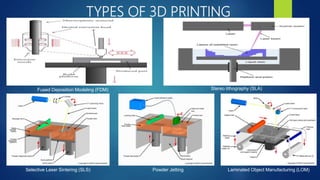
Umang Dadheech presented a seminar on 3D printing to Mr. Ashutosh Kumar at Poornima College of Engineering. 3D printing, also known as rapid prototyping or additive manufacturing, refers to manufacturing methods that quickly produce physical prototypes directly from 3D CAD data using a layer-by-layer process. It does not require molds and can produce multiple parts simultaneously without limitations on geometric complexity. Common 3D printing processes discussed included fused deposition modeling, stereo lithography, selective laser sintering, and powder jetting. Applications mentioned are products with good touch and feel, validation of inventions, jewelry design, medical prototypes, and mass customization.