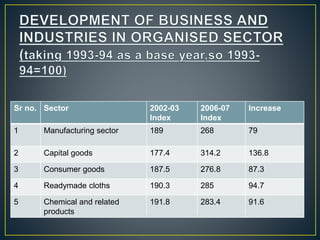
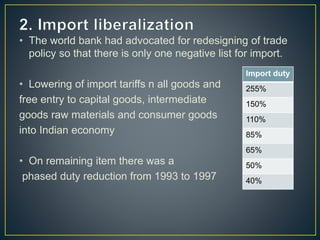
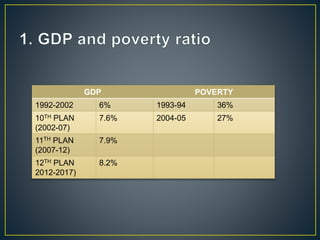
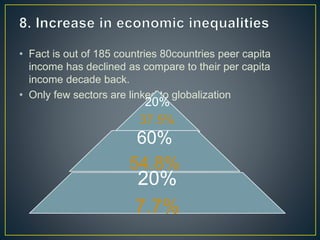
The document discusses significant shifts in India's economy beginning in the 1990s, particularly the adoption of the LPG model (liberalization, privatization, globalization) which aimed to address fiscal deficits and inefficiencies in public sector undertakings. It highlights the impacts of these reforms, including increased accountability in the private sector, efficiency concerns, and the challenges faced by both public and private sectors, alongside the effects of globalization on trade and employment. The document concludes by pointing out a mixed outcome of these reforms on economic growth, infrastructure, and social welfare objectives.