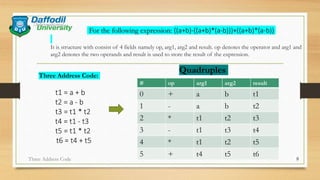
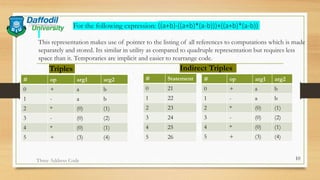
The document discusses three address code, an intermediate representation in compilers that uses at most three operands and one operator per instruction. It explains how three address code works, different implementations like quadruples and triples, and provides an example of converting the expression ((a+b)-((a+b)*(a-b)))+((a+b)*(a-b))) to three address code. Three address code simplifies intermediate code generation and machine code conversion in compilers.