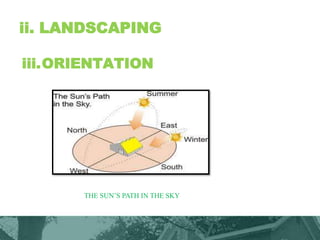
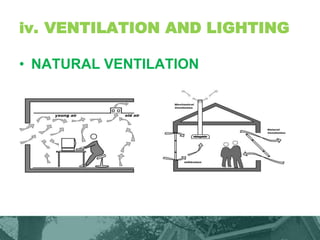
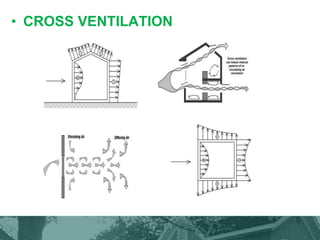
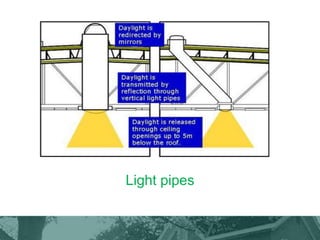
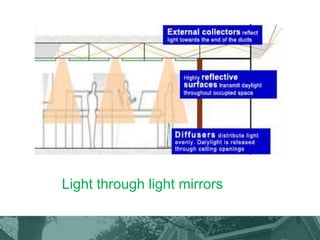
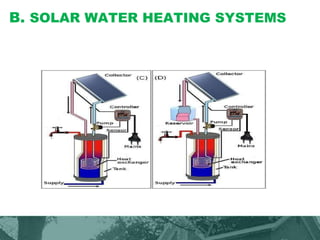
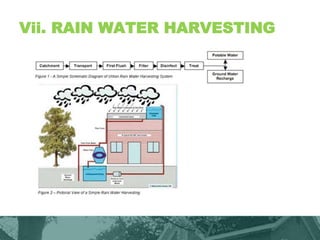
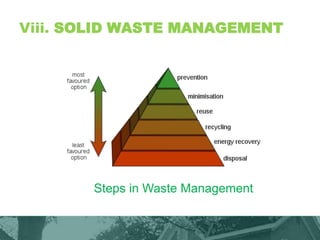
This document provides an overview of green building techniques for sustainable development. It discusses rating systems for green buildings like LEED and BREEAM. It also outlines various green building techniques used, including site planning, landscaping, orientation, lighting and ventilation, energy efficiency, indoor air quality, rainwater harvesting, and solid waste management. Specific techniques are described, such as using solar panels, windmills, and green materials like fly ash bricks. The document concludes with case studies and references.