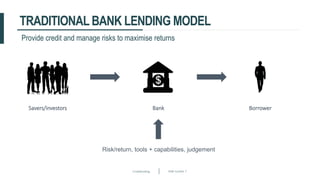
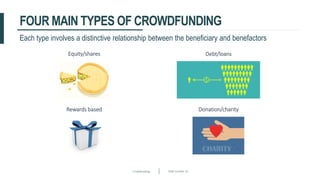
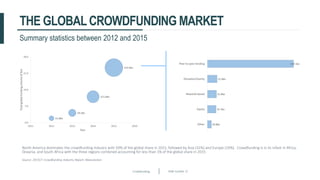
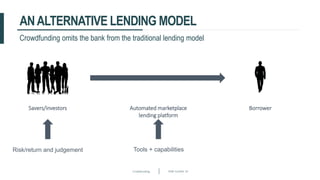
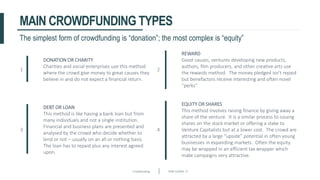
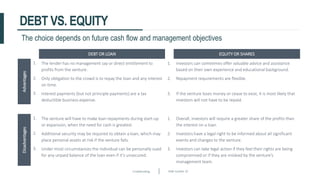
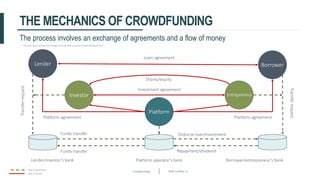
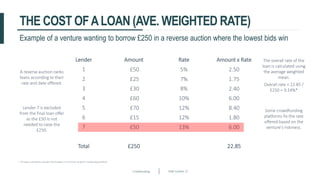
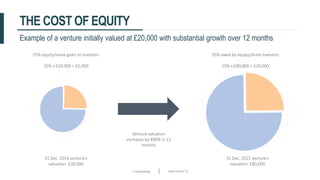
This document discusses crowdfunding and provides an overview of the crowdfunding process. It begins with an introduction to crowdfunding, noting that crowdfunding involves sourcing funds from a large group of individuals online. It then discusses the different types of crowdfunding, including rewards-based, debt/loans, and equity/shares crowdfunding. The document provides details on how crowdfunding works as an alternative lending model compared to traditional bank lending. It also examines what factors investors look for in deciding whether to invest in a crowdfunding campaign.