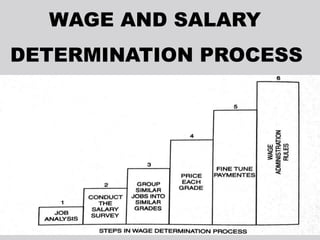
Wage and salary administration involves the development and management of compensation systems, distinguishing between wages (based on work done) and salaries (fixed amounts for regular periods). It outlines three types of wages: minimum wage, fair wage, and living wage, which vary in standards and criteria. Additionally, the document discusses the determination of wages through job analysis, salary surveys, pay grades, and wage administration rules.