This document provides an overview of social networks and their structure. It discusses how social networks form and influence individual behavior. Key concepts introduced include:
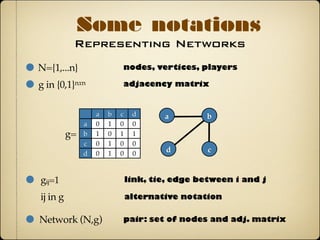
- Nodes represent individuals and links represent relationships between nodes in a social network.
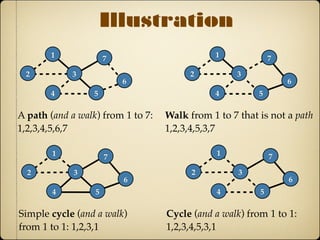
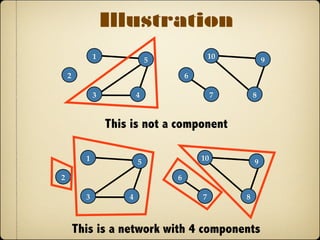
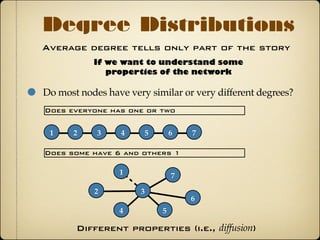
- Basic network properties like degree, neighborhood, paths, and components help describe network structure.
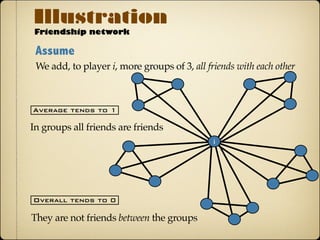
- Real-world networks tend to have short path lengths and exhibit clustering, degree distributions, and transitivity.
- Understanding network structure can provide insights into how behaviors and outcomes spread through social ties.