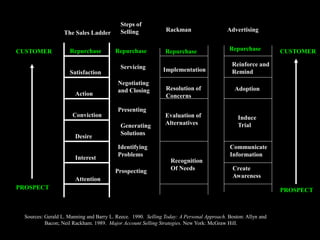
The document provides guidance on how to effectively present to prospects in order to move them up the sales ladder. It outlines objectives for presentations such as creating value, building desire, and establishing conviction. It then discusses structuring calls, dealing with objections, conditions, and discussion tactics. Finally, it offers tips for delivery including establishing eye contact, varying voice, keeping it concise, and tapping into emotions. The overall goal is to create a compelling presentation that differentiates your solution and gets a commitment.