This document provides an overview of number theory concepts including:
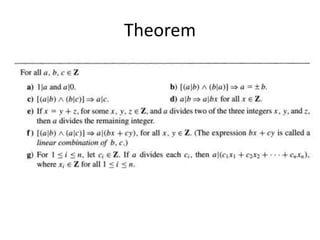
- The definition of divisibility and what it means for one integer to divide another.
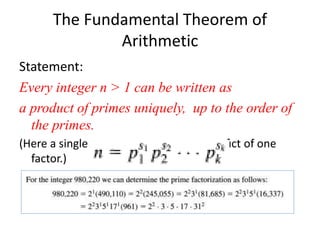
- That primes are integers with exactly two positive divisors and all other integers greater than 1 are called composite.
- Primes are infinite in number and examples of some small prime numbers are provided.
- Divisibility tests are discussed for certain numbers like 2, 4, 5, 8, 10 and their reasons.
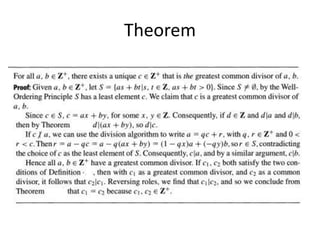
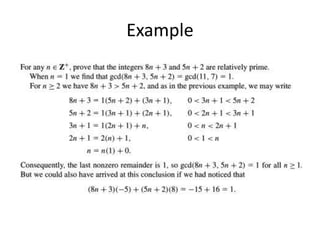
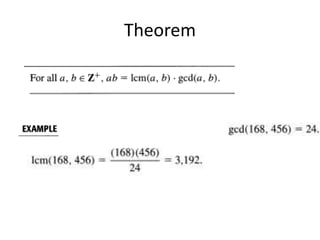
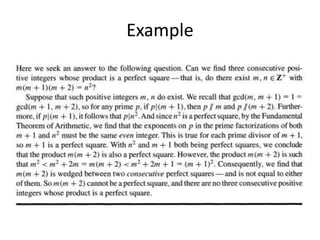
- The greatest common divisor and the Euclidean algorithm to find it are introduced.