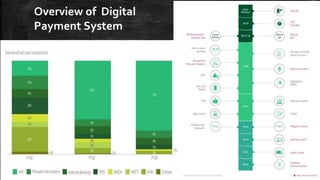
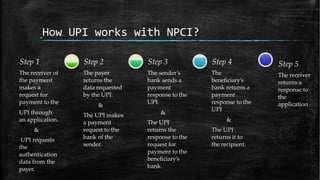
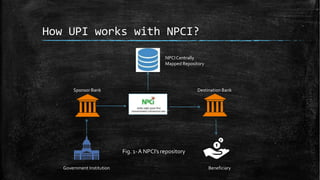
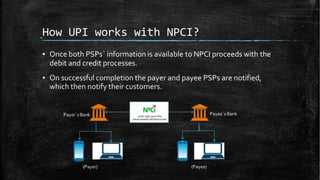
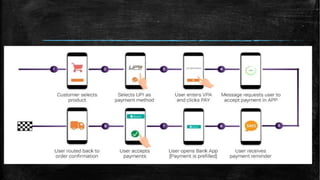
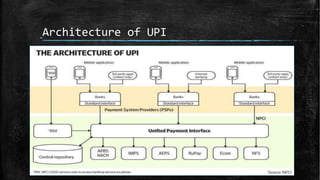
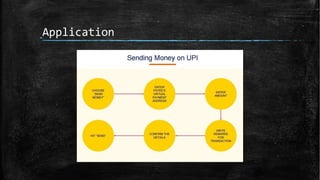
UPI (Unified Payments Interface) allows bank account holders to send and receive money between bank accounts instantly using a virtual address without entering additional bank details. UPI is operated by NPCI (National Payments Corporation of India) and allows inter-bank fund transfers through IMPS. It uses a virtual ID instead of bank account and IFSC codes, and provides secure two-factor authentication for payments. UPI enables various online payment options like sending money to contacts, collecting payments remotely, and buying items online or through apps.























![References
▪ [1] “RBI PaymentSystemVision document”, RBI, 2012-15,
http://rbi.org.in/scripts/PublicationVisionDocuments.aspx?ID=664
▪ [2] “Committee onComprehensive Financial Services for Small Businesses and Low Income
Households”, RBI, January 2014,
http://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/PublicationReportDetails.aspx?UrlPage=&ID=727
▪ [3] “Report of theTechnicalCommittee on Mobile Banking”, RBI, February 2014,
http://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/PublicationReportDetails.aspx?UrlPage=&ID=760#8
▪ [4] “Report on Enabling PKI in Payment System Applications”, RBI,April 2014,
http://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/PublicationReportDetails.aspx?UrlPage=&ID=765
▪ [5] “Pradhan MantriJan-DhanYojana”, Ministry of Finance,August 2014,
http://www.pmjdy.gov.in/financial_literacy.aspx
▪ [6] “Report of theTask Force on an Aadhaar-EnabledUnified Payment Infrastructure”, Finance
Ministry, February 2012,
http://finmin.nic.in/reports/Report_Task_Force_Aadhaar_PaymentInfra.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-221219055012-d5f9d4a5/85/present-pptx-32-320.jpg)