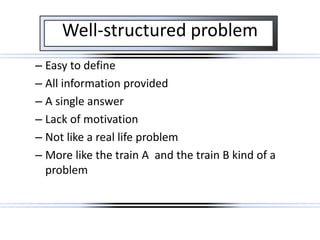
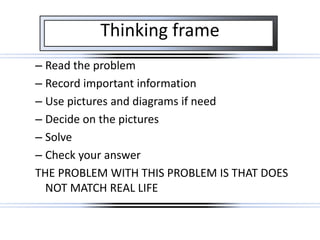
The document discusses using problem-based learning (PBL) to make classroom learning more engaging for students. It describes PBL as involving real-world problems that require critical thinking, research, teamwork and problem-solving skills. The document outlines the steps of PBL, including defining an ill-structured problem, analyzing it to identify knowledge gaps, testing theories, and presenting solutions. It argues that PBL is more motivating for students compared to traditional teaching because it uses hands-on, student-centered approaches focused on real problems.