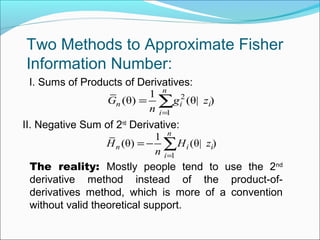
- The document compares two methods for approximating Fisher information in the scalar case: sums of products of derivatives and the negative sum of second derivatives.
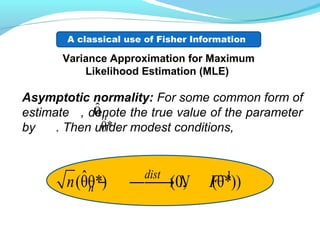
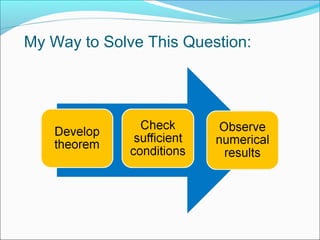
- For independent and identically distributed random variables, the asymptotic variances of the two methods can be estimated using Taylor expansions. Conditions are derived under which the second derivative method is more accurate.
- For a case study with normal distributions, the conditions are met, showing the second derivative method outperforms the product of derivatives method. The analysis provides theoretical justification for commonly using the second derivative approximation.

 (θ| ) ,nF E H=− z
where
log ( |θ)
(θ| )
θ
p
g
∂
=
∂
z
z
and 2
2
log ( |θ)
(θ| )
θ
p
H
∂
=
∂
z
z
1 2[ , ,..., ]T
nZ Z Z=z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-3-320.jpg)

dist
(θ) (θ) 0,var ( )n in H F n N H z− →
2 2
( ) (θ| )g g• = • ( ) (θ| )H H• = •
nG
nH
We wonder which one of the estimates and
is more accurate !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-10-320.jpg)
![For independent and non-identically distributed
random variables:
( ) ( )dist
(θ) (θ) 0,n gn G F n N V− →
( ) ( )dist
(θ) (θ) 0,n Hn H F n N V− →
1 2
1
lim var ( )
n
g i iin
V n g z−
=→∞
= ∑where
and [ ]1
1
lim var ( )
n
H i iin
V n H z−
=→∞
= ∑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-11-320.jpg)

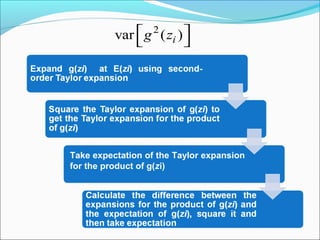
![[ ]var ( )iH z
Take expectation of the Taylor expansion
for H(zi)
Calculate the difference between the
expansions of H(zi) and the expectation of it,
square it and then take expectation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-14-320.jpg)
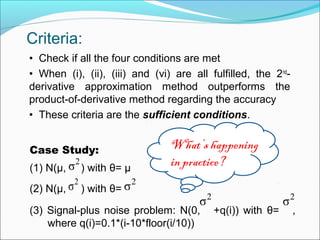
![Comparison:
a.Calculate the difference between the asymptotic
variances:
b.To see which method is more accurate, the following
conditions can be checked for the i.i.d. case
(conditions for i.n.i.d. case is provided in the paper):
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(vi) has the same sign with
[ ]2
var ( ) var ( ) ( )i i g Hg z H z or V V − −
2 2
2
4 (μ) (μ) (μ) 0i i i i i ig g H ′ ′− ≥
22 21
(μ) (μ) (μ) (μ) 0
4
i i i i i i i ig g g H
′ ′′ ′′+ − ≥ ÷
(μ) (μ) 0g g′′ ≥
( )2
[ (μ)] (μ) (μ)i i i i i ig g g′ ′′+
6 2 4
(μ)σ(μ)i i i i iE z E z − − − ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-15-320.jpg)
![3.1188e+08 3.6371 3.1812e-08
1.9226e+08 2.0632 1.9380e-08
1.6222 1.7628 3.3915
2 2
μ1,σ0.1= = 2 2
μ5,σ10= =2
μ0,σ1= =
2
var ( )g z
p-value 7.7846e-05 3.2146e-05 9.4938e-05
2 2
μ1,σ0.1= = 2
μ0,σ1= = 2 2
μ5,σ10= =
[ ]var ( )H z
[ ]2
var ( ) var ( )g z H z
Selected Numerical Results:
Case 2: [ ]2 8 1
var ( ) var ( ) 3 (2σ) 0g z H z − − = • > ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-17-320.jpg)
![Case Study 3:
6.1060e+07 1.0349 3.5680e-08
2.5194e+07 0.6584 2.0023e-08
2.783 1.5718 1.7820
p-value 0.0269 0.0025 2.3863e-07
[ ]2
var ( ) var ( )i ig z H z
[ ]var ( )iH z
2
var ( )ig z
2 2
σ0.1= 2
σ1 = 2 2
σ10=
2 2
σ0.1= 2
σ1 = 2 2
σ10=
[ ] 1002 1 2 4
1
var ( ) var ( ) 3 (200) (σ) 0i i ii
g z H z q− −
=
− = • + > ∑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-18-320.jpg)

![References:
[1] Guo, S. (2014), "Comparison of Accuracy for Methods to
Approximate Fisher Information in the Scalar Case," M. S. project final
report, Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, Johns
Hopkins Univ.; available at arXiv: http://arxiv.org/abs/1501.00218.
[2] Guo, S. (2015), “Analysis of Data-Based Methods for
Approximating Fisher Information in the Scalar Case,” Proceedings of
the 49th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and
Systems, 18−20 March 2015, Baltimore, MD.
submitted to Proceedings of the 49th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, 18−20 March 2015, Baltimore, MD.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-20-320.jpg)
![( )
2
22 2 2 2 2
4 4 2 2 3
2 4
var ( )
4 (μ)[ (μ)]σ[ (μ)] (μ) (μ) var (μ)
1
[ (μ)] var (μ) [ (μ)] [ (μ)] var (μ)
16
4 (μ)[ (μ)] (μ) (μ)
i
i
i i
i
g z
g g g g g z
g z g g z
g g g E z
′ ′ ′′≈ + + −
′′ ′ ′′+ − + −
′ ′′+ −
( )( )2 2 6 2 41
[ (μ)] [ (μ)] (μ) (μ) (μ)σ(μ)
2
i ig g g g E z E z ′′ ′ ′′+ + − − −
[ ] [ ] [ ]2 22 21
var ( ) (μ)σ(μ) var (μ)
4
i iH z H H z ′ ′′≈ + −
i.i.d. case:
2
μ( ),σvar( )i iE z z= =Define and let ( |θ) ( ), ( |θ) ( )g g H H• = • • = •
Consider the symmetric density family:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-21-320.jpg)
![i.n.i.d. case:
( )
2
1
2 2
2 2 2 2
1 1
4 4 2 2 3
1 1
2
var ( )
4 (μ) (μ)σ[ (μ)] (μ) (μ) var (μ)
1
[ (μ)] var (μ) [ (μ)] [ (μ)] var (μ)
16
4 (μ)[ (μ)] (μ) (
n
i i
i
n n
i i i i i i i i i i i i i
i i
n n
i i i i i i i i i i
i i
i i i i i i
g z
g g g g g z
g z g g z
g g g E
=
= =
= =
′ ′ ′′ ≈ + + −
′′ ′ ′′ + − + −
′ ′′+
∑
∑ ∑
∑ ∑
( )( )
4
1
2 2 6 2 4
1
μ)
1
[ (μ)] [ (μ)] (μ) (μ) (μ)σ(μ)
2
n
i i
i
n
i i i i i i i i i i i i i
i
z
g g g g E z E z
=
=
−
′′ ′ ′′ + + − − −
∑
∑
[ ]
2 2
2 2
1 1 1
1
var ( ) (μ)σ(μ) var (μ)
4
n n n
i i i i i i i i i
i i i
H z H H z
= = =
′ ′′ ≈ + − ∑ ∑ ∑
Define and let
2
μ( ),σvar( )i i i iE z z= = ( |θ) ( ), ( |θ) ( )i i i ig g H H• = • • = •](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5c57a97d-dfeb-43fa-a7ba-14fb3cc20d85-150406225101-conversion-gate01/85/ppt_tech-22-320.jpg)