This document contains notes and exercises on different English tenses:
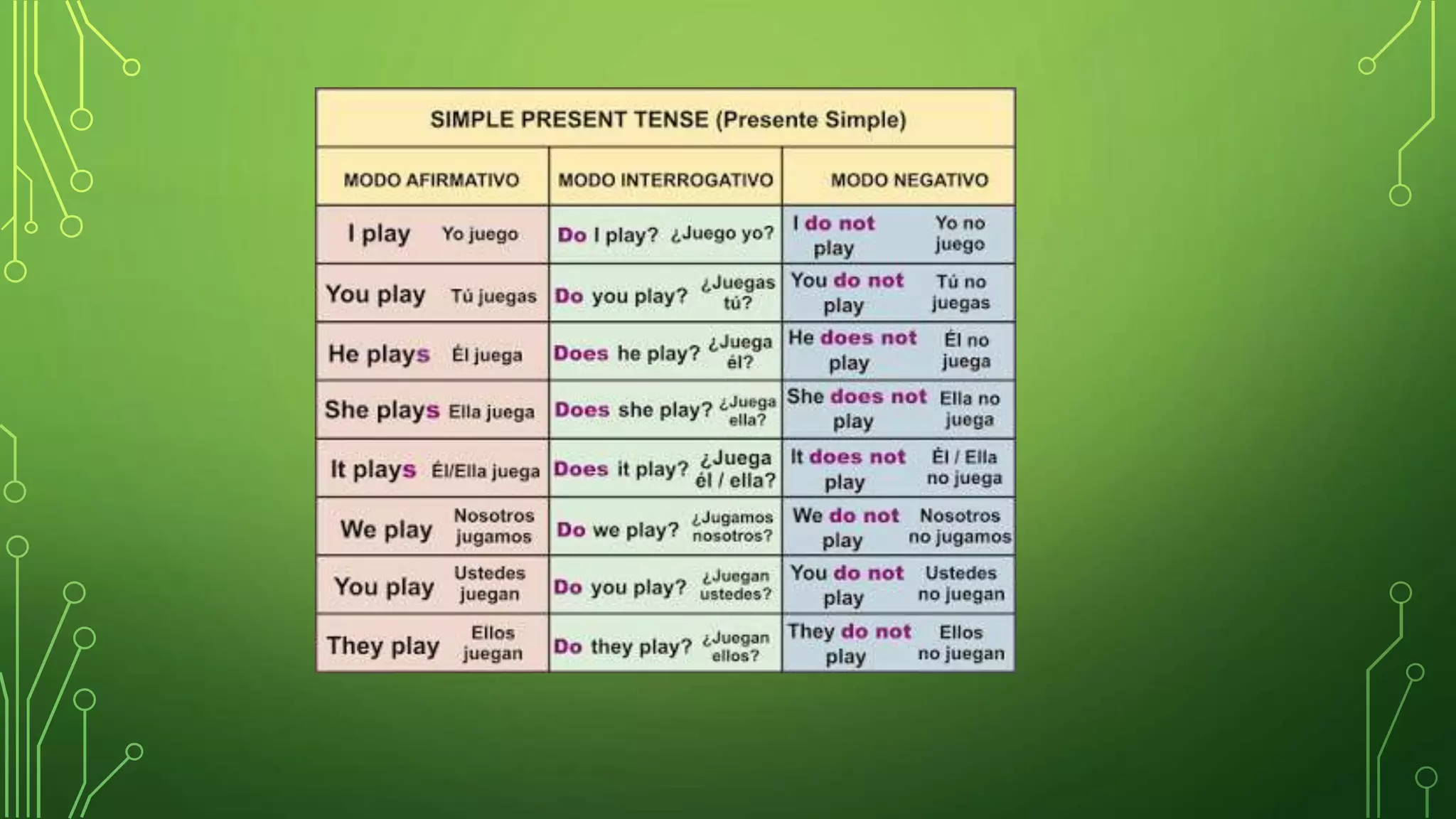
- The Simple Present tense is used to describe habitual or repeated actions. Examples of exercises are provided.
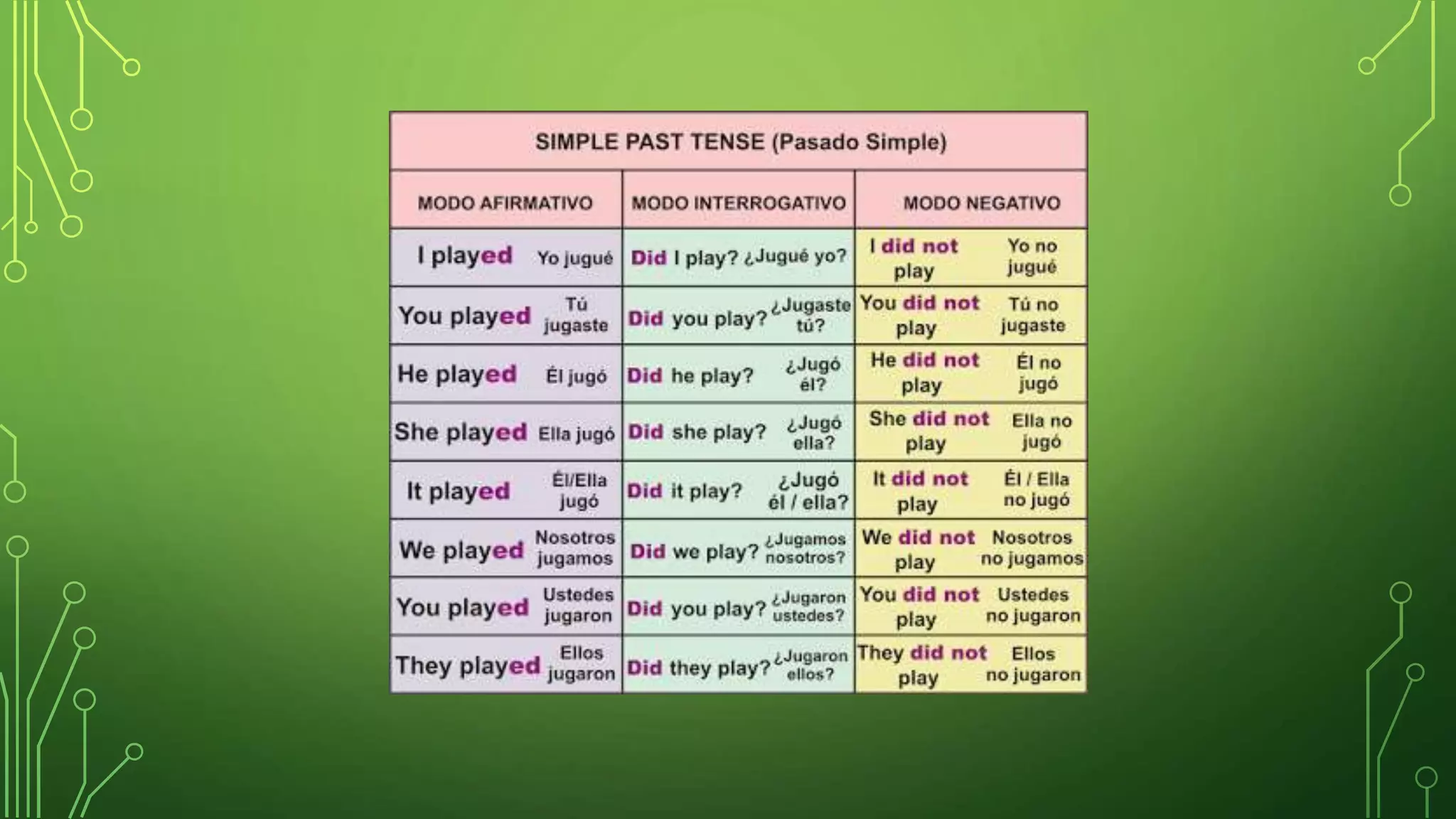
- The Simple Past tense is used to describe actions that have already occurred. Example sentences using common past tense verbs are given.
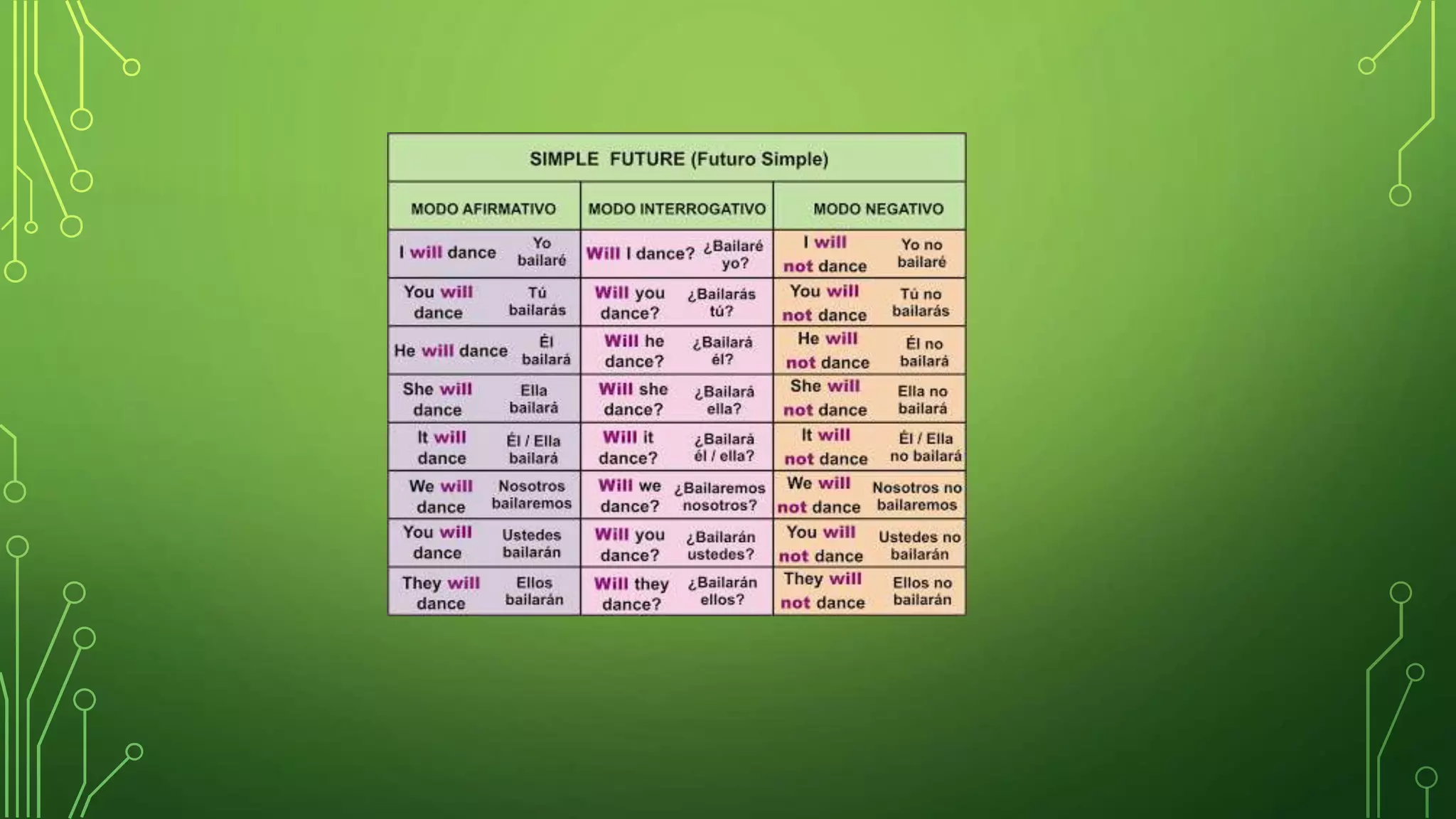
- The Simple Future tense is used to describe actions that will occur in the future. An exercise asks the student to complete sentences using future tense verbs.
- Other tenses discussed include the Present Perfect, Past Perfect, and Future Perfect along with examples and exercises for each.