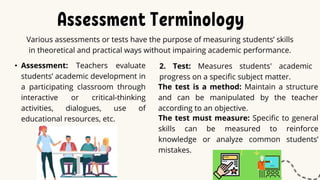
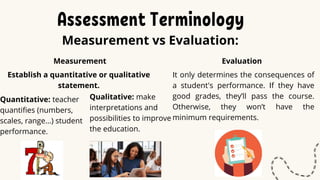
This document discusses principles of language assessment. It defines key terms like assessment, tests, evaluation, and measurement. Assessment refers to how teachers evaluate student development through classroom activities, while tests measure progress on specific subjects. Evaluation determines student performance outcomes.
The document also distinguishes between formal and informal assessment, and formative and summative assessment. Formal assessment uses objective criteria to measure skills over time, while informal assessment lacks structured criteria. Formative assessment provides feedback to strengthen learning, and summative assessment measures knowledge and skills in a graded way.
Finally, it outlines different types of language assessments like achievement, diagnostic, placement, and proficiency tests. It discusses principles of reliable assessment like practicality, validity