1. There are several criteria that can be used to distinguish between languages and dialects, including standardization, vitality, historicity, autonomy, reduction, mixture, and de facto norms.
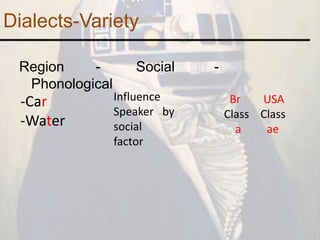
2. Dialects are considered subordinate varieties of a language that can differ based on region, social factors, and phonological influences. British and American English are examples of dialects that vary in terms of pronunciation of certain words.
3. Language styles, registers, and beliefs also contribute to differences within and between languages. Style refers to formal vs informal speech, register is associated with occupational and social groups, and beliefs influence perceptions of what constitutes proper language use.