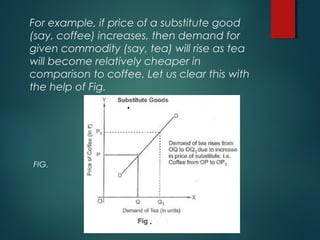
The document discusses various types of goods including inferior, normal, luxury, complementary, Giffen, snob, and substitute goods. It explains how each type of good responds to changes in income or price, with examples illustrating their behavior in markets. The key concept is that substitute goods are alternatives for consumers, where an increase in the price of one typically leads to an increase in demand for the other.