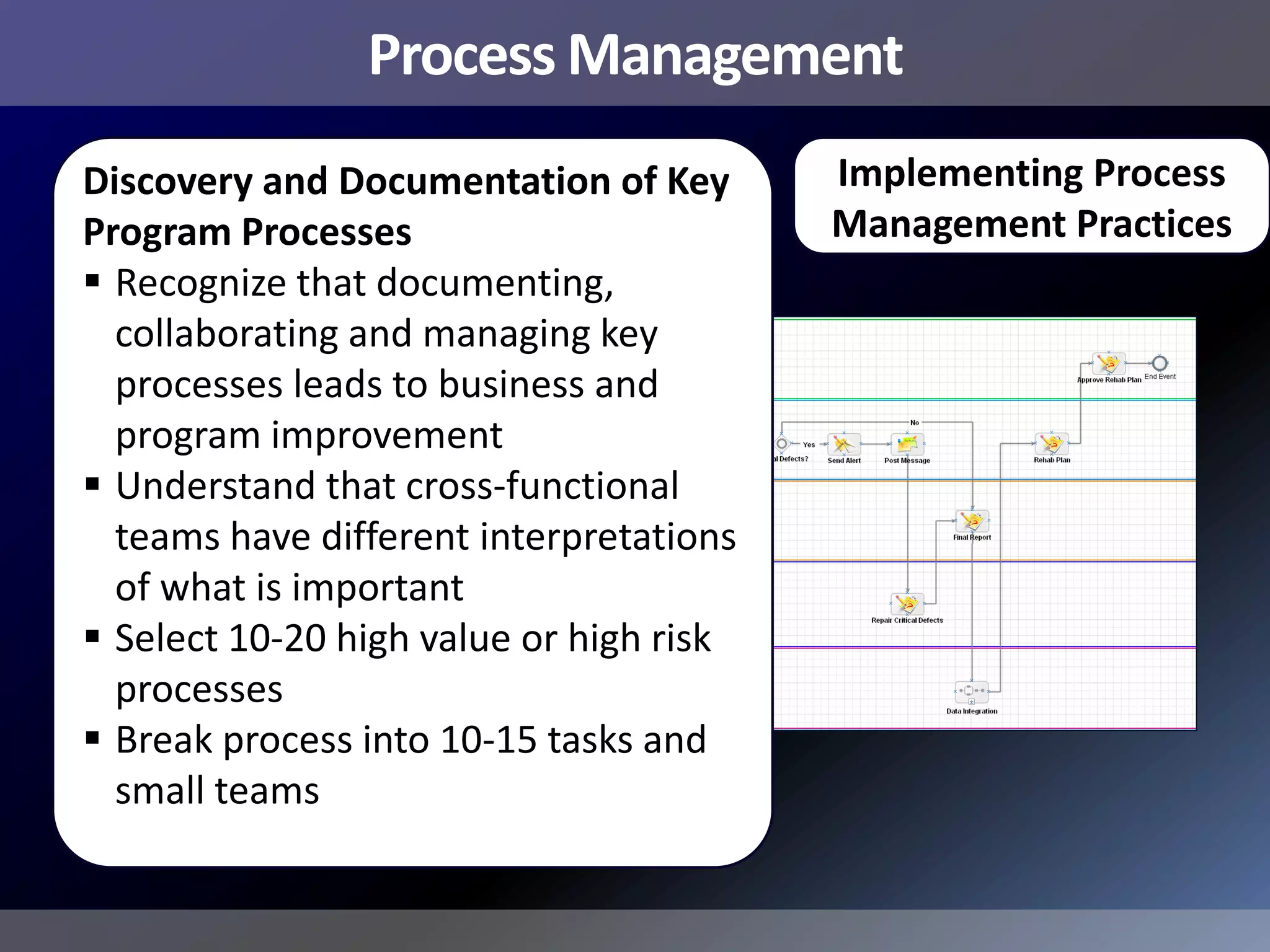
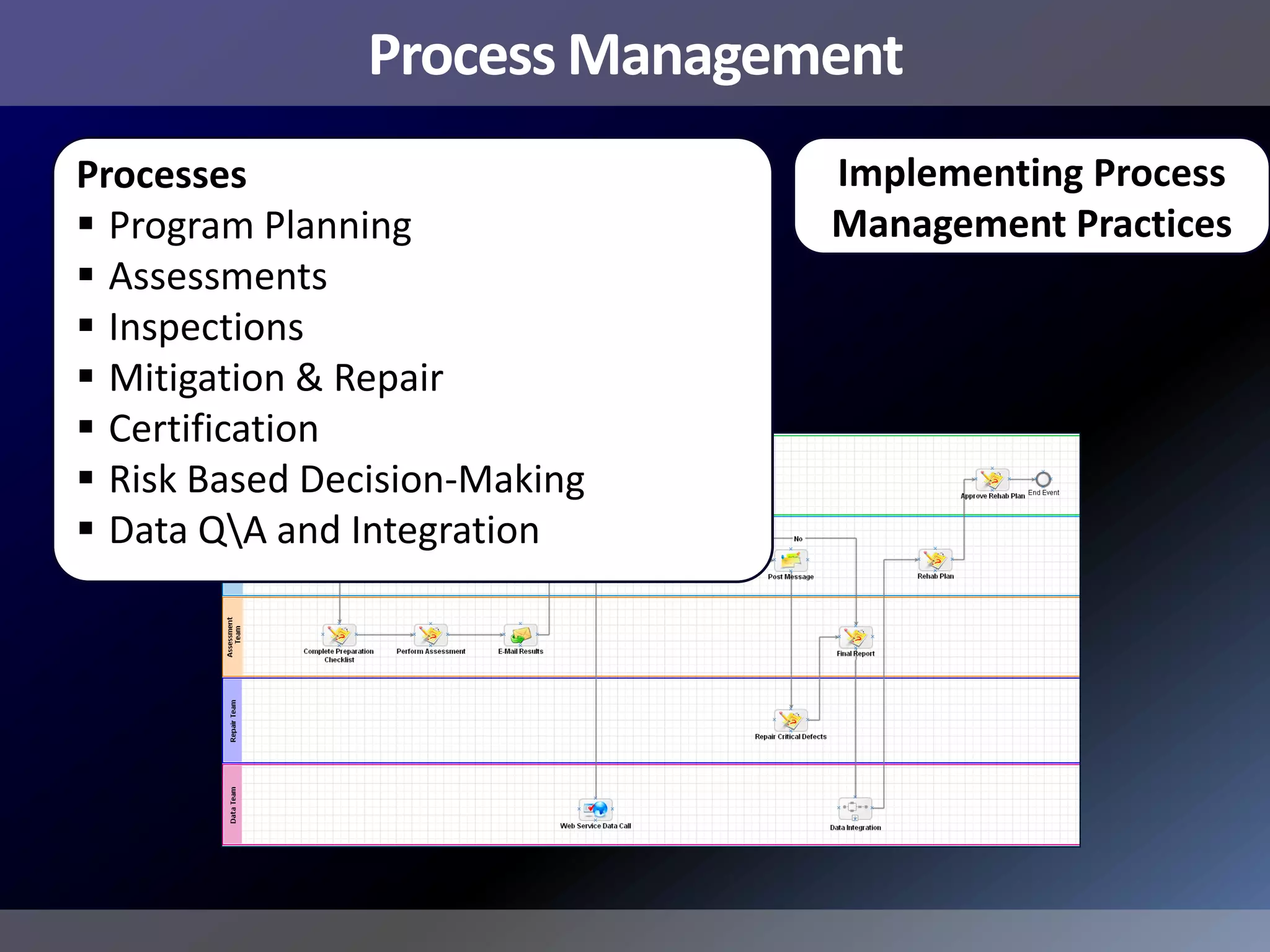
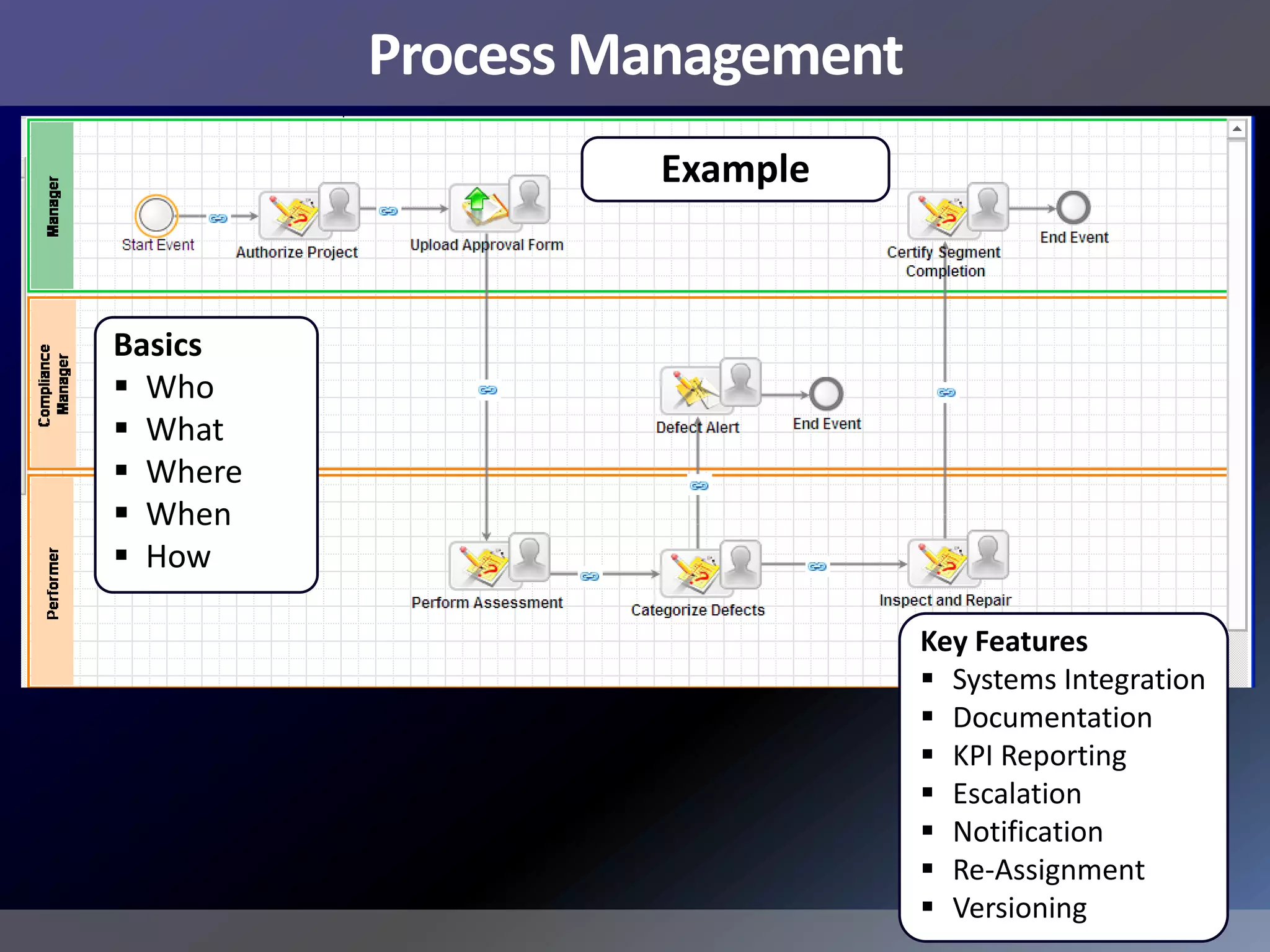
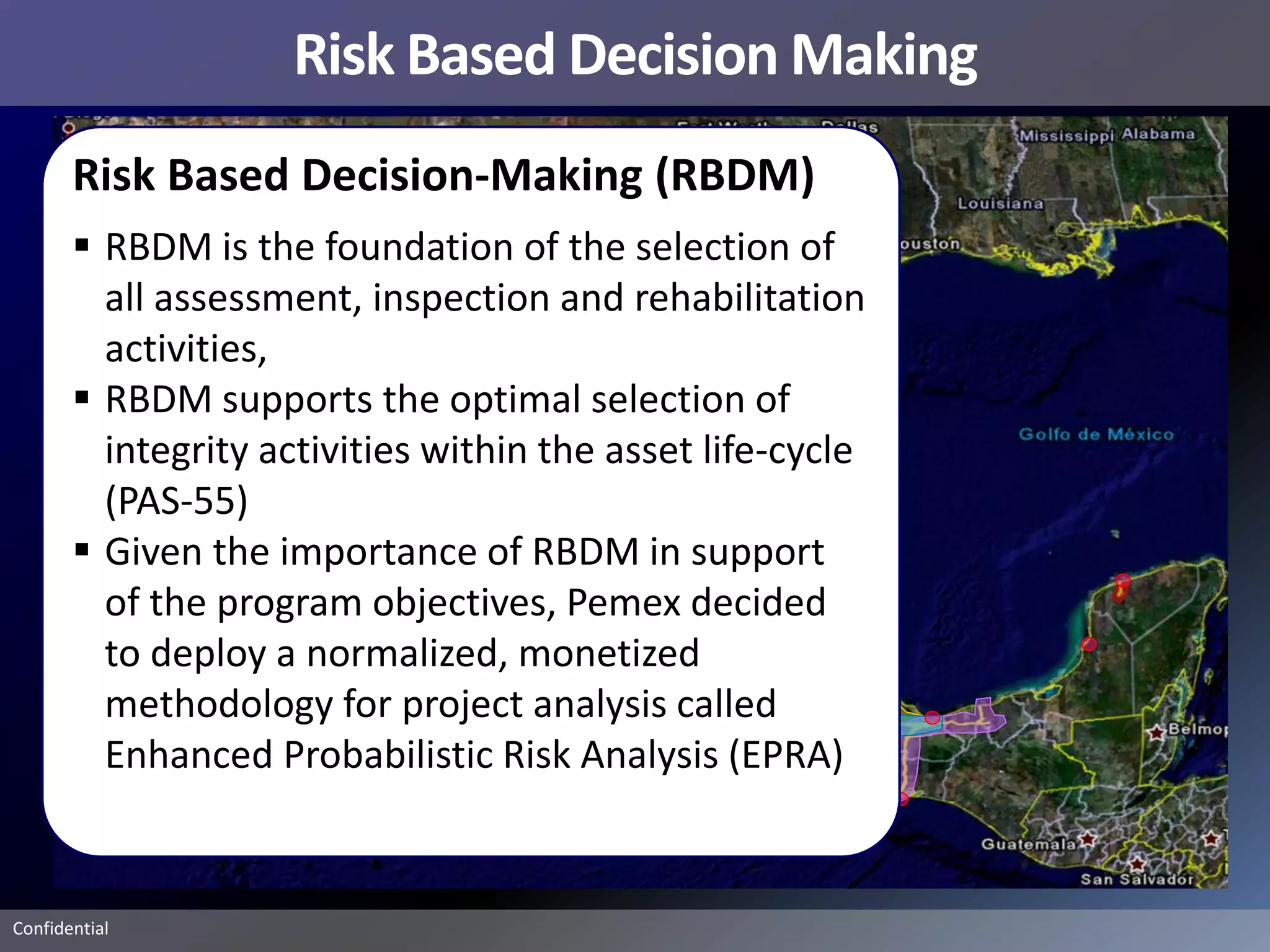
Pemex Refining is implementing a best practices pipeline integrity management program for its 14,000 km pipeline system. It is using an asset management framework based on BSI PAS-55 standards and risk-based decision making. It has selected key processes to document and improve using Lean and Six Sigma. It is supporting the program with a web-based integrity management system to manage the asset lifecycle and risk-based activities.







![Risk Based Decision Making
PFIM LOF Algorithm Structure
Broaden KPI’s to AM Life-
Threat EC IC SCC TPD WOF MFG CON IO
Cycle
EQ
Categories
What is value of asset
given it’s operational risk
Variable Exposure Mitigation Resistance
profile, required
Categories
maintenance investments
Attributes and business value?
Attribute
Score E1 E2 E3 M1 M2 M3 R1 R2 R3
Variable
Weight WE1 WE2 WE3
Exposure = Mitigation = Resistance =
(VariableE1 * WE1) + … 1 – [(1 - VariableM1) * … 1 – [(1 - VariableR1) * …
(VariableEn * WEn) (1 - VariableMn) (1 - VariableRn)
WOF Threat Score = (Exposure) * (1 - Mitigation) * (1 – Resistance)
LOF Score = 1 – [(1-EC) * (1-IC) * (1-SCC) * (1-TPD) * (1-WOF) * (1-MFG) * (1-CON) * (1-IO) * (1-EQ)]
ROF Score = LOF Score * COF Score
Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imspemexcasestudy-monterrey2009-120325212513-phpapp02/75/Process-Centric-Integrity-Management-20-2048.jpg)