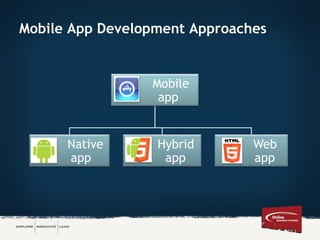
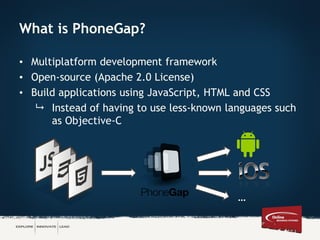
The document discusses various approaches to mobile app development, including native, web, and hybrid apps, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages. It emphasizes the role of tools like PhoneGap and Sencha Touch in cross-platform development, enabling developers to build applications using familiar web technologies. Ultimately, it underscores the importance of understanding requirements when choosing an approach for mobile app development.