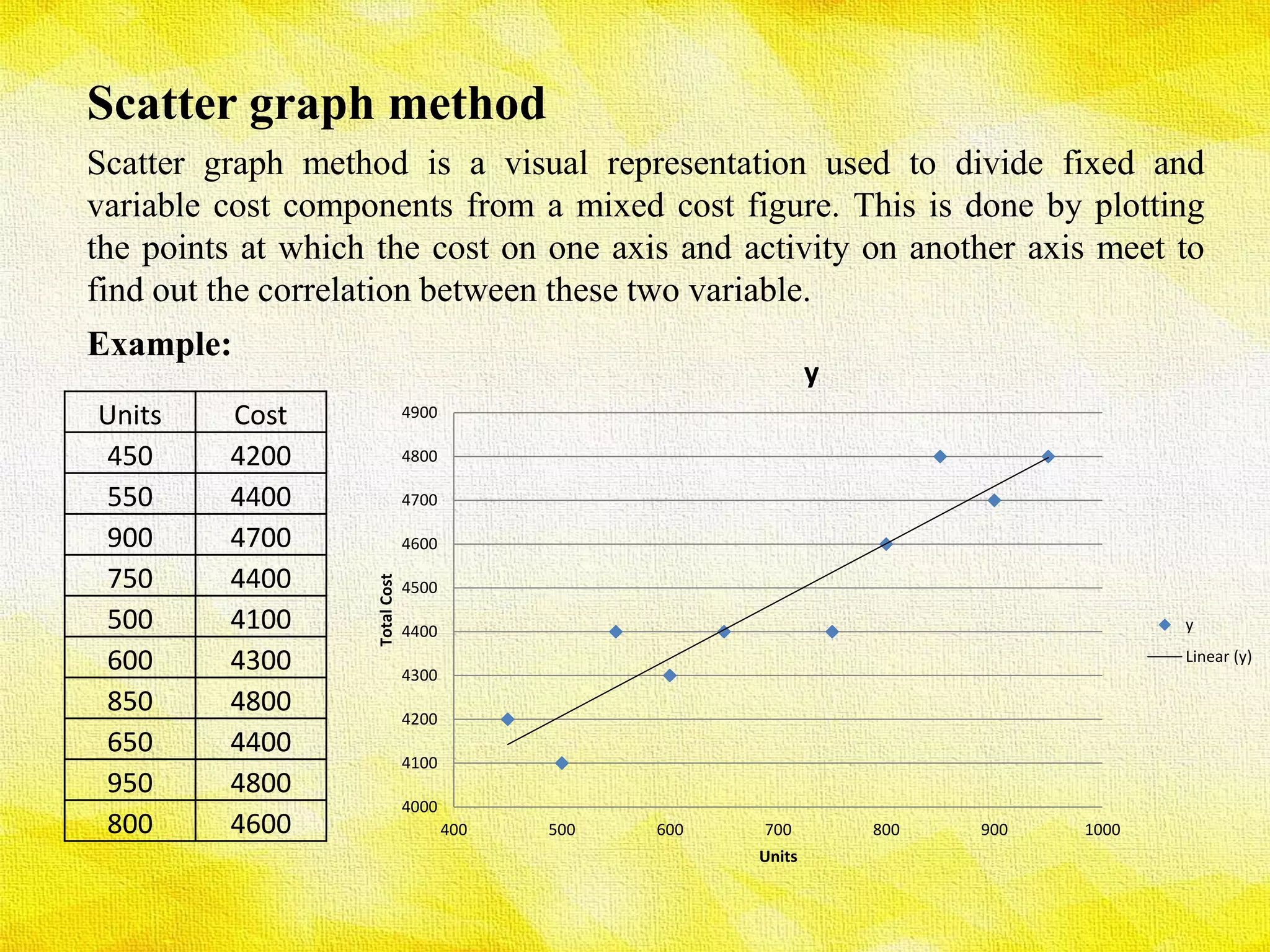
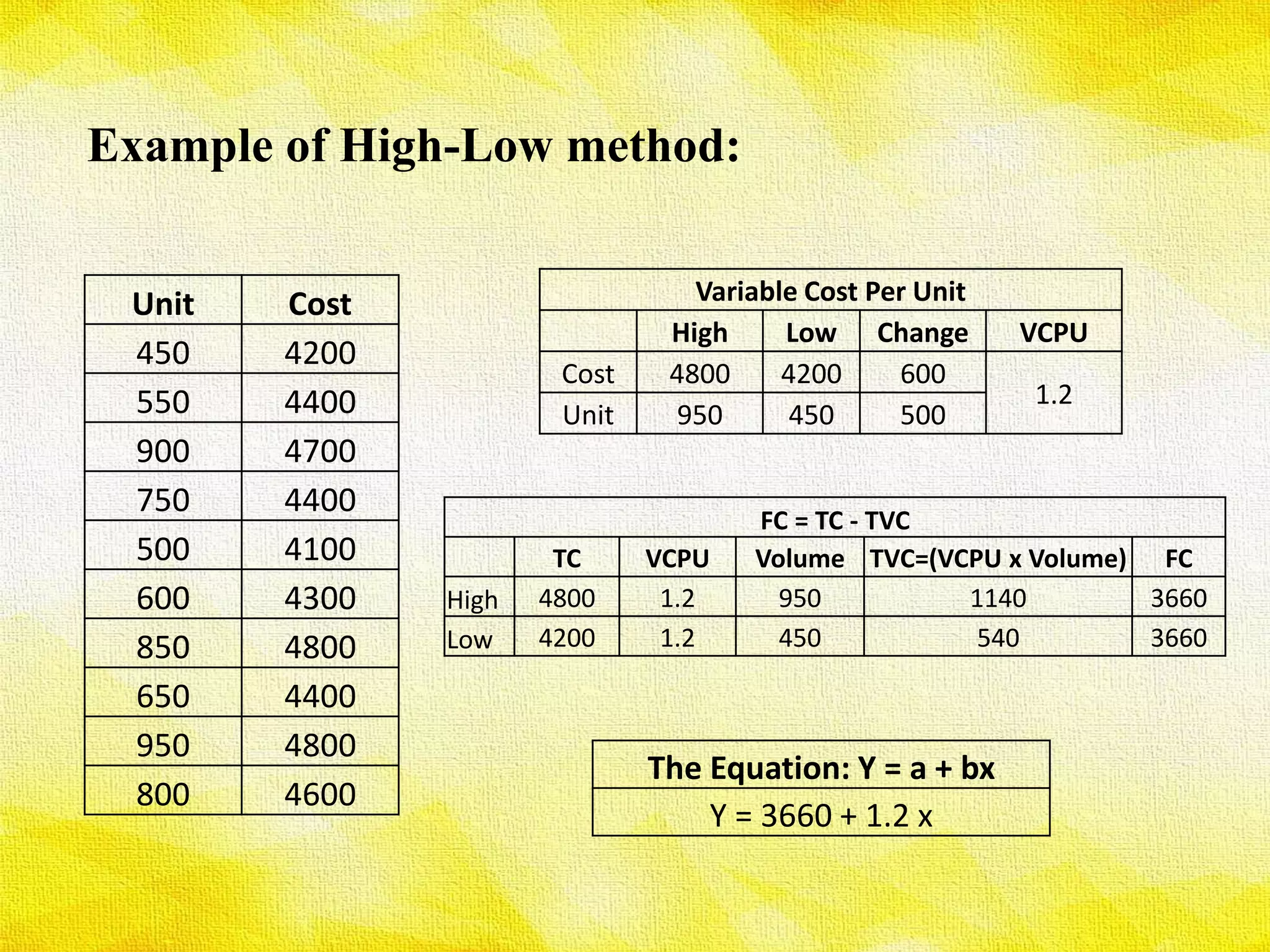
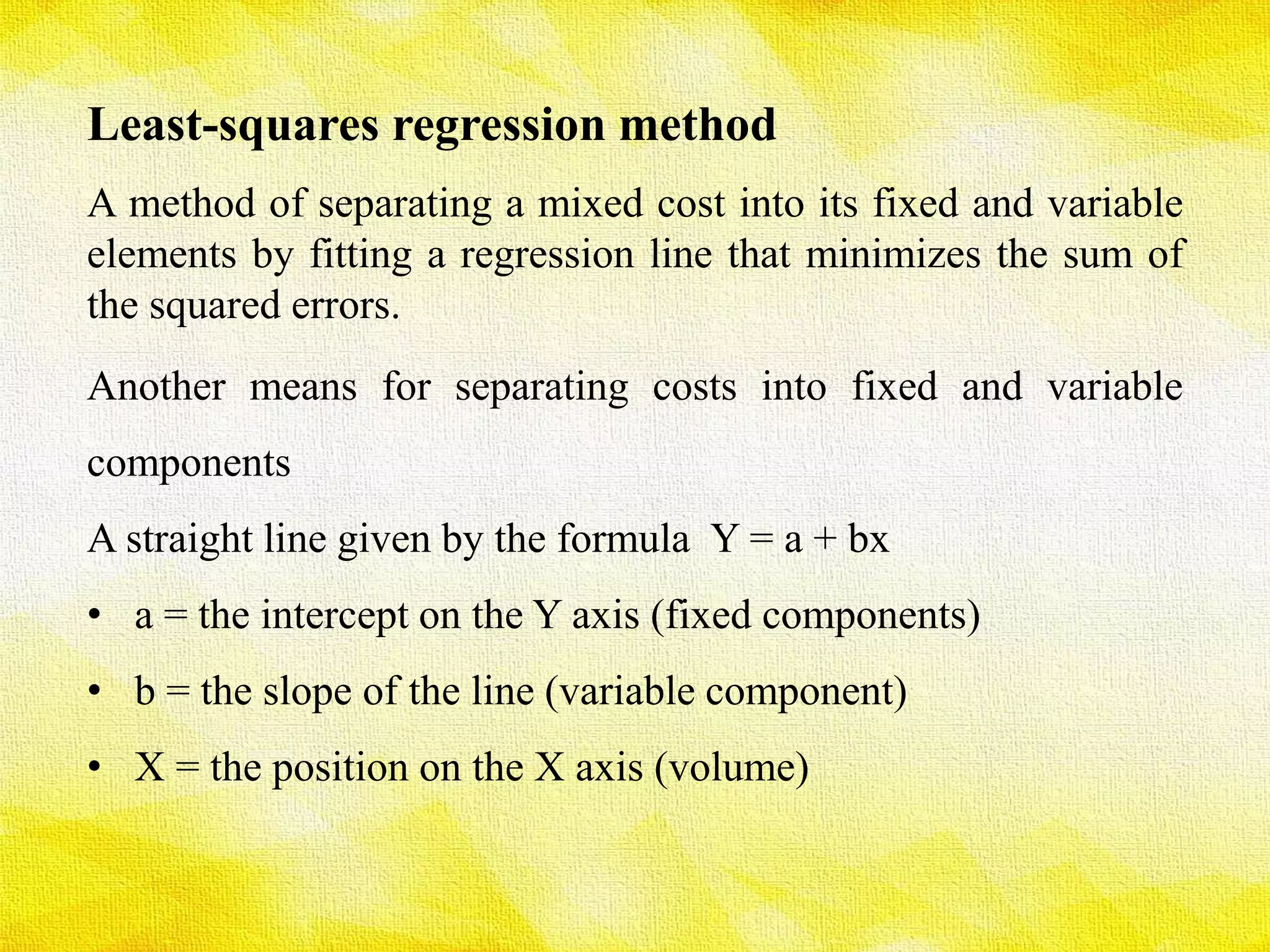
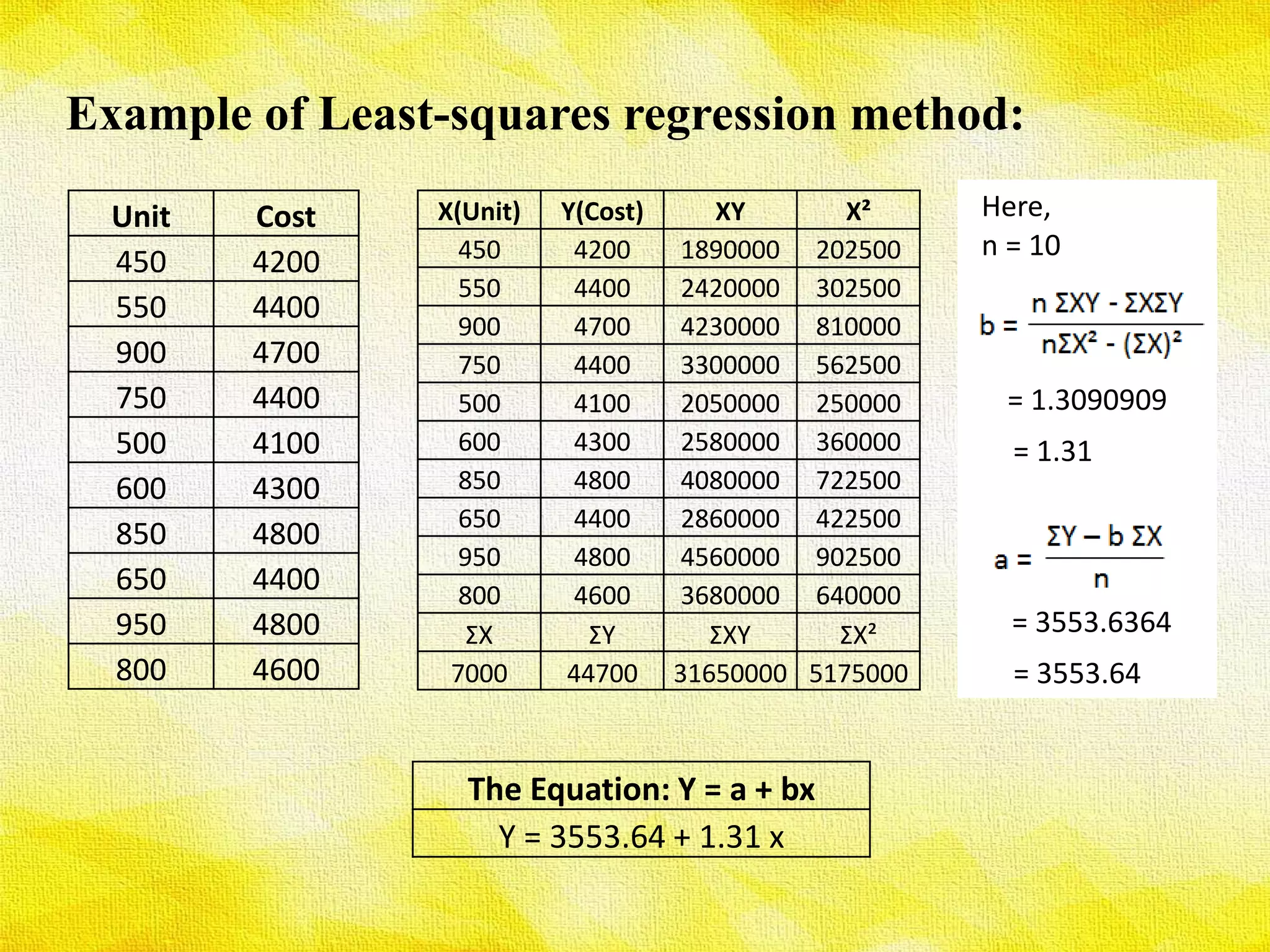
The presentation discusses various methods for determining cost behavior, including industrial engineering approach, account analysis method, scatter plot method, high-low method, and least-squares regression method. Each method provides unique ways to analyze and classify costs as either fixed or variable through different techniques such as visual representation and regression analysis. Key equations and examples illustrate the practical application of these methods in evaluating cost behavior.