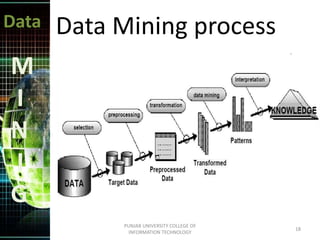
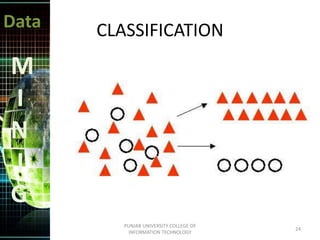
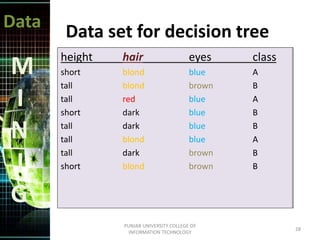
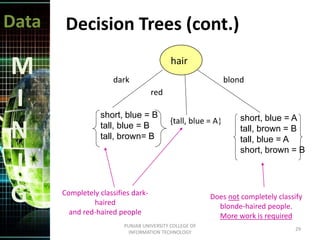
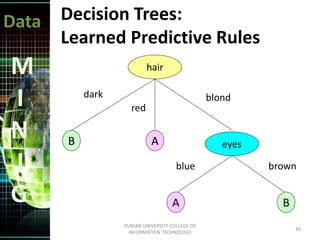
This document discusses data mining techniques. It defines data mining as the non-trivial extraction of previously unknown information from large databases. Several techniques are covered, including prediction, classification, clustering, and decision trees. Prediction involves classifying records to predict future behavior, while classification assigns data to predefined groups. Clustering groups similar data items together without human input. Decision trees use a tree structure to generate rules that classify data.