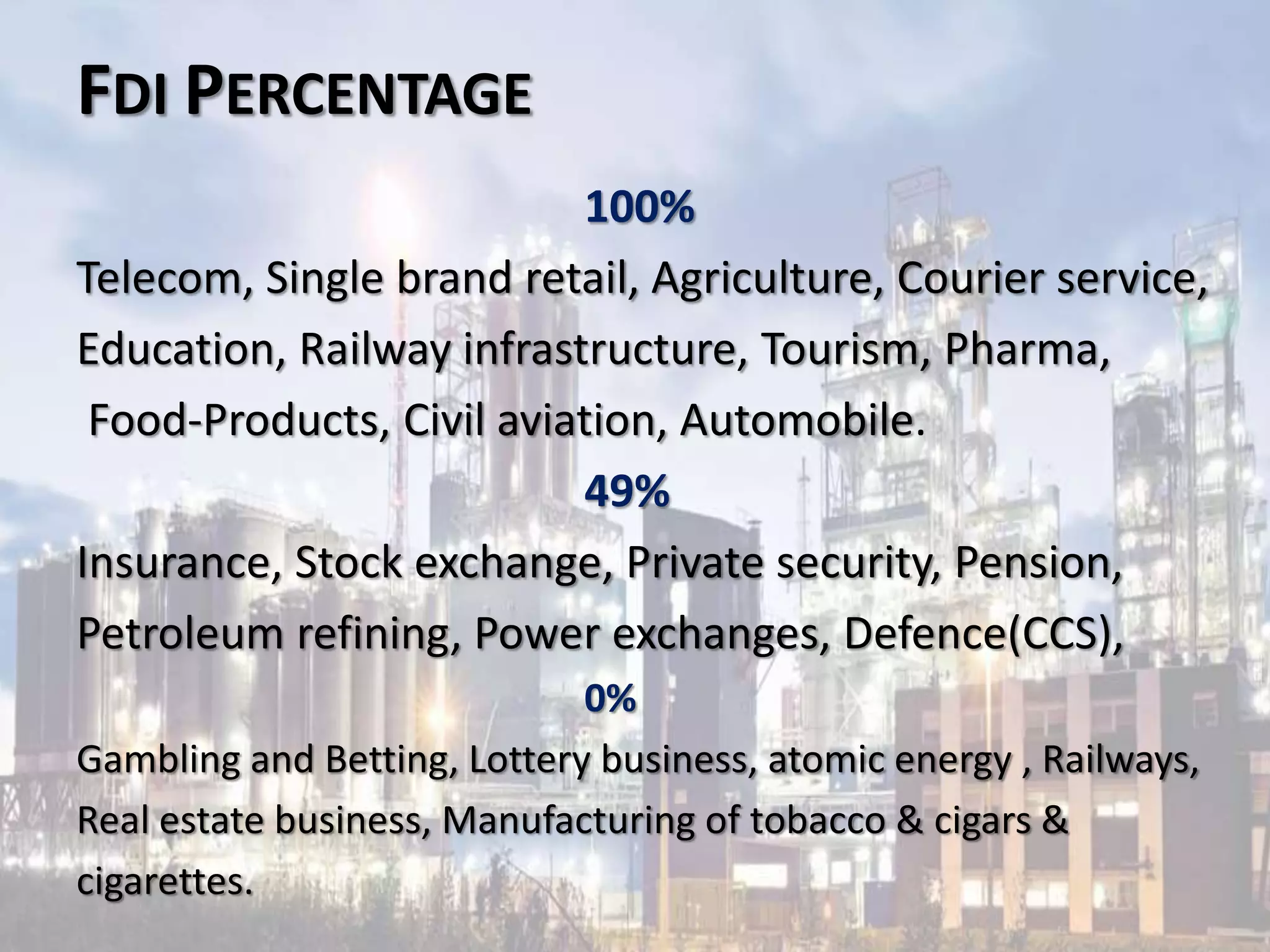
Privatization in India, introduced in 1991, involves transferring businesses and services from public to private ownership to improve efficiency and attract investment. Its goals include restructuring the public sector, creating jobs, and optimizing resource use, resulting in significant GDP growth and increased foreign direct investment across various sectors. However, it also poses challenges such as the potential for natural monopolies, regulatory issues, and overlooking weaker societal segments.