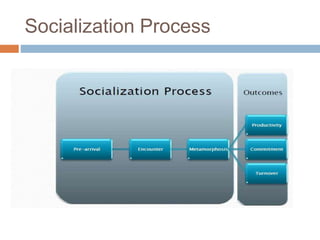
The document discusses how organizational culture is created and sustained. Culture is created by the founders' values and behaviors serving as role models for employees. It is sustained through selection practices that hire employees with compatible values, the actions of top management that establish norms, and socialization methods that adapt new employees to the existing culture. Socialization involves three stages - pre-arrival learning, encountering reality, and lasting changes as skills are mastered. Together, these factors shape the culture over time.