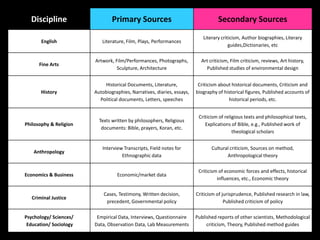
This document discusses the differences between primary and secondary sources. Primary sources are original materials created at the time under study, such as diaries, autobiographies, speeches, historical documents, first-hand accounts, photos, videos, and letters. Researchers create primary sources when collecting original data. Secondary sources are records or interpretations created after the event by someone not directly involved, such as biographies, encyclopedias, dictionaries, almanacs, book reviews, movie adaptations, and newspapers. Primary sources provide direct information while secondary sources analyze or interpret primary sources.