Database Management System
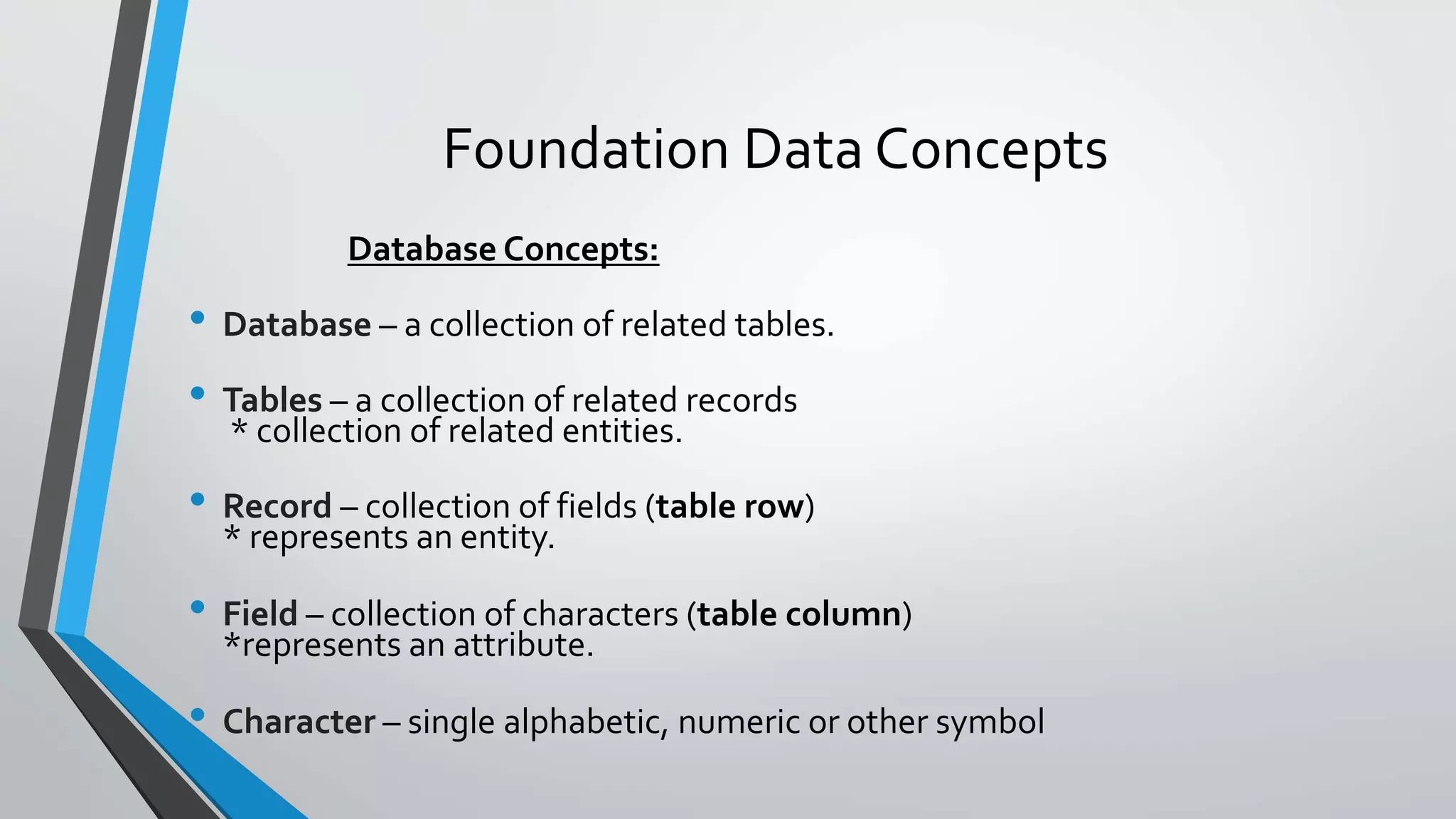
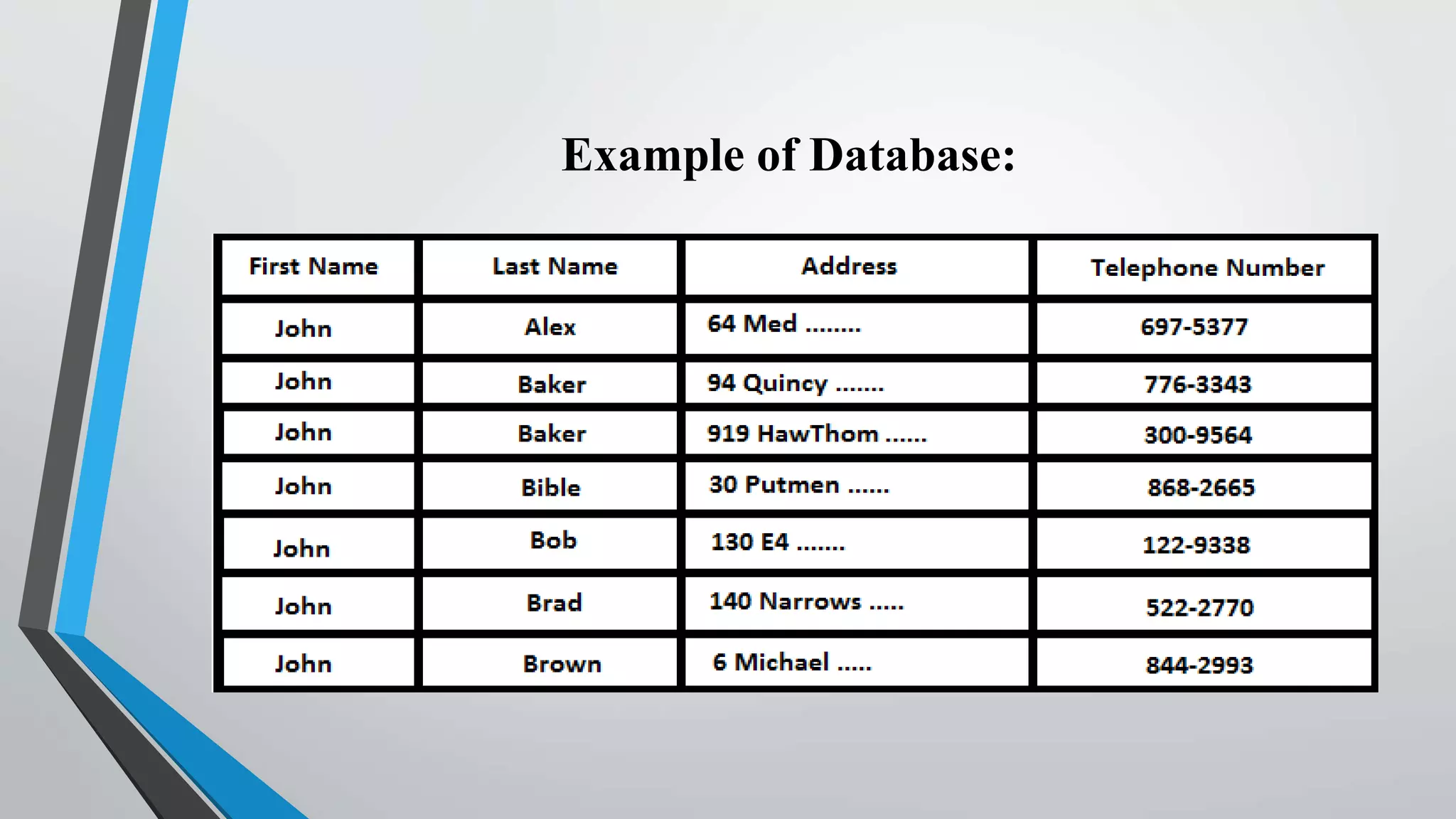
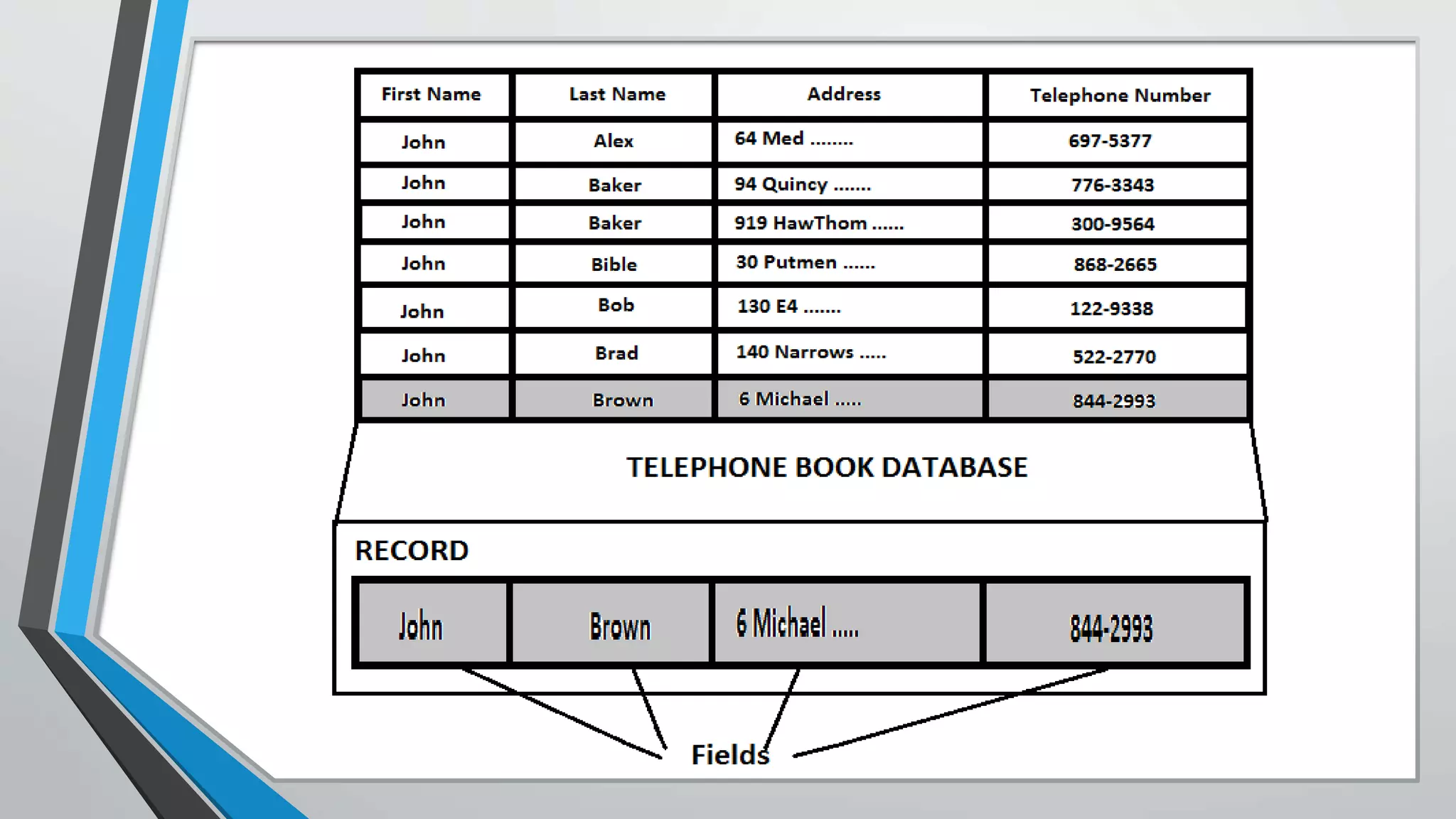
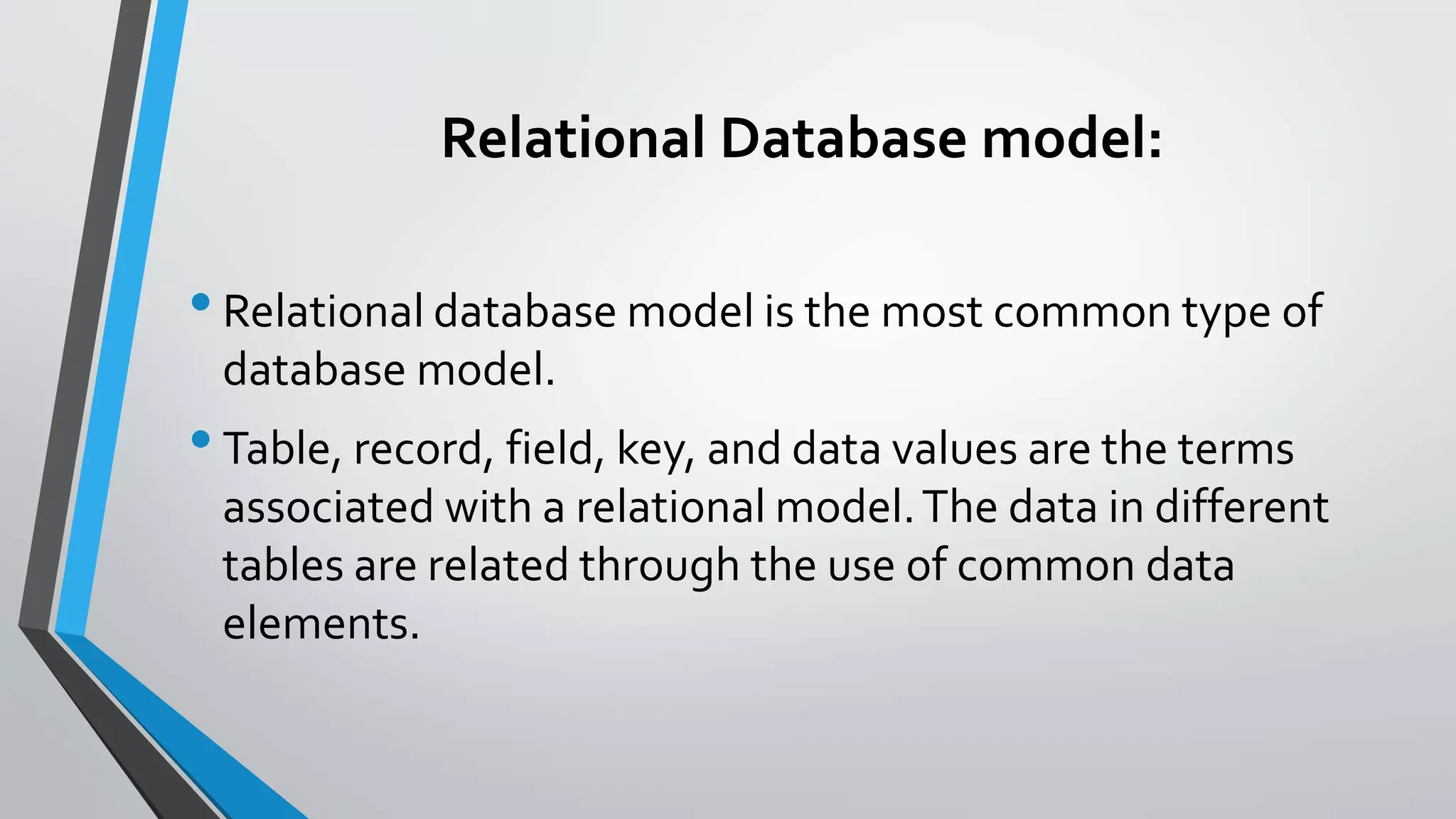
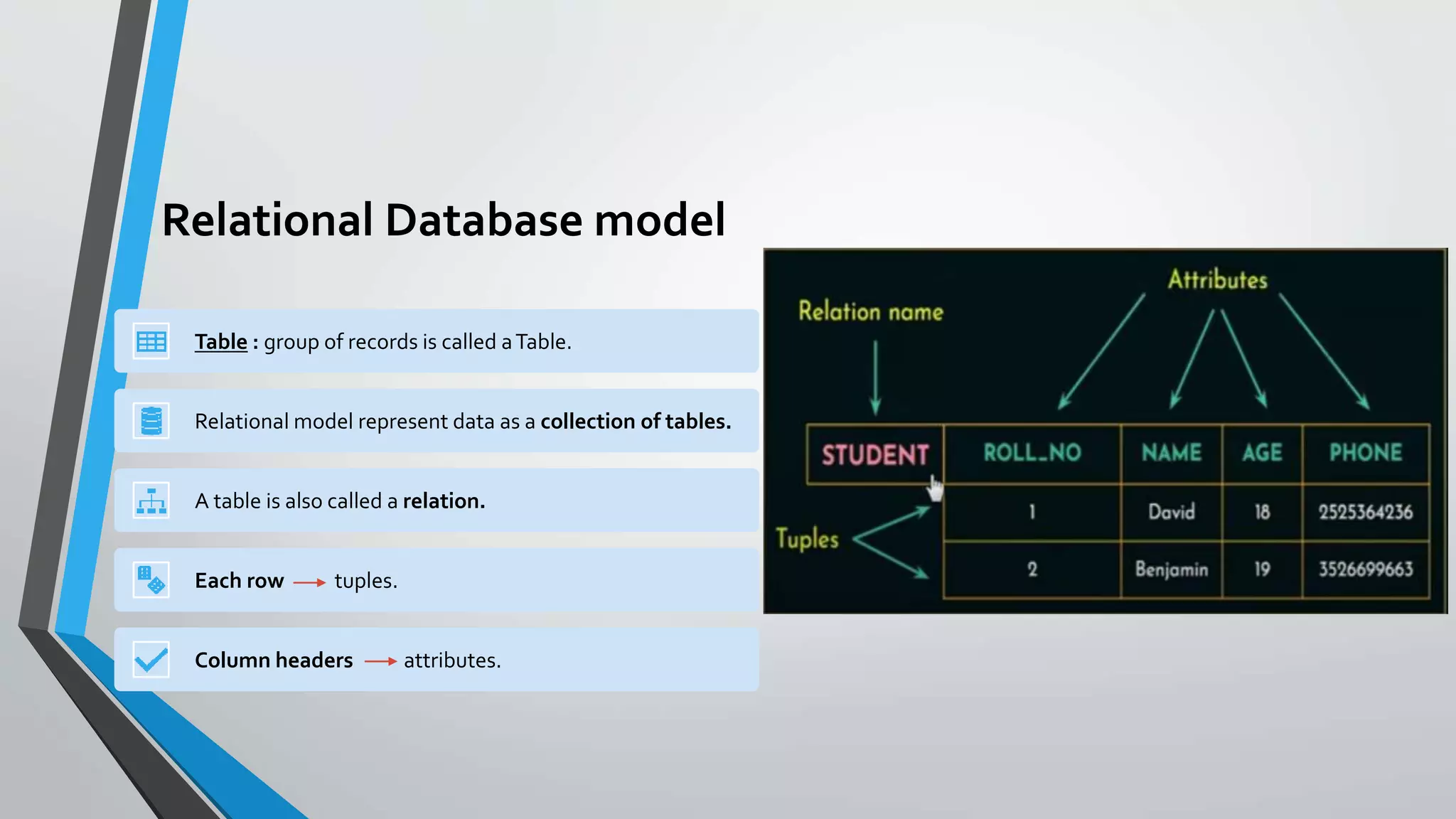
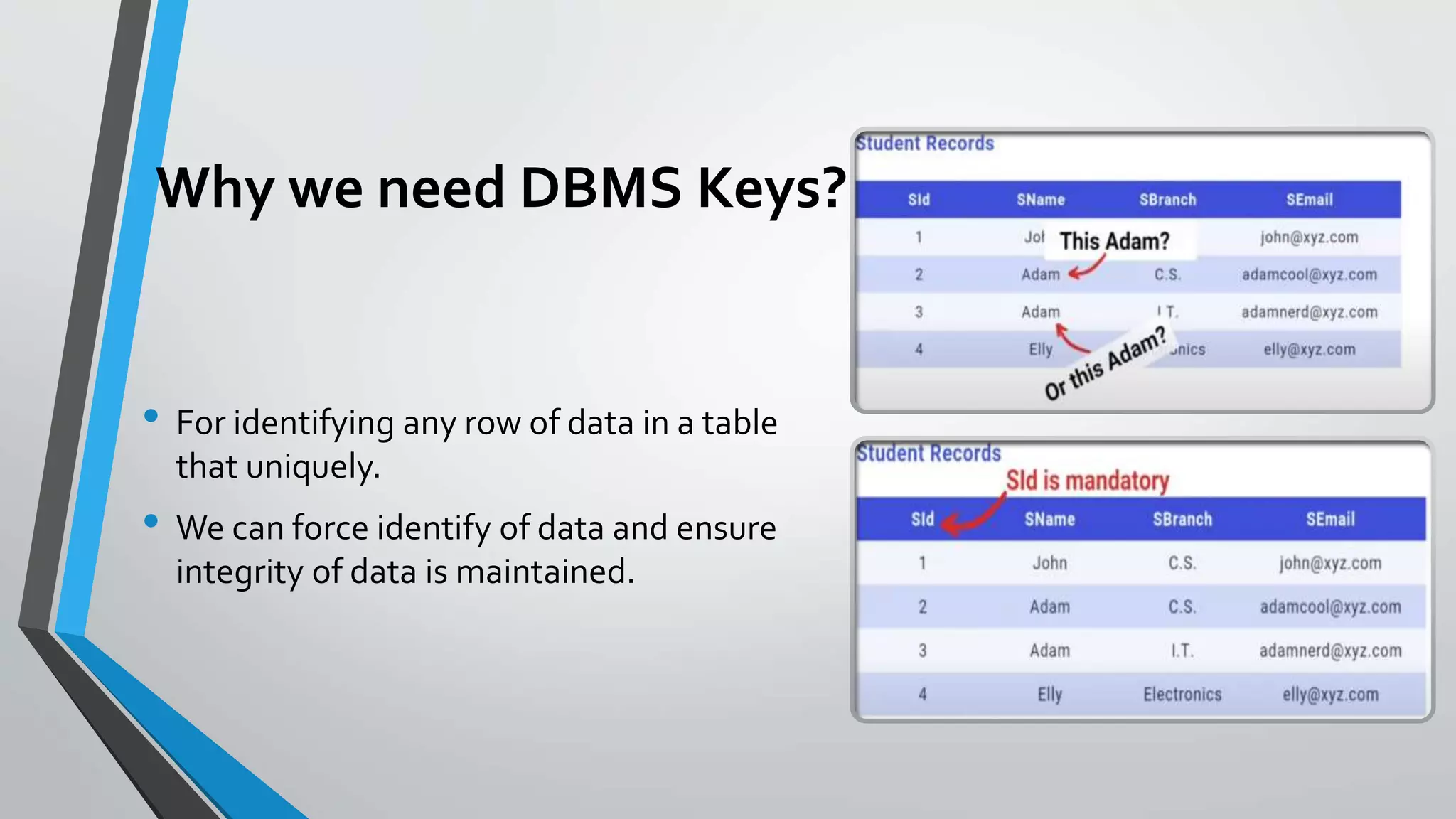
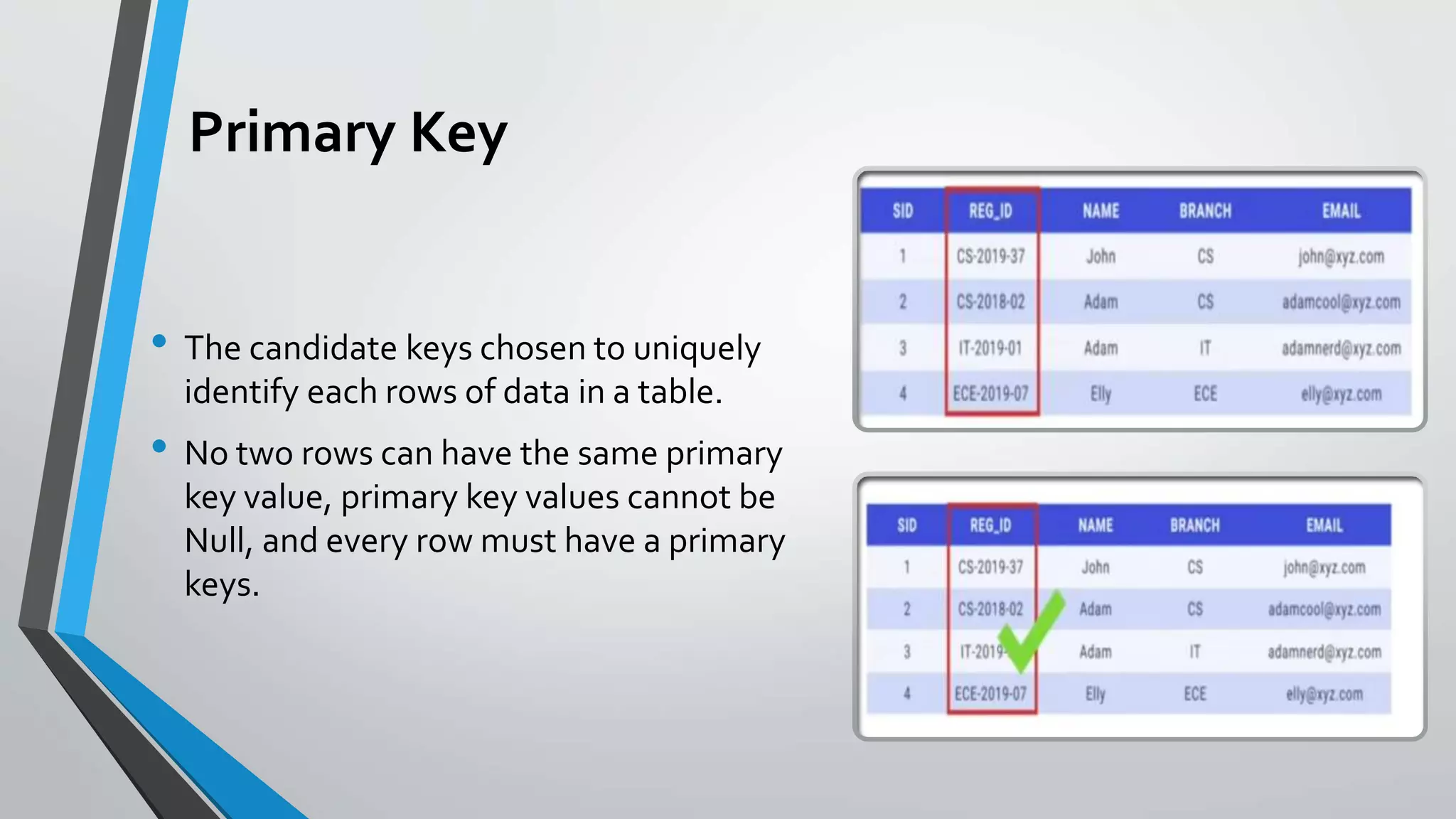
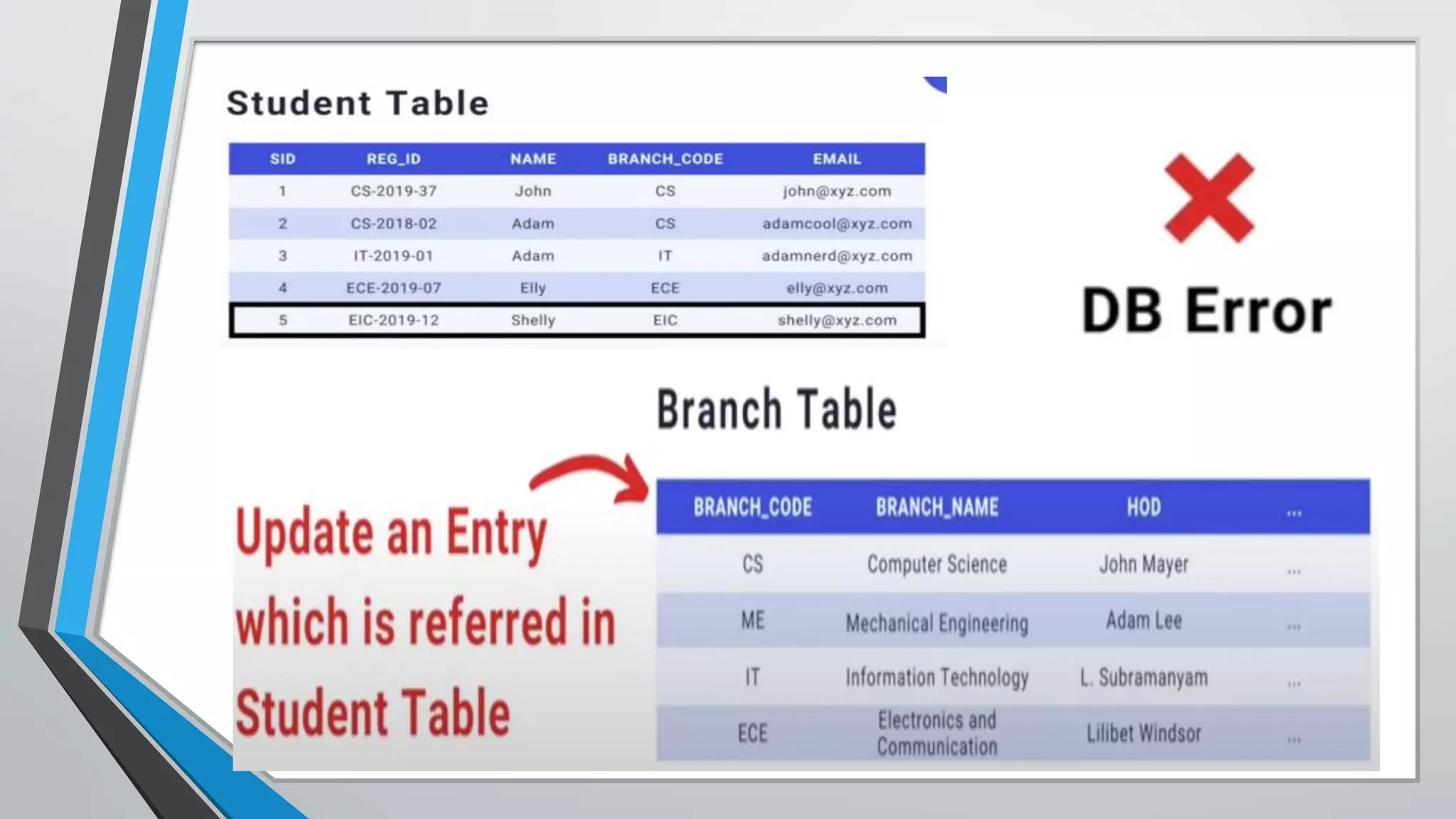
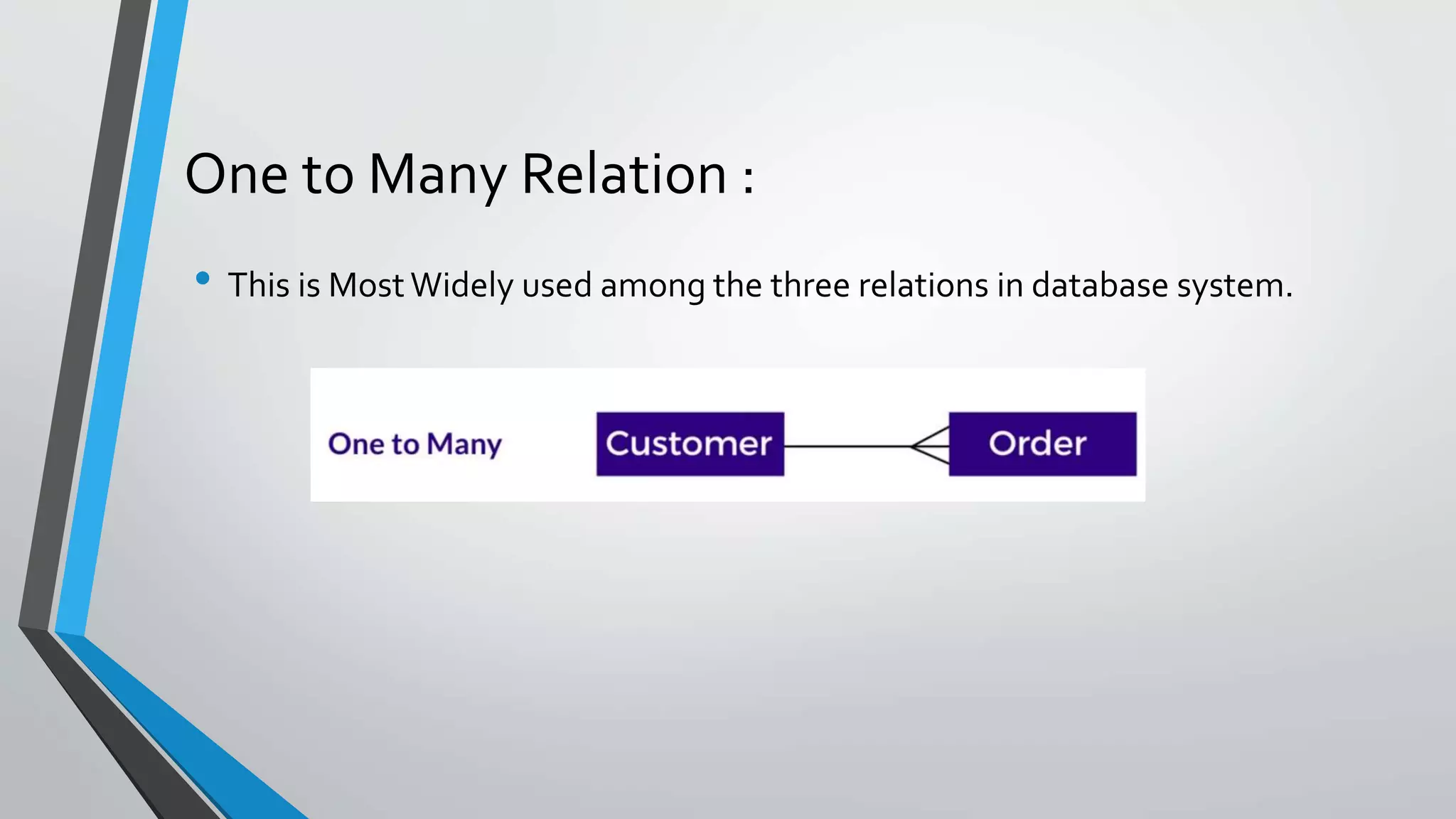
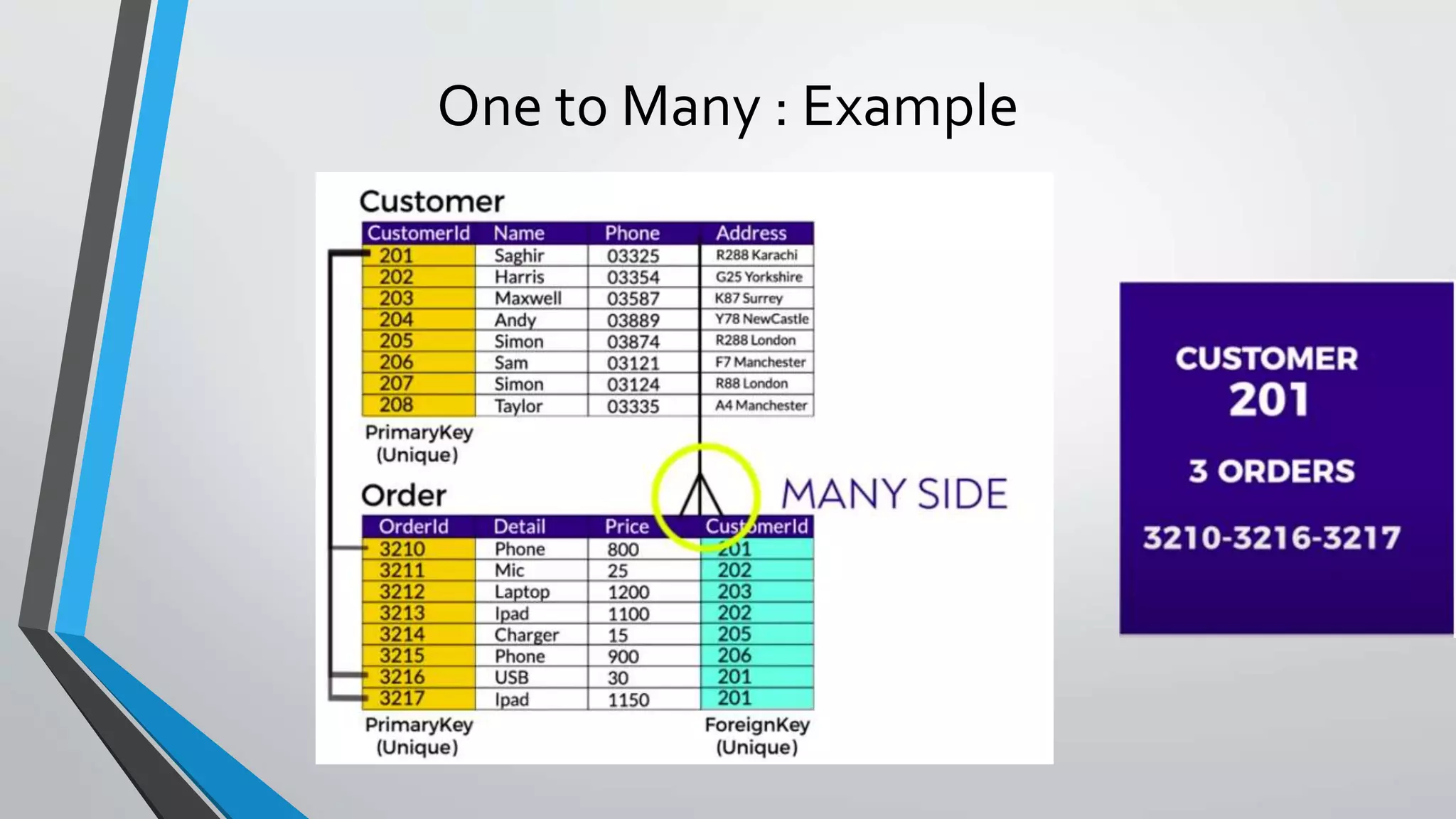
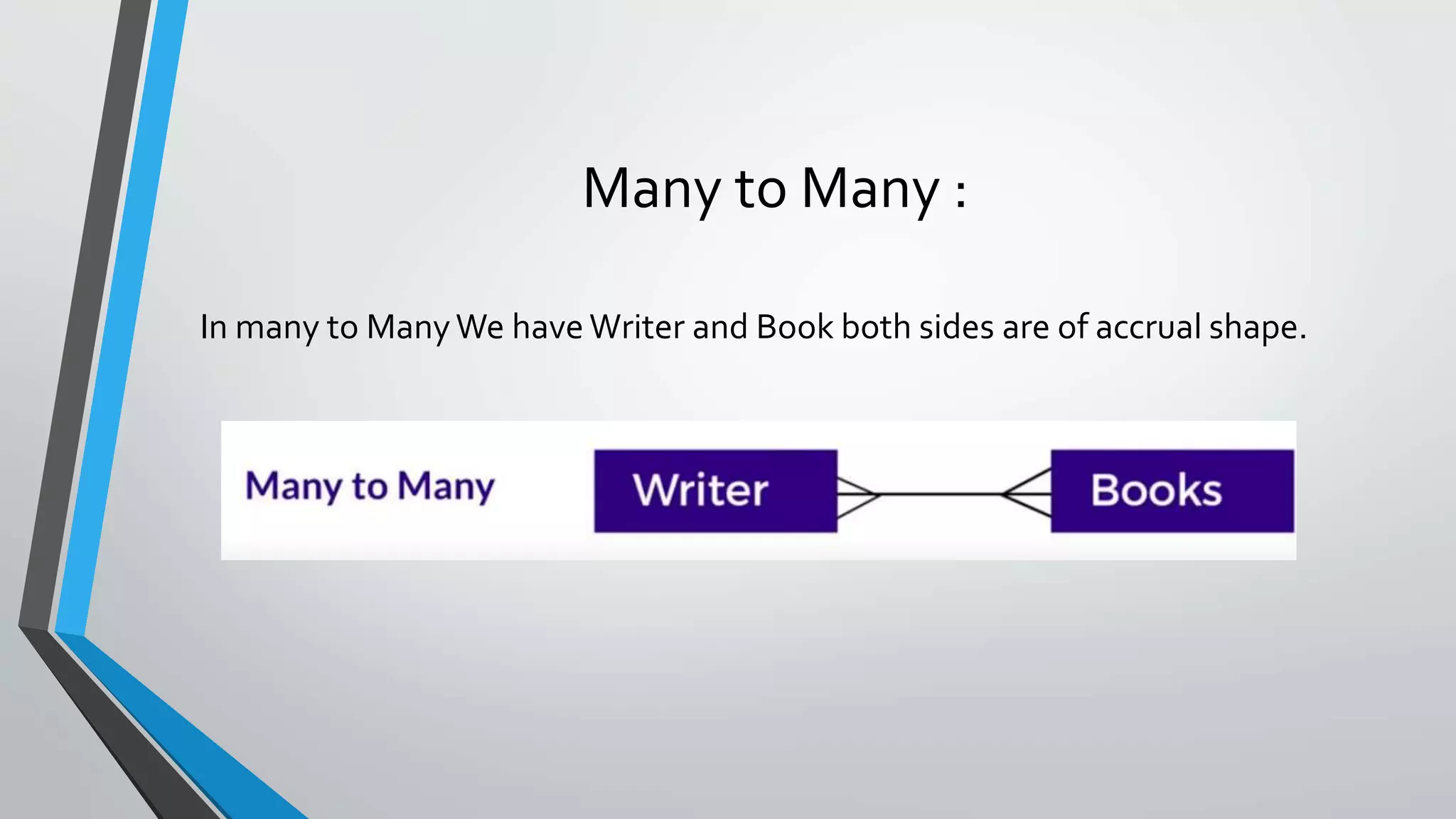
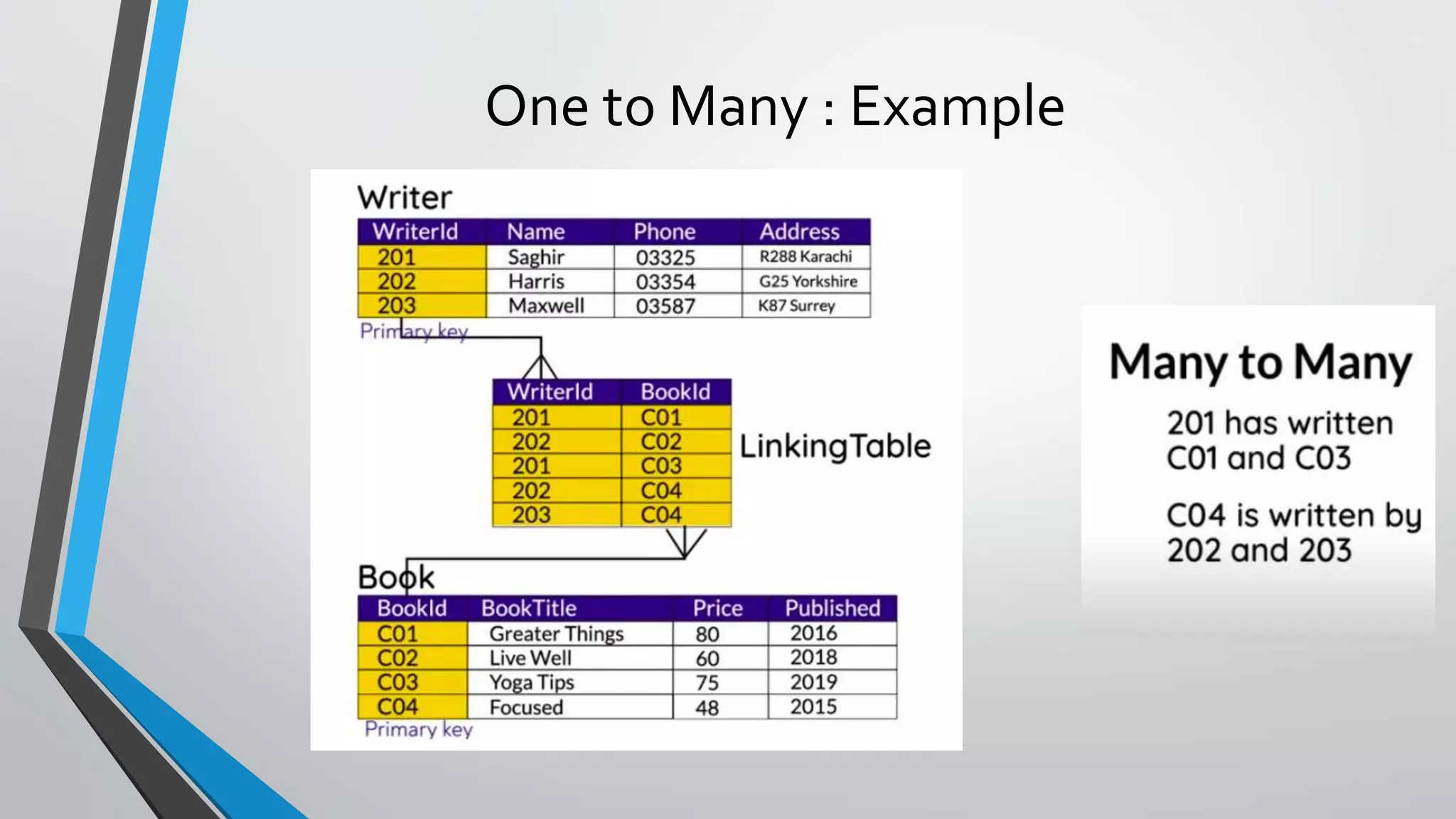
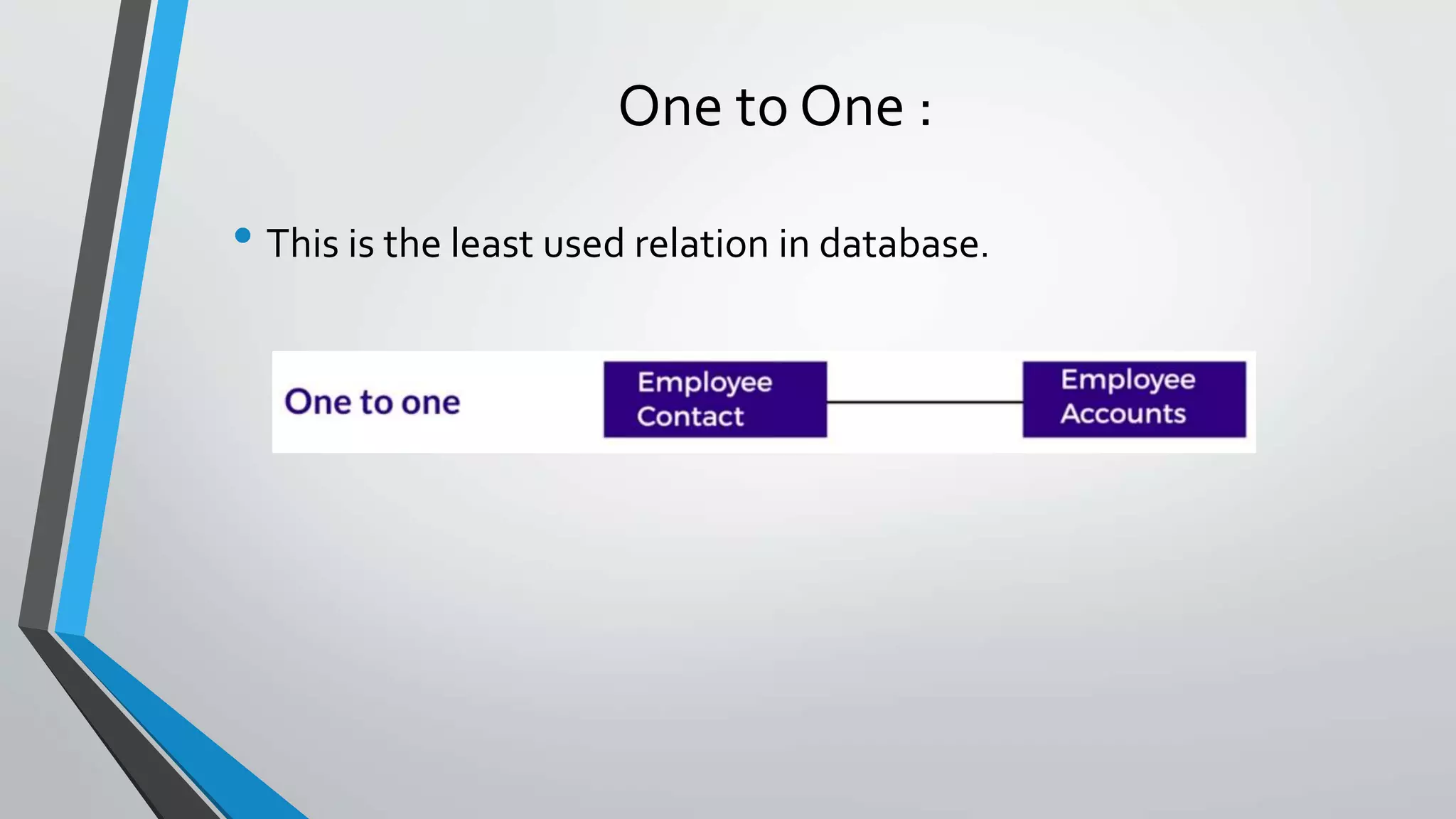
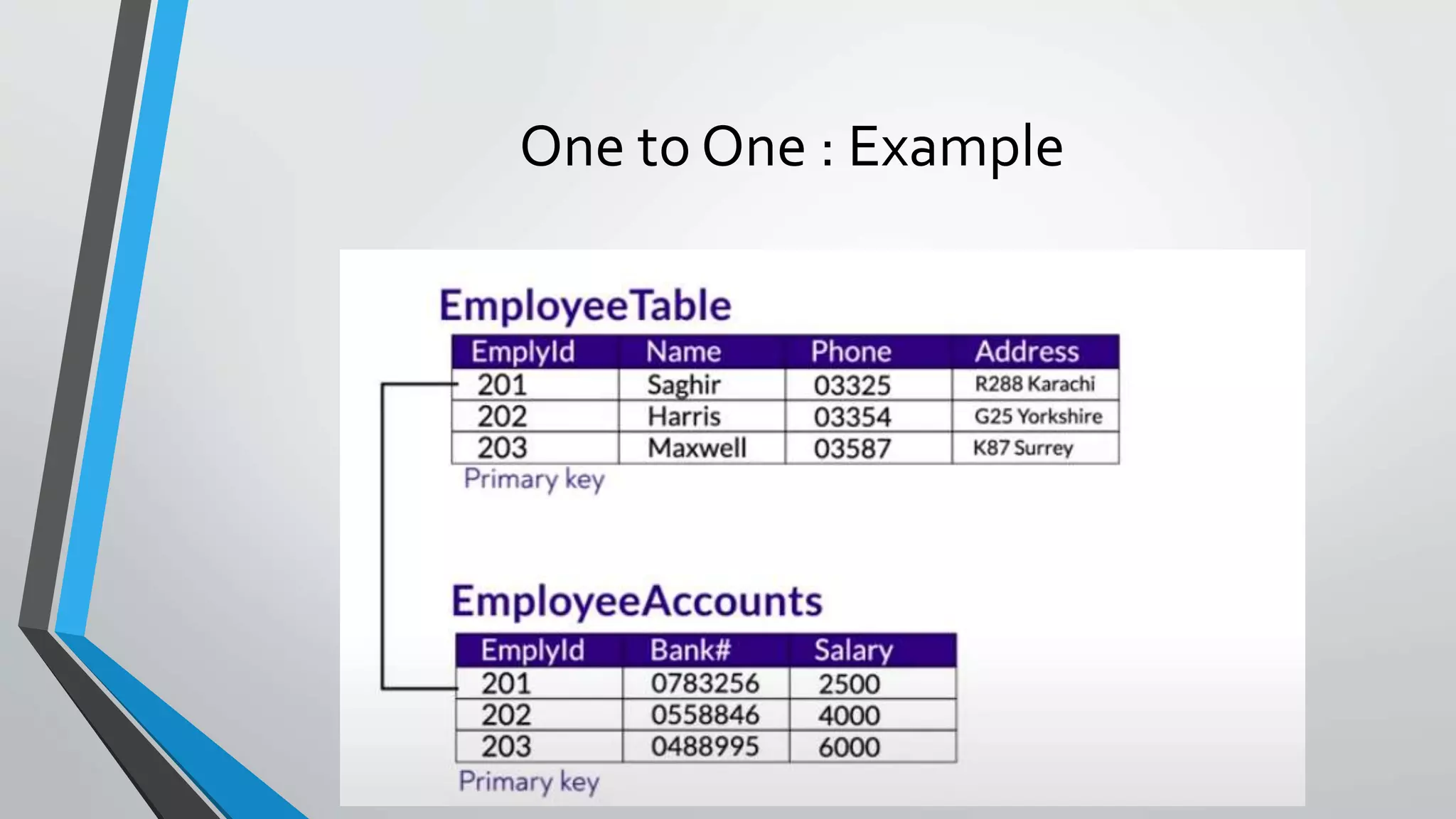
The document defines key concepts related to database management systems (DBMS). It explains that a DBMS is software that allows users to store, manipulate, and retrieve data from a database. Popular examples of DBMS include MySQL, Oracle, and IBM DB2. The document also discusses database concepts like tables, records, fields and keys. It provides examples of one-to-many, many-to-many, and one-to-one relationships and explains how relational databases use these relationships. Finally, it outlines some advantages of using a DBMS like reduced data redundancy, improved data sharing and security, and easier data backup and recovery.