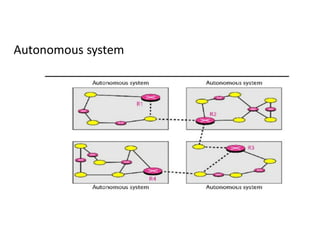
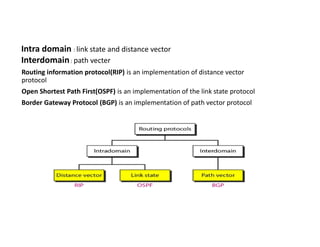
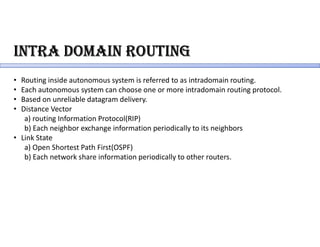
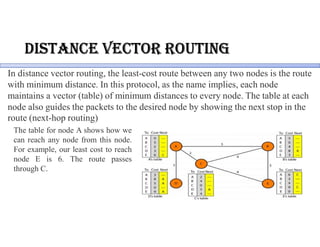
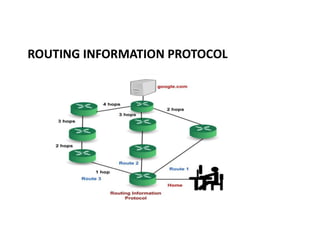
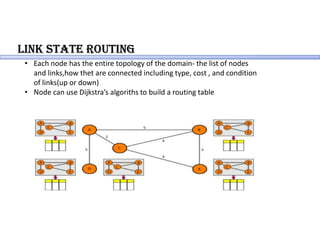
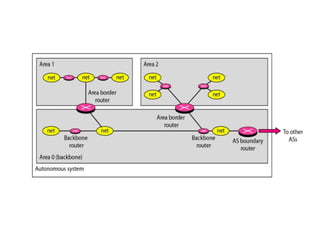
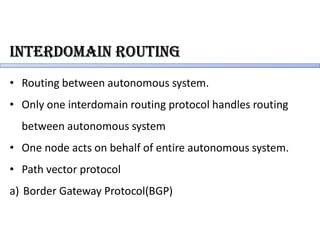
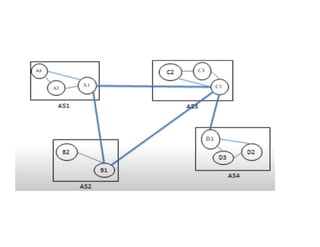
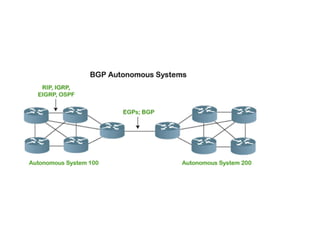
Routing protocols allow routers to share information about changes on the internet and their neighborhoods. Intra-domain routing handles routing within autonomous systems using distance vector or link state protocols like RIP and OSPF. Inter-domain routing between autonomous systems uses the path vector BGP protocol. Distance vector protocols like RIP exchange periodic updates between neighbors, while link state protocols like OSPF share periodic topology information between all routers. BGP establishes sessions between directly connected routers of different autonomous systems to exchange routing information.