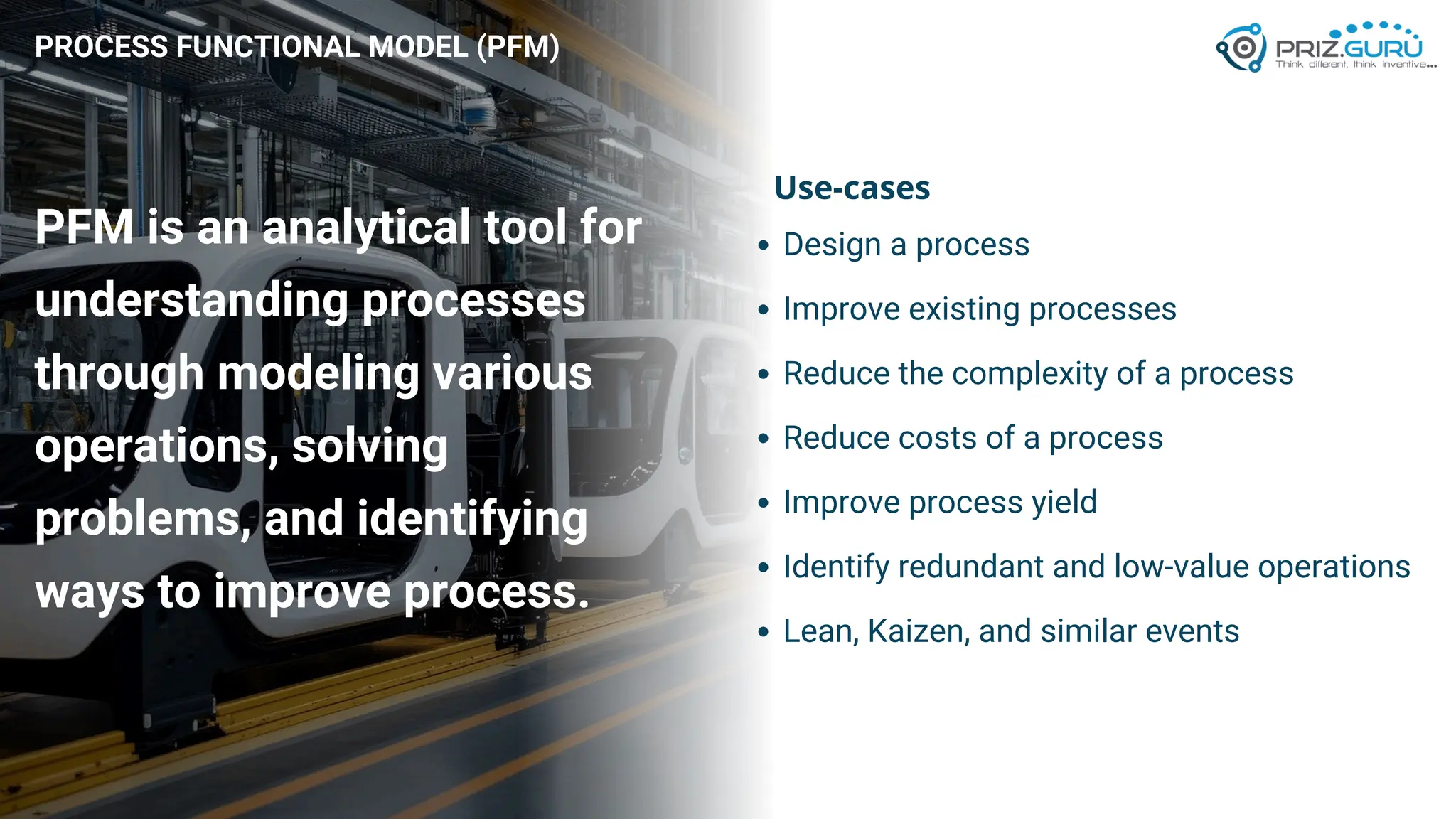
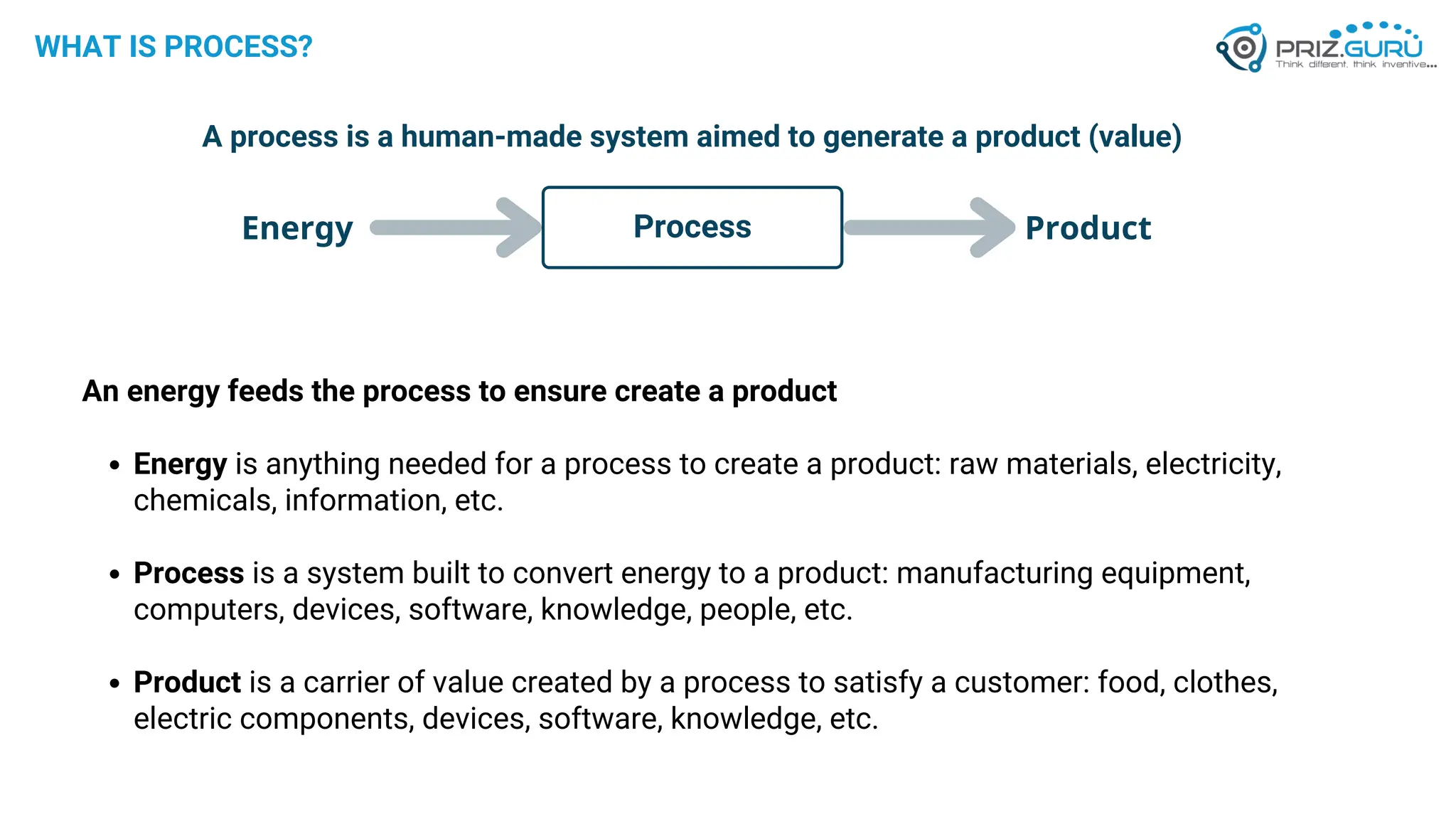
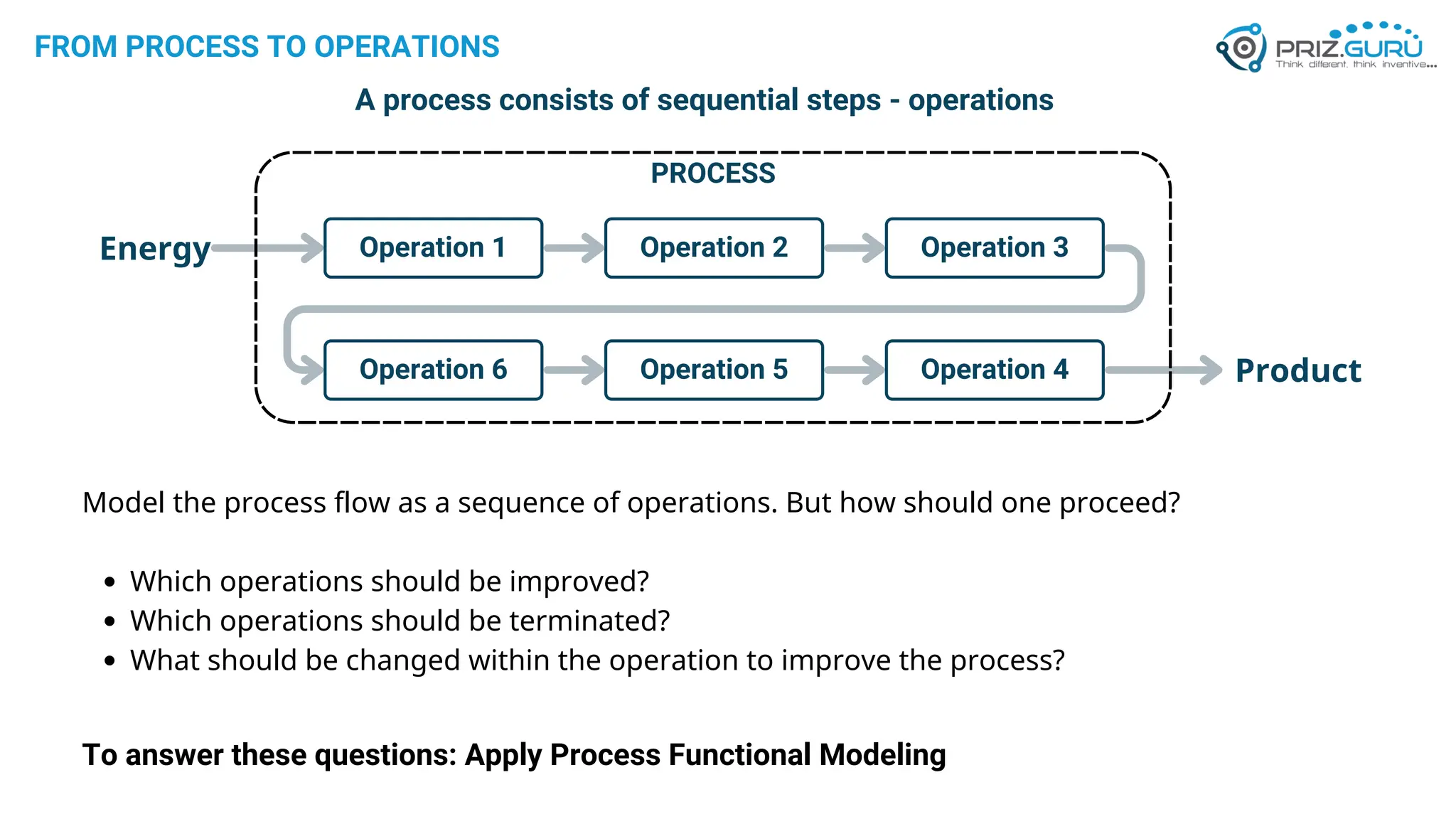
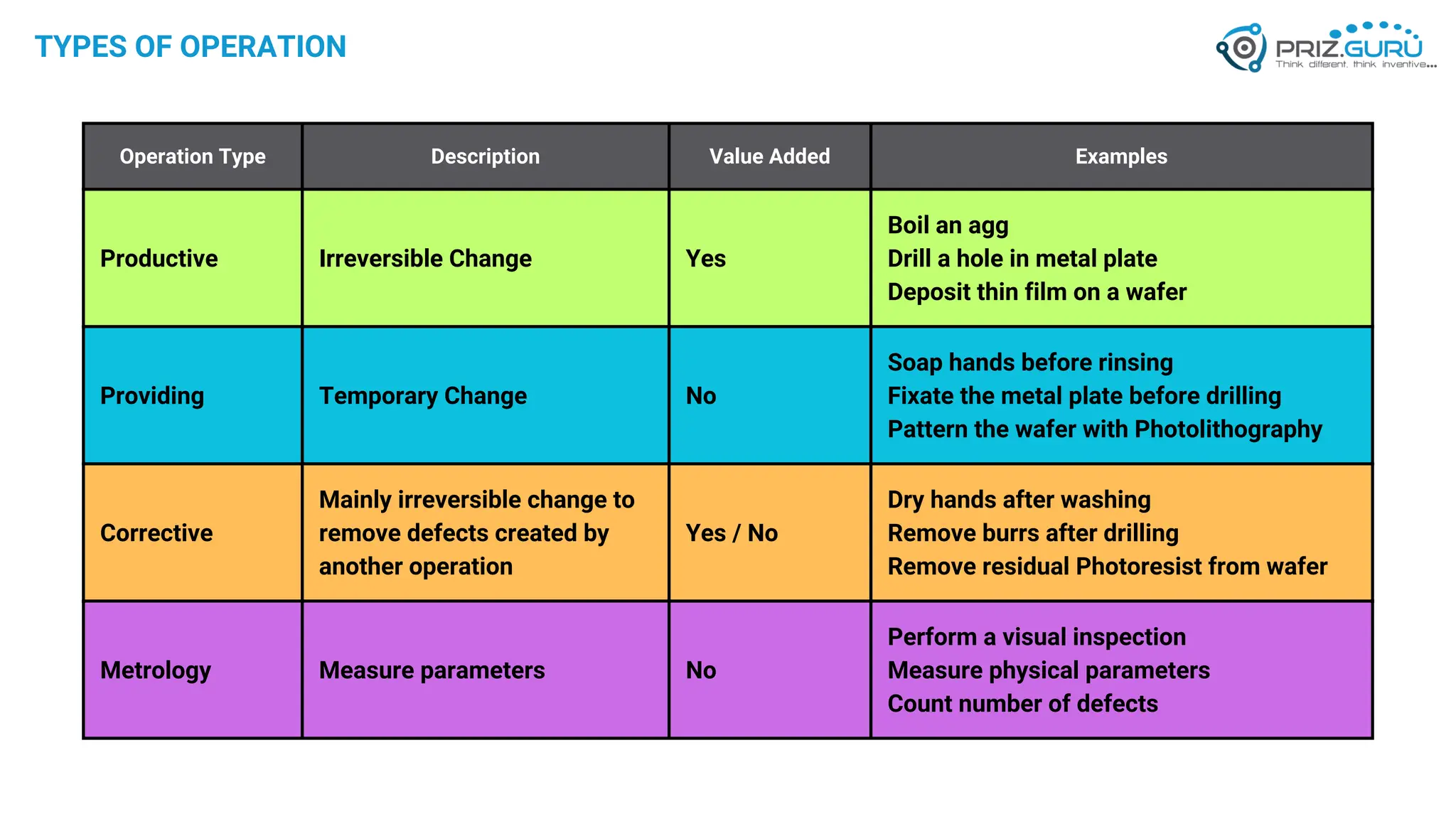
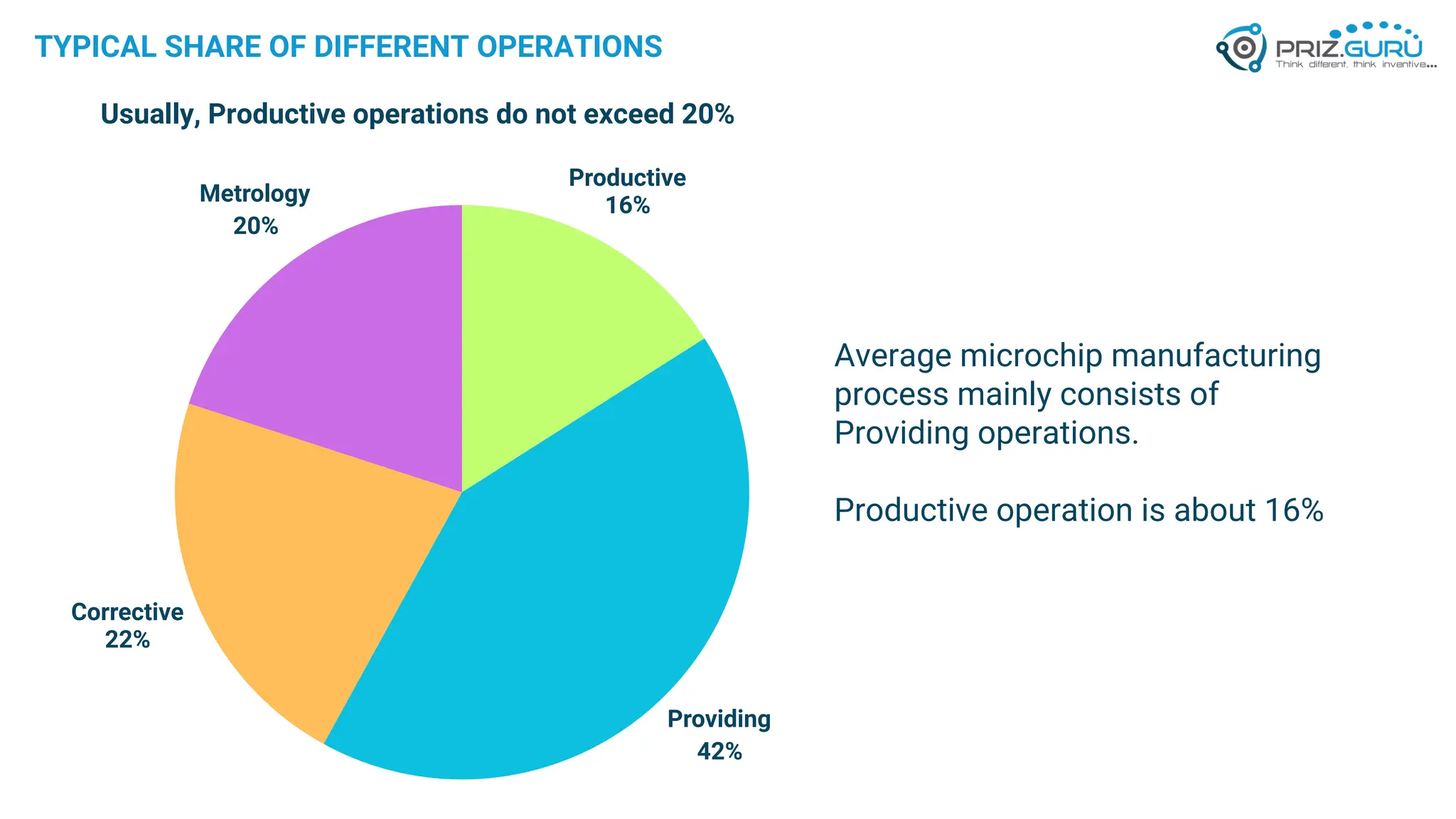
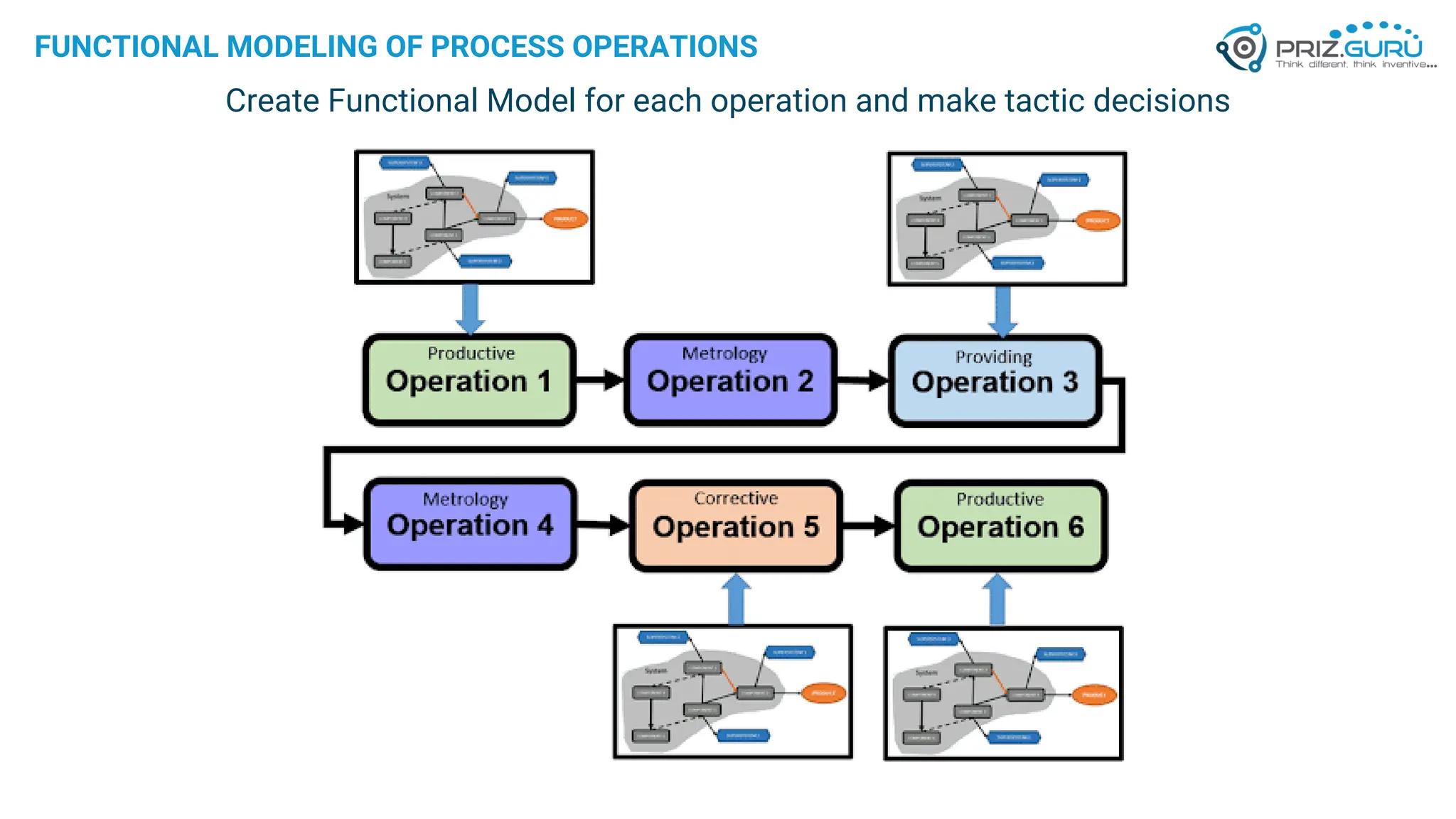
Discover how Process Functional Modelling (PFM) helps teams understand, analyze, and improve operational processes. This presentation from PRIZ Academy explores how to classify and evaluate each operation in a process, reduce complexity, and boost productivity using the PRIZ Engineering Thinking Platform. Ideal for QA leaders, engineers, and process improvement professionals.