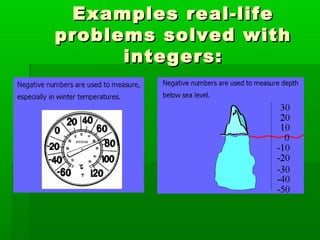
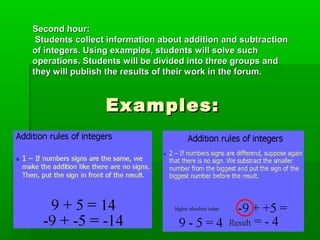
This document describes a lesson on teaching integers in mathematics using the IntelTeach method of project-based learning. The lesson involves dividing students into groups to research concepts of integers like definition, opposites, ordering and operations. Students find real-life problems involving integers and represent them graphically. They then practice operations, equations, inequalities and evaluate their understanding through discussion, worksheets and presenting their findings. The teacher found students engaged with applying concepts to problems and collaborating in groups.











![8. References8. References
[1] http://www.didactic.ro/index.php?[1] http://www.didactic.ro/index.php?
cid=cautare&action=search&words=Numerecid=cautare&action=search&words=Numere
+intregi&cat=10&cls+intregi&cat=10&cls
%5B6%5D=true&disciplina=0 [03/27/2010]%5B6%5D=true&disciplina=0 [03/27/2010]
[2][2] Textbook course IntelteachTextbook course Intelteach
[3][3] Textbook for grade VI-th, Dana Radu,Textbook for grade VI-th, Dana Radu,
Eugen Radu-Editura TeoraEugen Radu-Editura Teora](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptlucianvladescu-150413062639-conversion-gate01/85/Ppt-lucian-vladescu-14-320.jpg)