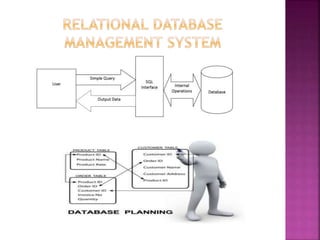
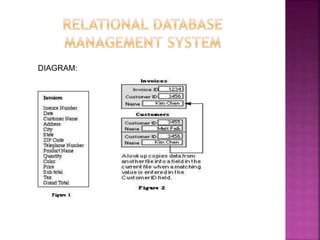
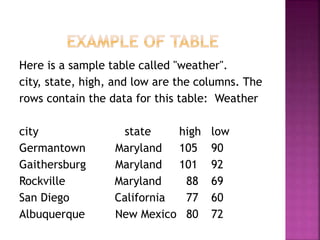
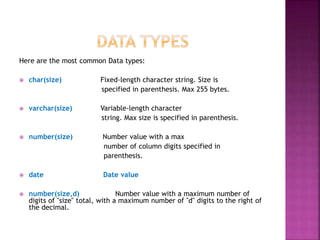
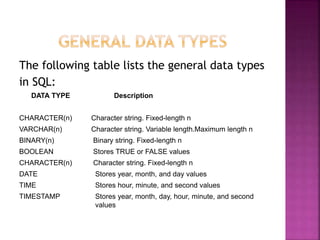
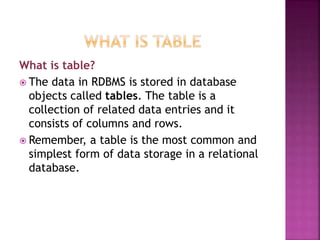
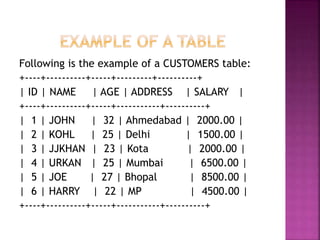
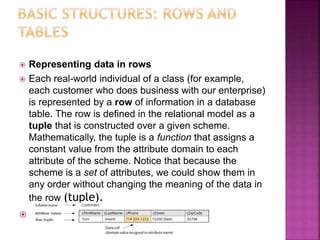
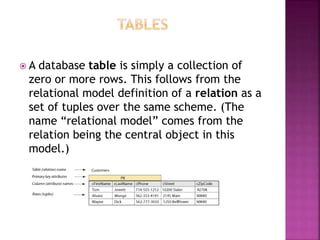
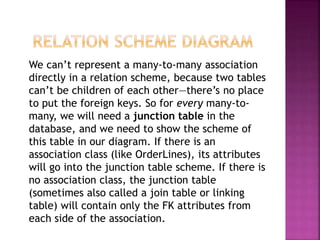
This document provides an overview of relational databases, highlighting their superiority over flat file databases in terms of data management, including advantages such as avoiding data duplication, ensuring data consistency, and facilitating easier data updates. It explains the structure of data in relational databases through tables, fields, and records and introduces SQL as a language used to perform database operations. The document also covers SQL commands, data types, and the importance of primary keys in maintaining unique records.



























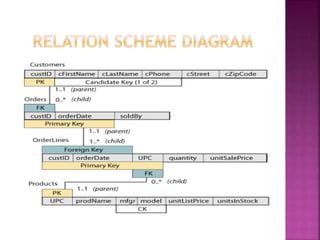




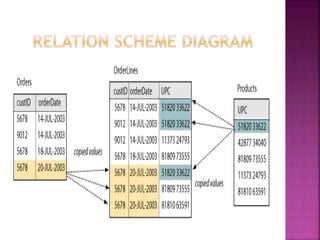

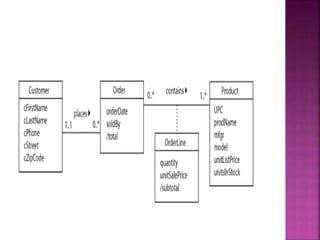






![ Once a table is created in the database, there are many occasions where one may wish to change
the structure of the table. In general, the SQL syntax for ALTER TABLE is,
ALTER TABLE "table_name"
[alter specification];
[alter specification] is dependent on the type of alteration we wish to perform. We list a number
of common changes below:
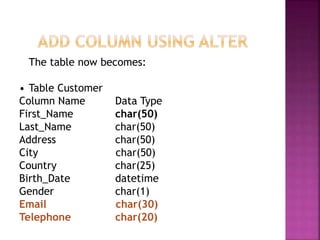
ADD COLUMN
MODIFY COLUMN
RENAME COLUMN
DROP COLUMN
ADD INDEX
DROP INDEX
ADD CONTRIANT
DROP CONSTRAINT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptsqlclass-220921220747-9e28a6ed/85/PPT-SQL-CLASS-pptx-56-320.jpg)



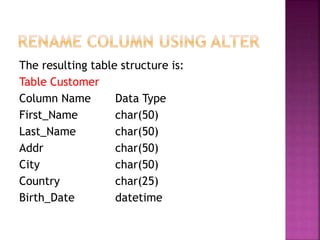
![ Sometimes we want to change the name of a
column. To do this in SQL, we specify that we
want to change the structure of the table using
the ALTER TABLE command, followed by a
command that tells the relational database that
we want to rename the column. The exact
syntax for each database is as follows:
In MySQL, the SQL syntax for ALTER TABLE
Rename Column is,
ALTER TABLE "table_name"
Change "column 1" "column 2" ["Data Type"];
In Oracle, the syntax is,
ALTER TABLE "table_name"
RENAME COLUMN "column 1" TO "column 2";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptsqlclass-220921220747-9e28a6ed/85/PPT-SQL-CLASS-pptx-61-320.jpg)





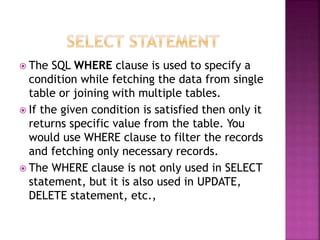
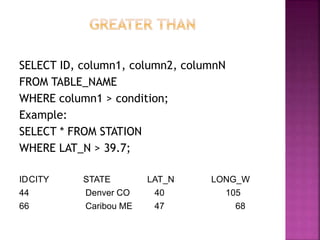
![Select (SQL) The SQL SELECT statement returns
a result set of records from one or more tables.
A SELECT statement retrieves zero or more rows
from one or more database tables or database
views. In most applications, SELECT is the most
commonly used data manipulation language
(DML) command.
Syntax:
The basic syntax of SELECT statement with WHERE
clause is as follows:
SELECT column1, column2, columnN
FROM table_name
WHERE [condition]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptsqlclass-220921220747-9e28a6ed/85/PPT-SQL-CLASS-pptx-70-320.jpg)