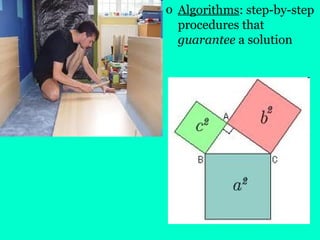
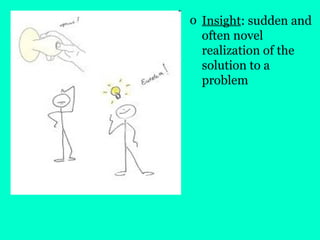
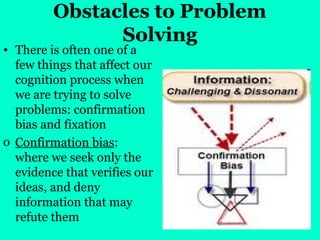
The document discusses cognition, focusing on concepts, problem-solving methods, and creativity. It outlines various strategies for problem-solving, including trial and error, algorithms, and heuristics, while also identifying obstacles such as confirmation bias and fixation. Creativity is defined as the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas, emphasizing the importance of expertise, imaginative thinking, personality traits, intrinsic motivation, and a supportive environment.