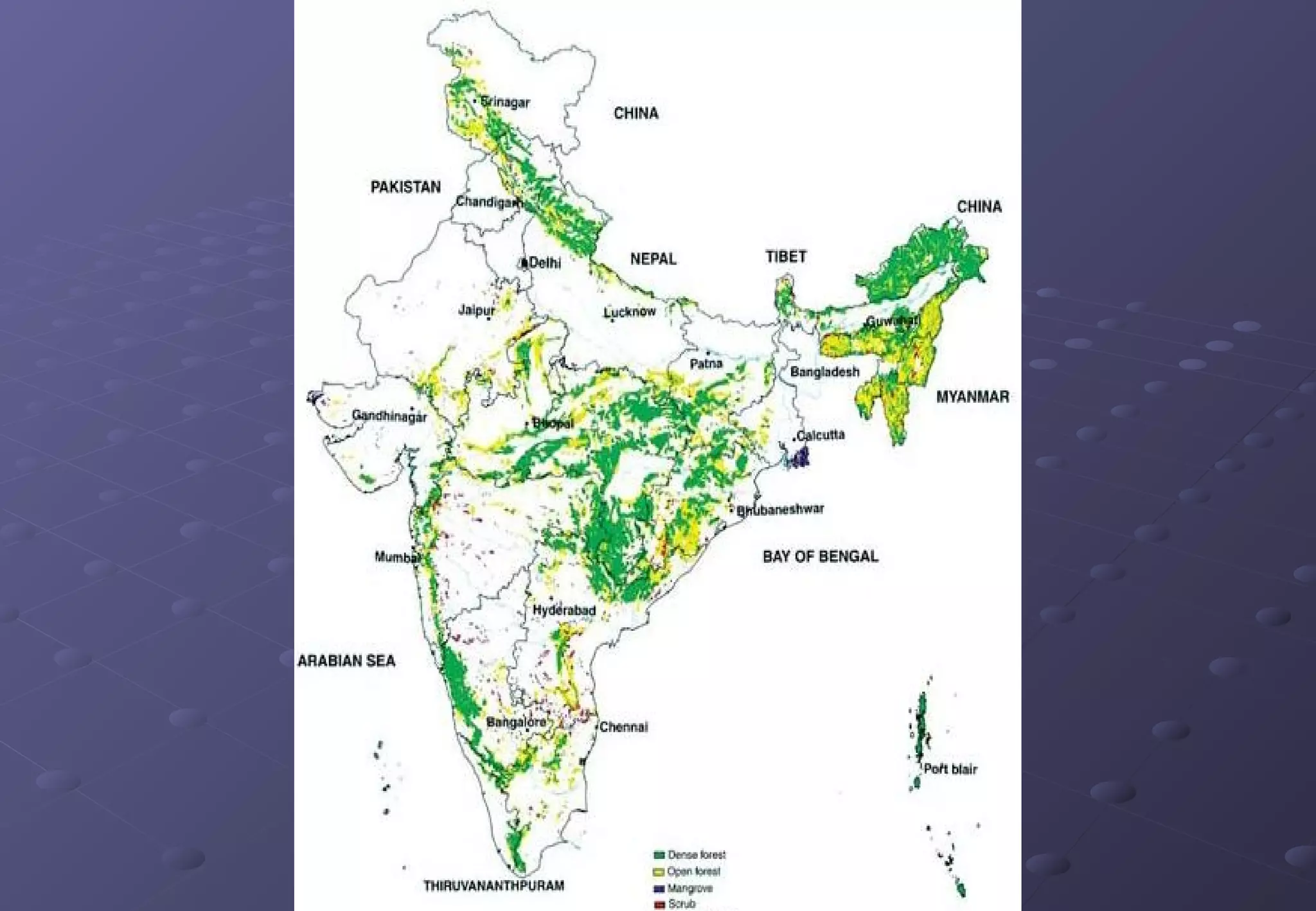
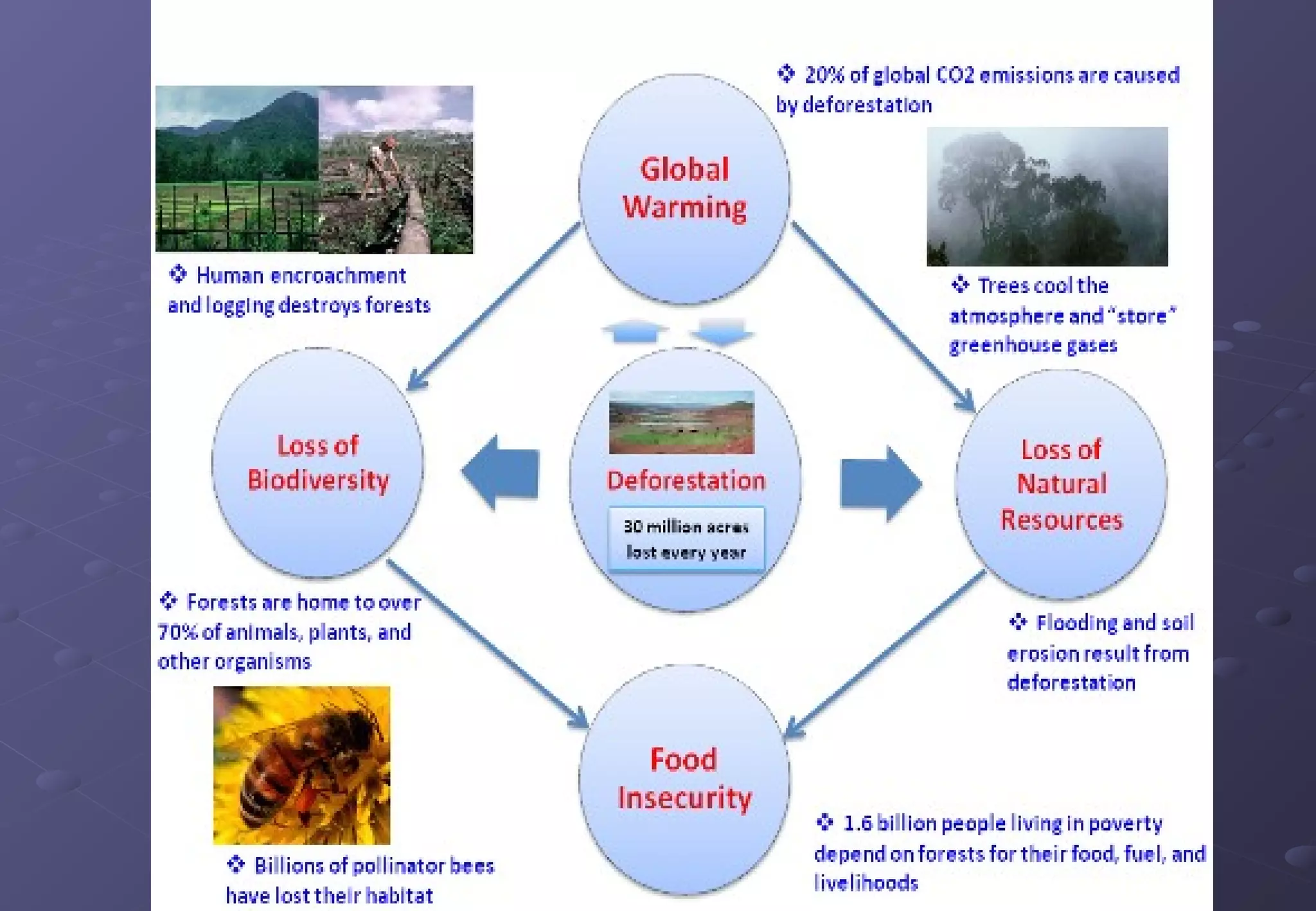
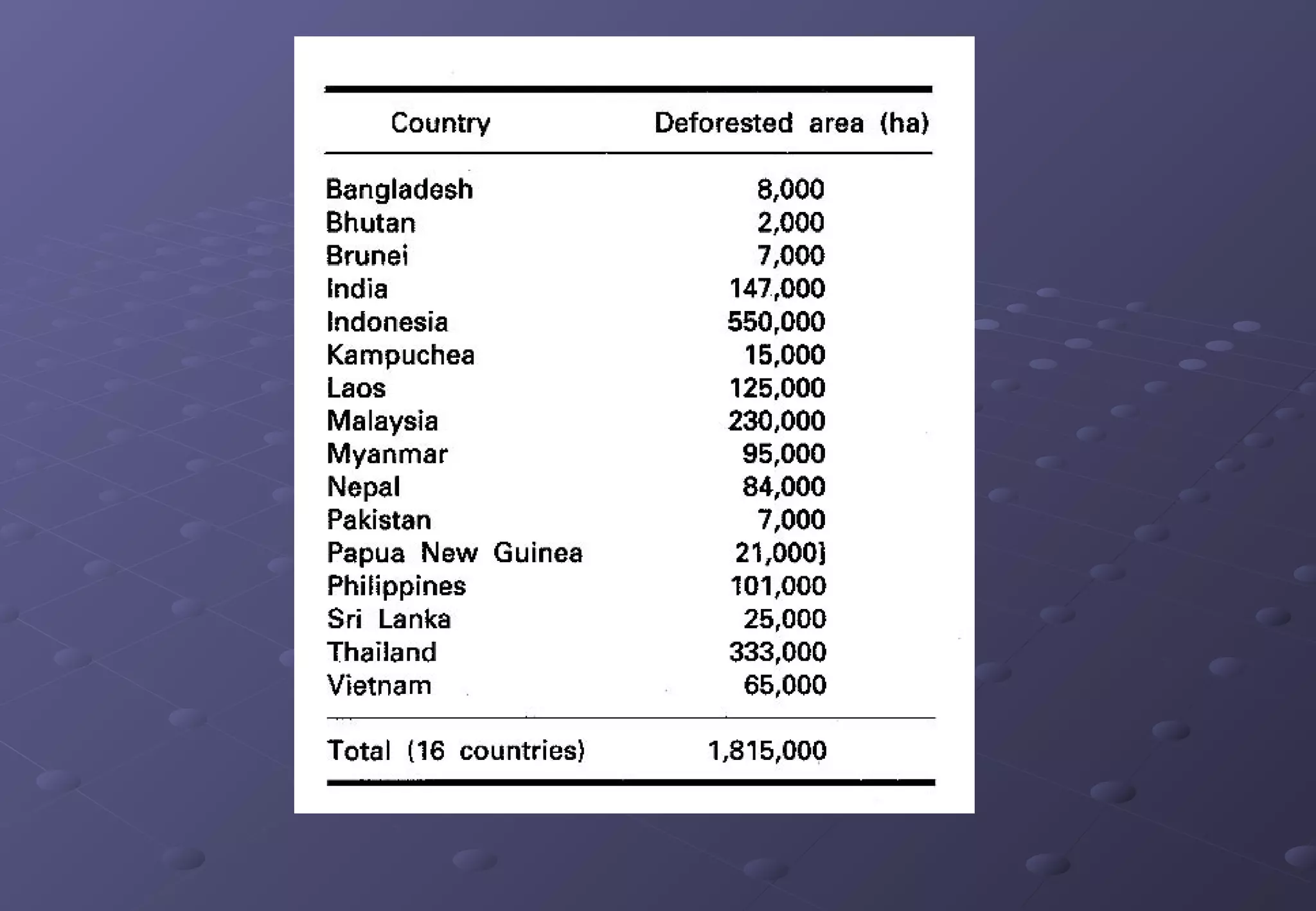
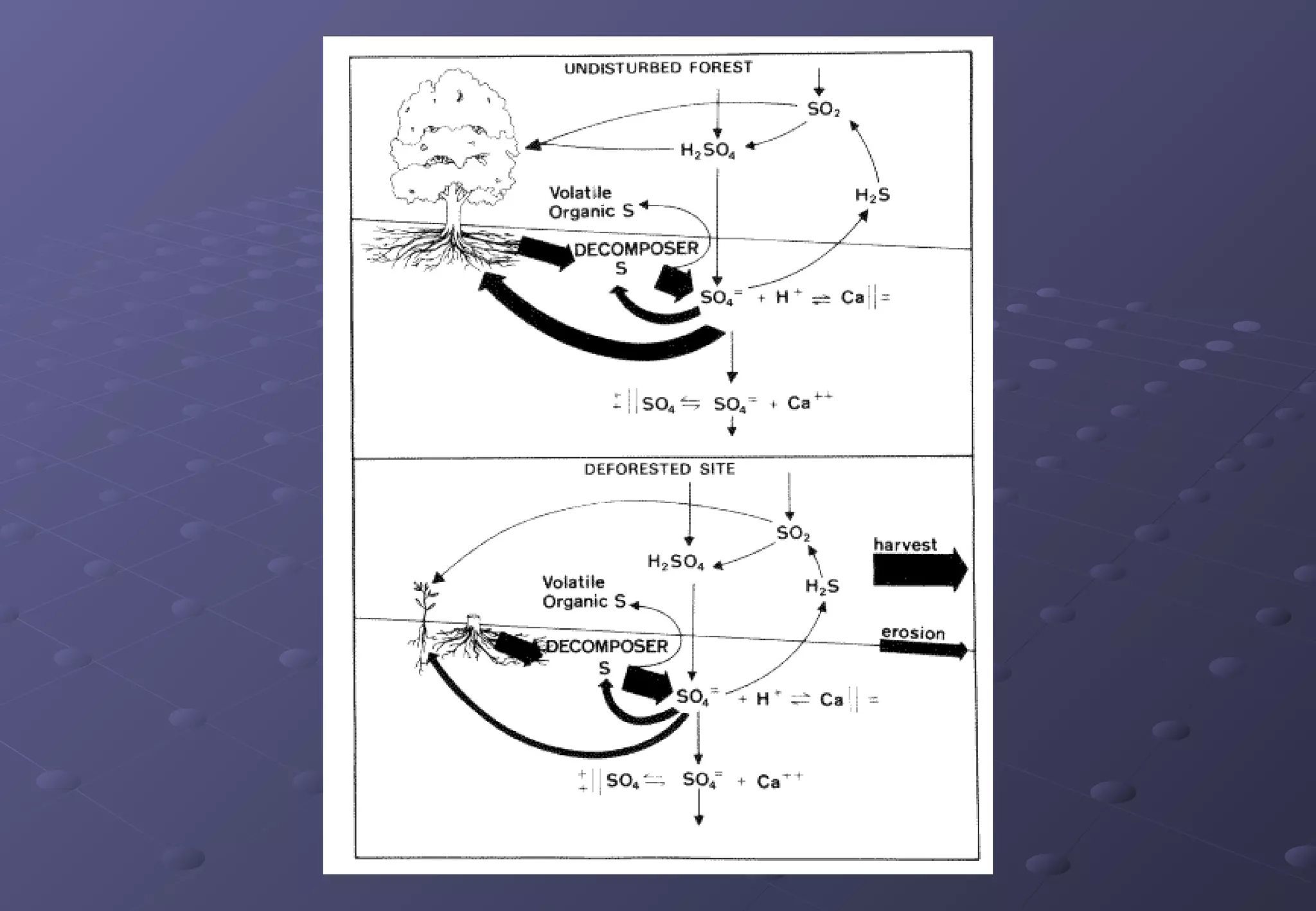
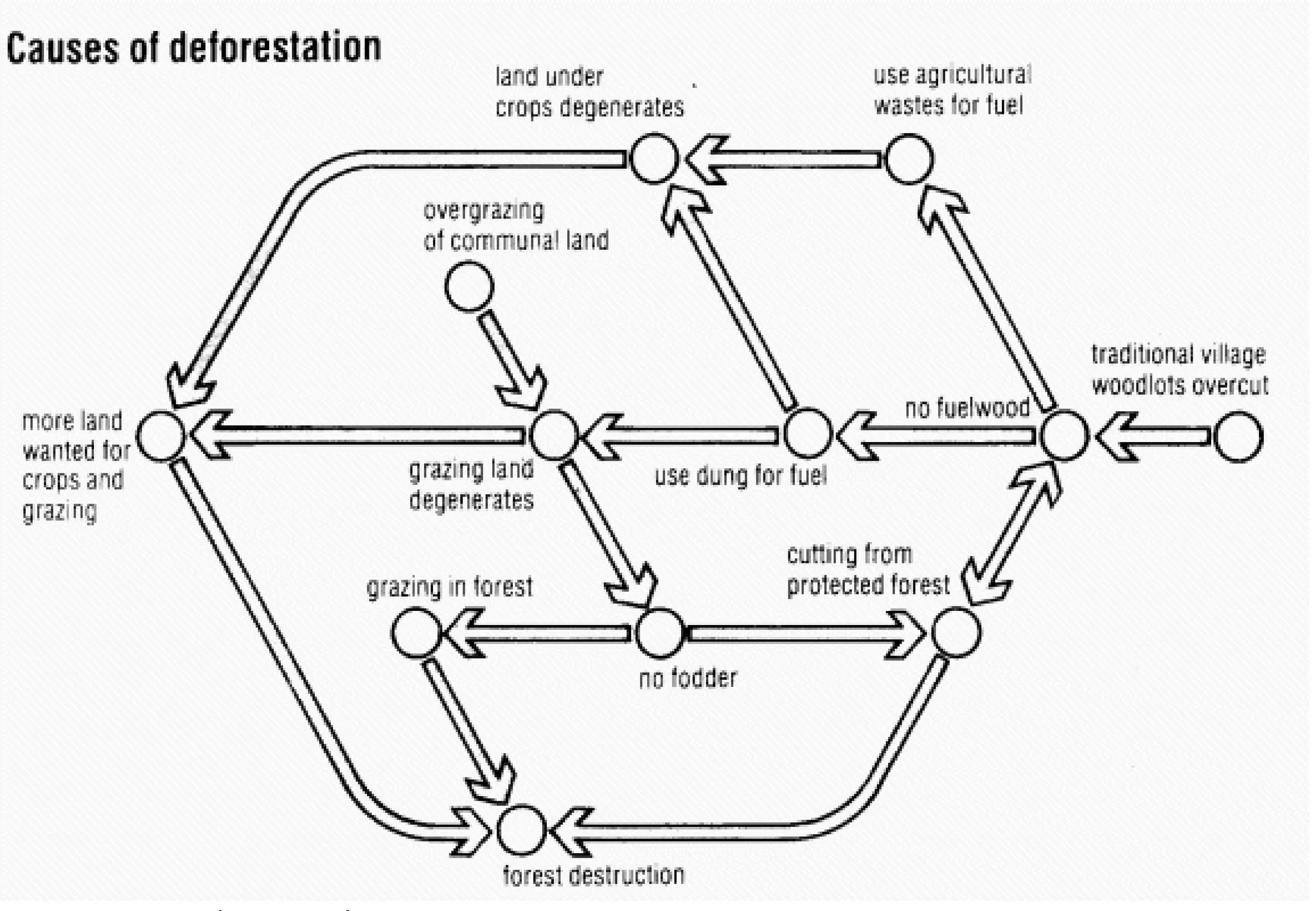
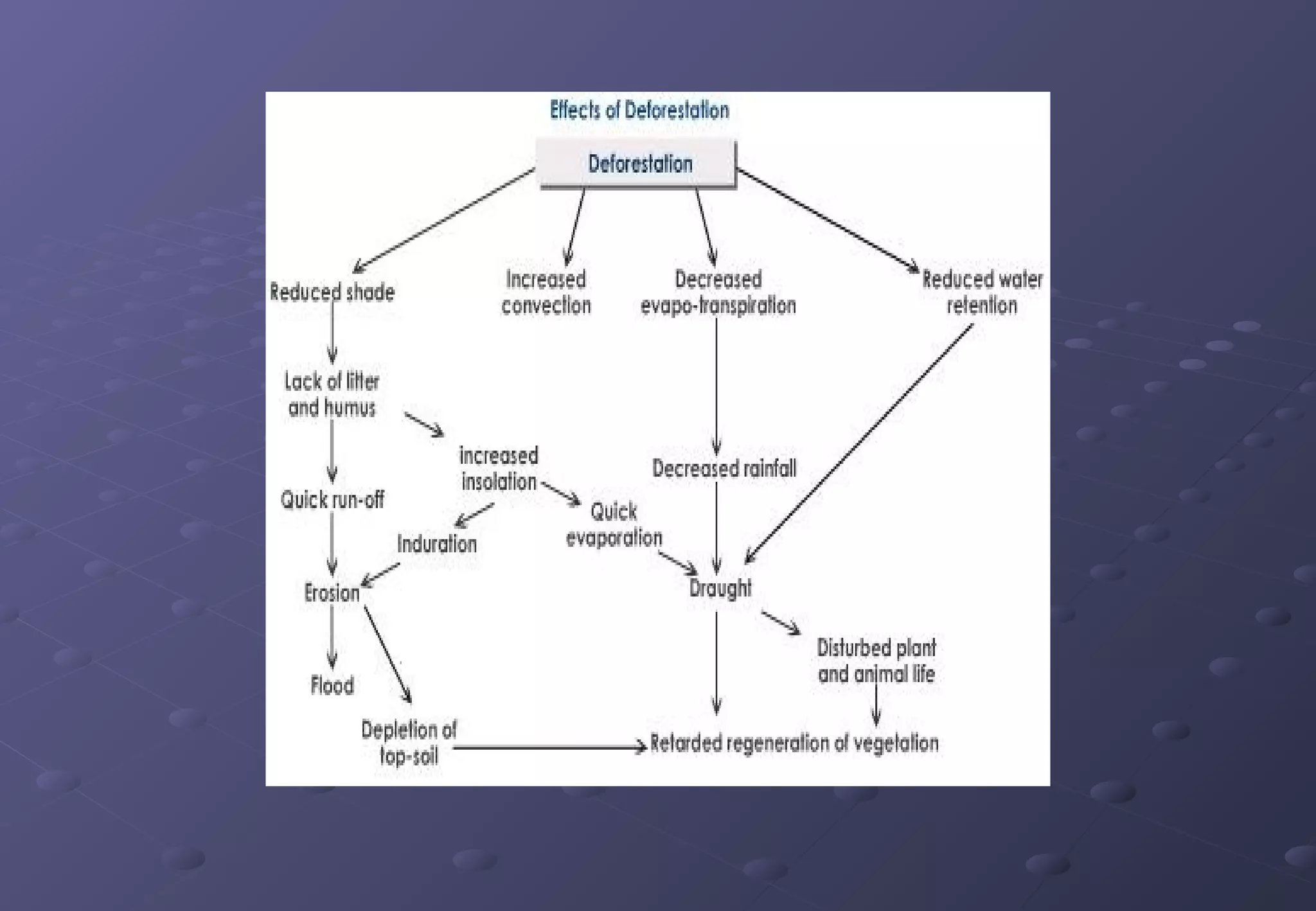
This document discusses the importance of forests and the impacts of deforestation. It notes that forests provide valuable products for human use and consumption as well as ecosystem services. It then outlines some of the key forest products such as wood for building materials and paper, and non-wood products like berries, nuts, and maple syrup. The document also discusses the causes of deforestation including logging, mining, cattle ranching, and agriculture. It lists some of the major effects of deforestation such as loss of biodiversity, habitat fragmentation, soil erosion, climate change, and impacts to indigenous peoples.