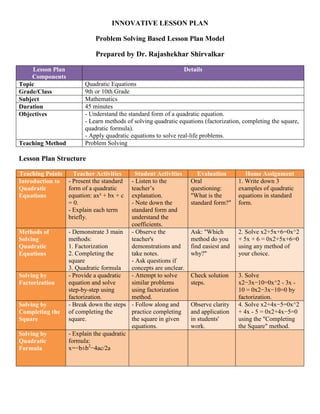
The document details three innovative lesson plans in mathematics focusing on Arithmetic Progression, Quadratic Equations, and Number Systems for grades 7-10. Each plan includes learning objectives, teaching methods, activities, and evaluation components, encouraging real-life application and group collaboration. The plans emphasize understanding mathematical concepts through interactive demonstrations, problem-solving methods, and concept maps.
![INNOVATIVE LESSON PLAN
Project-based lesson plan model
Topic "Arithmetic Progression"
Prepared by Dr. Rajashekhar Shirvalkar
Title: Arithmetic Progression (AP)
Subject: Mathematics
Grade/Level: 9-10
Duration: 3 Class Periods
Topic: Arithmetic Progression
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the concept of Arithmetic Progression (AP)
- Derive the formula for the nth
term and sum of the first n terms
- Apply AP concepts in real-life situations
Project Outline:
Title: Understanding and Applying Arithmetic Progression
Goal: Students work in groups to identify real-life examples of AP and create a presentation
explaining the scenario, deriving the nthn^{th}nth term, and calculating the sum of terms.
Expected Outcome: Presentations or posters showcasing AP's role in everyday contexts.
Stage Teaching Points Teacher
Activities
Student
Activities
Evaluation Home
Assignment
Introduction - Definition and
examples of
Arithmetic
Progression
- Introduce the
concept of AP
through a
storytelling or
real-life
scenario
- Listen and
participate in
the
discussion
- Oral
questioning to
check initial
understanding
- Find 5
examples of APs
in daily life
situations (e.g.,
savings plan,
seating
arrangement,
etc.)
Development - General form of an
AP: a,a+d,a+2d,…
nth term:
an=a+(n−1)d
a_n = a + (n - 1)
- Derive the
general form
and nth
term
formula using
number
patterns
- Participate
in formula
derivation
and practice
using
examples
- Ask students to
find the 5th or
10th term of a
given AP
- Calculate the nth
term for different
AP sequences
and show the
working
Group
Activity
- Sum of first n terms:
Sn=n/2×[2a+(n−1)d]
- Guide a
group project:
Calculate the
sum of the first
10 terms of a
chosen AP
scenario (e.g.,
daily savings)
- Collaborate
to create a
problem
statement and
solve the AP
scenario
- Evaluate group
presentations
based on
accuracy,
teamwork, and
problem-solving
approach
- Create a small
project on AP:
Compare costs
saved using an
AP sequence
over time for a
hypothetical
budget
Real-Life - Identifying AP in - Show videos - Identify and - Quiz on real- - Create a poster](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innovativelessonplan-241005020443-6fe90ebf/75/Innovative-Lesson-Plan-Project-based-Lesson-Plan-Problem-Solving-Concept-map-1-2048.jpg)