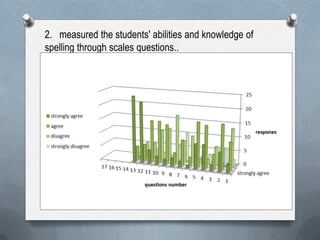
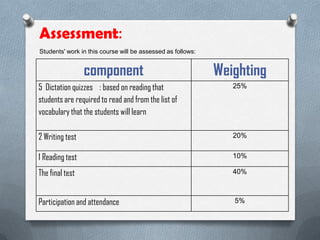
This document outlines an English spelling course for 10th grade students. It discusses conducting a needs analysis through a questionnaire that found over 55% of students were not good spellers. The course aims to improve students' spelling abilities through developing strategies like breaking words into syllables. It will have skills-based content covering prefixes, suffixes, spelling rules. Students will be assessed through dictation quizzes, writing tests, and a final exam. The course will be taught using various interactive methods and activities. Challenges include coordinating members' schedules and distributing the needs analysis survey.