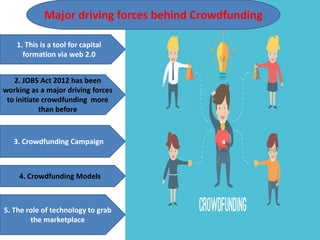
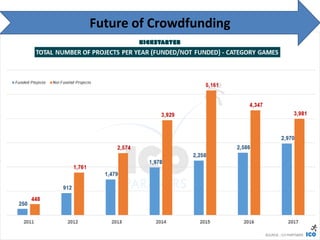
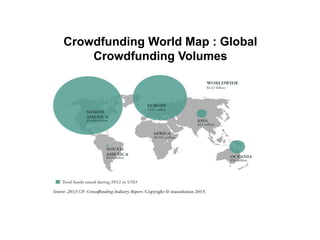
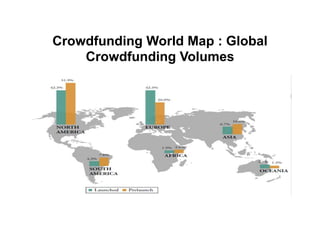
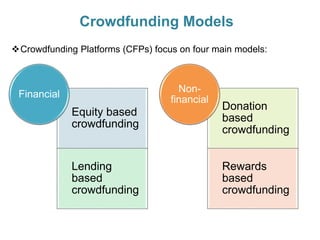
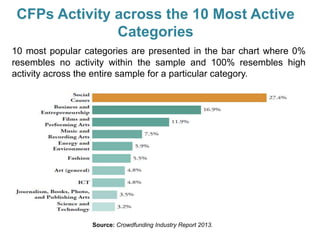
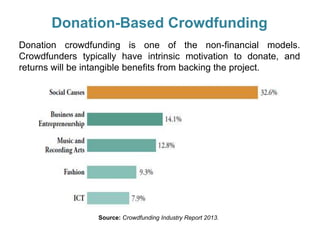
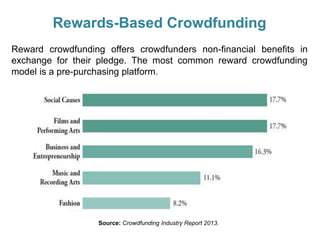
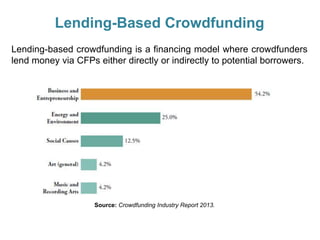
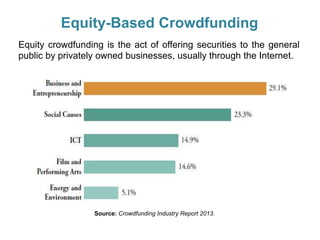
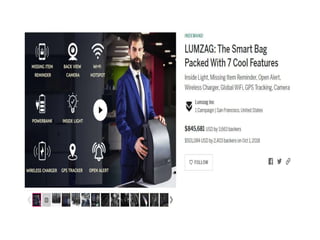
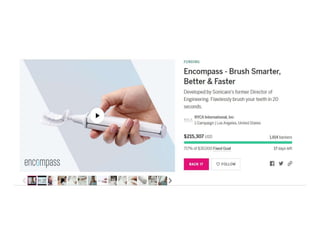
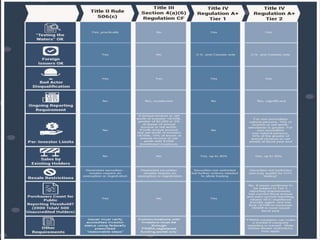
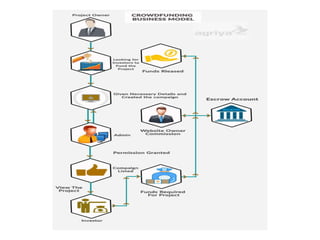
Crowdfunding involves soliciting financial contributions from a large number of individuals for a business venture or project. It began in 2006 and has grown due to factors like the JOBS Act of 2012 and the role of technology and social media. There are different models of crowdfunding including donation-based, rewards-based, lending-based, and equity-based. An entrepreneur seeking crowdfunding must understand key aspects like developing a crowdfunding campaign and disclosure document that outlines the business plan, financial details, intended use of funds, and projections. Crowdfunding has grown globally and various industries have been successfully funded, though success requires significant effort and there are some financial risks.