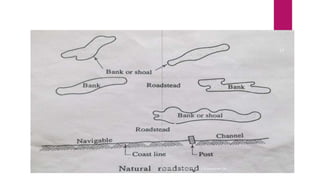
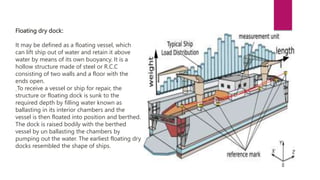
This document provides definitions and classifications of harbors and docks. It defines a harbor as a partially enclosed body of water that provides safe anchorage for boats. Harbors are classified based on their level of natural protection, utility, and location. Docks are enclosed areas for berthing ships and are classified as wet docks for loading/unloading or dry docks for ship repairs. Key harbor requirements include sufficient depth and anchorage space. Ideal harbor sites have favorable marine conditions and foundation soil to support structures.