Linux is an open source operating system that manages hardware and resources. It includes commands like ls, mkdir, cat, touch, cp, cd, mv, pwd, whereis, whatis, which, man, uname, sudo, su, history, passwd, date, cal, clear.
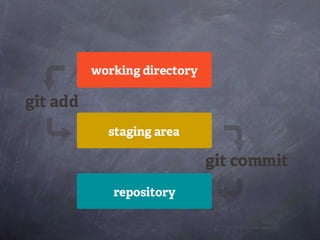
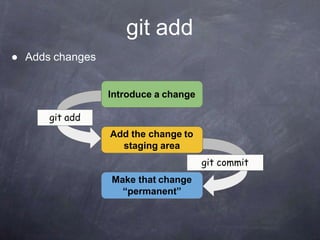
Git is a distributed version control system that tracks changes to files. Common git commands include git init, git clone, git log, git diff, git status, git add, git commit.
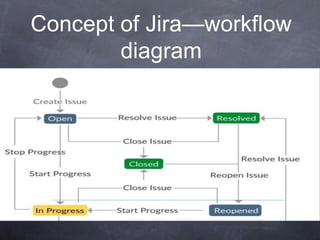
Jira is a project management tool that helps track issues, bugs, tasks and projects. It allows issue tracking, reporting, custom workflows, and integrates with other tools through APIs and add-ons.