This document summarizes Nepal's new trade policy of 2072. It aims to promote domestic industries, manage growing imports, and boost exports in order to make trade an engine of economic development. Some key points are:
- It was formulated based on previous trade policies and to take advantage of bilateral, regional, and multilateral trade arrangements.
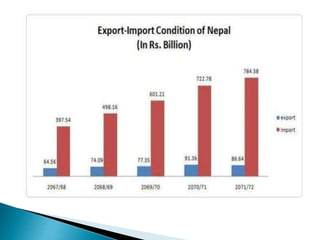
- Nepal faces a large trade deficit due to high imports and low exports.
- The policy seeks to enhance export competitiveness, reduce the trade deficit, and align with other related policies to impact trade.