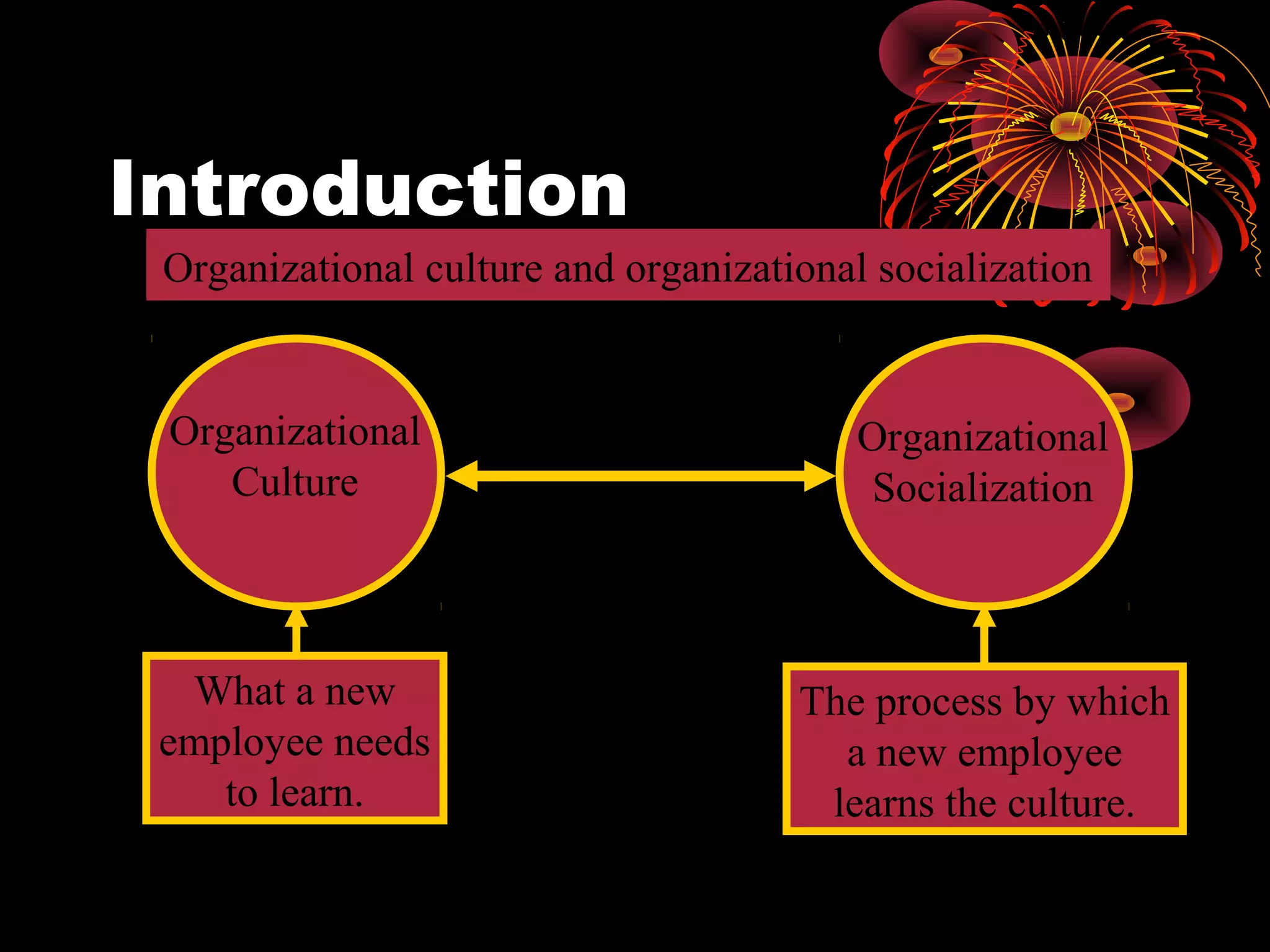
1. Organizational socialization is the process by which new employees learn the values, norms, and behaviors required of an organization's culture. It occurs through three stages - anticipatory socialization before joining, entry/encounter after joining, and metamorphosis as the employee adjusts fully.
2. In the entry/encounter stage, new employees compare expectations formed during anticipatory socialization to reality. The goal is to clarify roles and teach norms through indoctrination, apprenticeship, or training programs.
3. During metamorphosis, employees resolve socialization demands and fully accept their new role, with possible responses including rebellion, custodial acceptance, or innovative change/