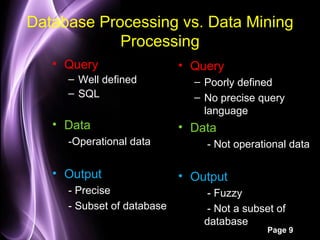
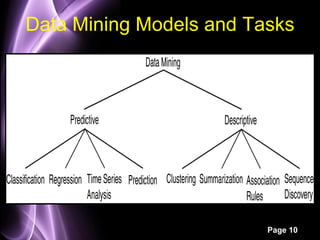
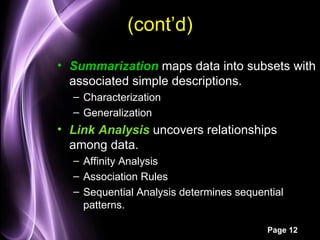
This document provides an overview of data mining. It defines data mining as the process of applying computer-based methods to discover knowledge from large amounts of data. The two main components of data mining are knowledge discovery, which extracts concrete known information from data, and knowledge prediction, which uses known data to predict future trends. Some common uses of data mining include developing AI/machine learning strategies, analyzing business strategies and customer patterns, and detecting fraud and product defects. The document also outlines different data mining models, tasks, and techniques used to classify, cluster, summarize, and analyze relationships in data.