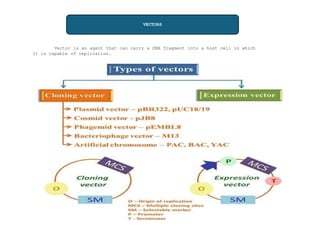
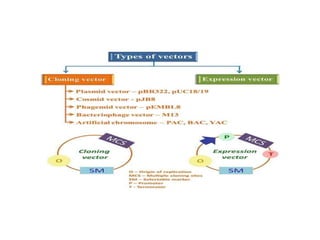
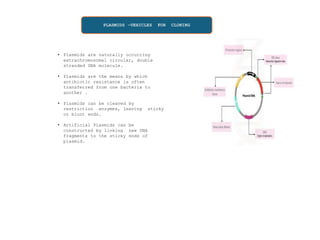
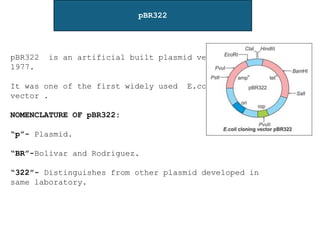
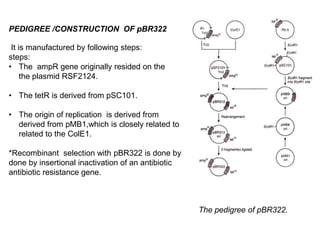
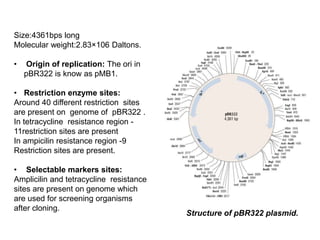
Vectors are agents that can carry DNA fragments into host cells. Plasmids are naturally occurring extrachromosomal DNA molecules that can be used as cloning vectors. pBR322 is an artificial plasmid vector constructed from segments of other plasmids. It is 4361 base pairs in length and contains genes for resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline, which allow for selection of recombinant DNA. pBR322 was one of the first widely used E. coli cloning vectors due to its small size and multiple restriction enzyme sites.