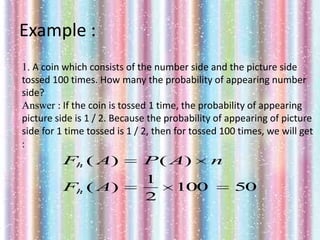
This document discusses probability and how it is calculated from a sample space. It provides the formula for calculating probability as the number of outcomes in the event divided by the total number of outcomes in the sample space. It gives examples of calculating probability when rolling a die and explains that probabilities range from 0 to 1, with 1 being a certain event and 0 being impossible. It also introduces the concept of expected frequency as the probability of an event occurring over many trials.