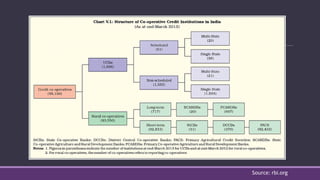
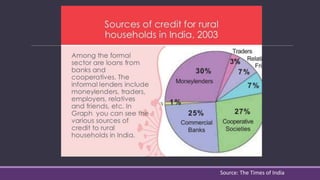
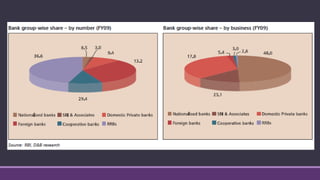
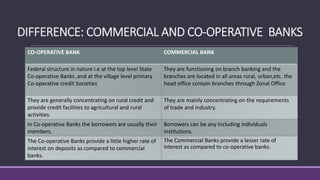
This document discusses cooperative banks in India. It provides background on cooperative banks, noting that they are owned and operated by their members and focus on serving local communities. The document outlines the history and regulations governing cooperative banks in India. It then describes the roles of different types of cooperative banks, including primary cooperative credit societies, central cooperative banks, and state cooperative banks. The summary highlights the focus of cooperative banks on rural areas and agriculture as well as their importance in providing credit to those sectors in India.