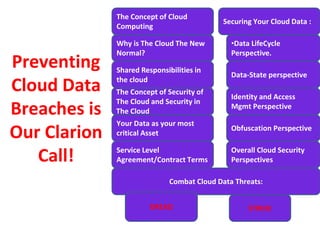
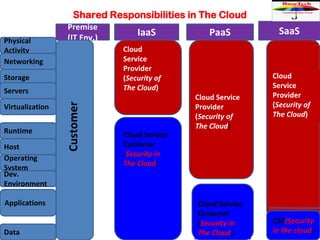
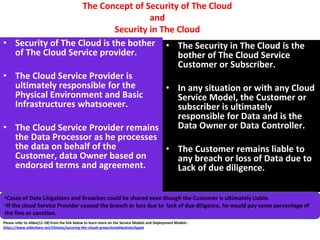
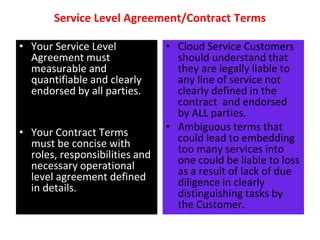
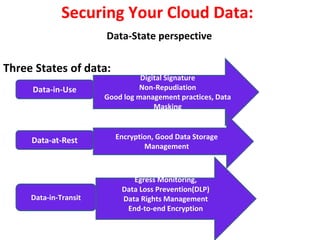
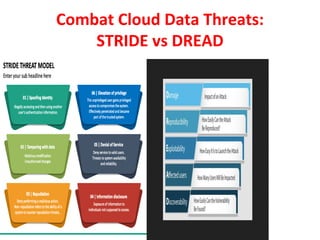
The document discusses cloud data security, emphasizing the responsibilities of both cloud service providers and customers in protecting data. With a significant increase in cloud adoption, organizations are increasingly concerned about security threats, requiring measures like data lifecycle management and risk assessment strategies. Key concepts include the shared responsibility model, service level agreements, and various security perspectives to combat potential breaches.