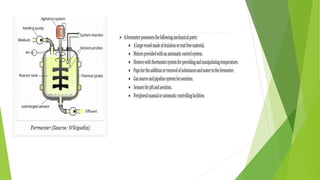
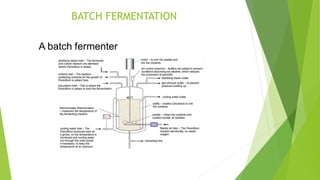
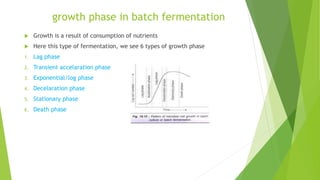
This document discusses different types of fermentation processes used in industrial fermentation. It describes three main types: continuous fermentation, batch fermentation, and fed-batch fermentation. Continuous fermentation involves continuously removing and replacing culture medium to keep the volume constant and microbes in exponential growth. Batch fermentation is a closed system where nothing is added or removed until harvesting. Fed-batch fermentation periodically adds substrates to prolong the growth phase without removing cells. The document provides details on the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each fermentation method.